Impact of employees engagement and knowledge sharing on organizational performance: Study of HR challenges in COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
PURPOSE:
When the economy’s in terrible shape, any of us is lucky to have a job, human resources managers worrying about whether or not employees are contributing to the organizational goals and objectives, and how to pursue the recruitment and selection process, employee’s engagement, and, training and development activities, these are the current human resource management challenges which are created due to COVID-19 pandemic. Organizations around the world are facing a tough situation, first time in history, the worth of one-barrel oil fell to less than nothing on 20th April 2020, the only reason is behind this is the current lockdown around the world. The physical workplace is converted into a virtual workplace, now the HR managers are planning how to engage the employees efficiently. This study pursued to examine the effect of employee’s engagement on organizational performance through the mediating effect of knowledge sharing for employees of higher educational institutions.
METHOD:
A quantitative research method is used in this study, non-probability sampling design with a focus on convenient sampling frame is deployed in this study. The questionnaire is adapted from the past studies, Initially Google forms were used to collect the data, due to lower response rate questionnaire were distributed in hard copies and sent to the targeted respondents. Structured Equation Modeling (SEM) is used to test the conceptual framework.
RESULTS:
The results showed that employee engagement has a significant and positive impact on organizational performance. Further, it was found that knowledge sharing has a significant and positive impact on organizational performance. Moreover, knowledge sharing only partially mediated the association between employee engagement and organizational performance. Covid-19 pandemic is destroying global economies, but at the same time its bringing different opportunities for organizations also. Now organizations have to think about how to avail this opportunity, organizations are going virtually, and in this situation, it is the biggest challenge for the Human Resource (HR) managers to manage the employee effectively.
 Tanveer Ahmed is working in Iqra University as an Administrative Officer. He has his MBA in Human Resource Management from DHA Suffa University, Karachi. His research interests include strategic management in higher education, rewards & compensation and human resource management systems.
Tanveer Ahmed is working in Iqra University as an Administrative Officer. He has his MBA in Human Resource Management from DHA Suffa University, Karachi. His research interests include strategic management in higher education, rewards & compensation and human resource management systems.
 Dr Muhammad Shahid Khan is an assistant professor at College of Innovation and Management, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. His research interests include Knowledge Management, Leadership, Innovation and Human Resource Management.
Dr Muhammad Shahid Khan is an assistant professor at College of Innovation and Management, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. His research interests include Knowledge Management, Leadership, Innovation and Human Resource Management.
 Dr Duangkamol Thitivesa is an assistant professor at Faculty of Educaiton, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. Her specialization is language teaching approaches and methods, handling language training workshops for academic purposes and running researches on English for occupational purposes for service and industry sector.
Dr Duangkamol Thitivesa is an assistant professor at Faculty of Educaiton, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. Her specialization is language teaching approaches and methods, handling language training workshops for academic purposes and running researches on English for occupational purposes for service and industry sector.
 Dr Yananda Siraphatthada is an assistant professor at College of Innovation and Management at Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. Her research interests include marketing strategies, Management strategies and HRD.
Dr Yananda Siraphatthada is an assistant professor at College of Innovation and Management at Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. Her research interests include marketing strategies, Management strategies and HRD.
 Tawat Phumdara is working as a lecturer at College of Innovation and Management, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. His research interests include Political Behavior, Political Economy, Leadership, and Local Society Development.
Tawat Phumdara is working as a lecturer at College of Innovation and Management, Suan Sunandha Rajabhat University, Thailand. His research interests include Political Behavior, Political Economy, Leadership, and Local Society Development.
1Introduction
Due to current coronavirus pandemic employee engagement may have dropped, this might affect the organization productivity as well, but it’s one of the most important initiatives to keep at the forefront to be successful through engaging employees at home effectively. To ensure employees are staying healthy and engaged, for this human resource managers have to demonstrate a new level of understanding, the most efficient way to do this is to establish consistent communication, sharing of information and implementation of knowledge sharing practices. Knowledge has become a crucial component in a competitive business setting instead of the property and the fixed assets in the last decade [1]. Over two decades, employee engagement issues have attracted the attention of both academia and business, as this concept is not only related to organizational performance, but it is also crucial for employee career enhancement and long-term success of the organization [2]. Employee engagement is important for the success and sustainability of the business. Several organizations realize that employees are the greatest asset as they can compete with internal and external organizations in their sectors [3].
Knowledge sharing is related to the willingness to share knowledge with others. Employees’ desires are active communication, consultation with colleagues, exchange and voluntary share [48]. Research shows that in cases where knowledge is not actively common within employees, their intellectual resources will remain under-utilized within the team. When knowledge is not shared, not only individual performance is suffering but the organizational performance is also decreasing. A knowledge-sharing culture allows an individual to share his / her knowledge with the team and thus, achieve success in this way [3]. Every aspect and activity in a company involves “people”, a manager cannot achieve his goals and targets if he has subordinates who are not well equipped with knowledge, skills and attitude [4].
1.1Background of the study
Vance (2006) [5] stated that Employee engagement and commitment directly and highly affect the job performance of an employee and also impact the business results. Figure 1.1 shows that employer practices affect the employee engagement and level of commitment toward the organization and it shows that employer practices also affect the job performance of an employee.
Fig. 1.1
Employer Practices Ultimately Influence Business Results.
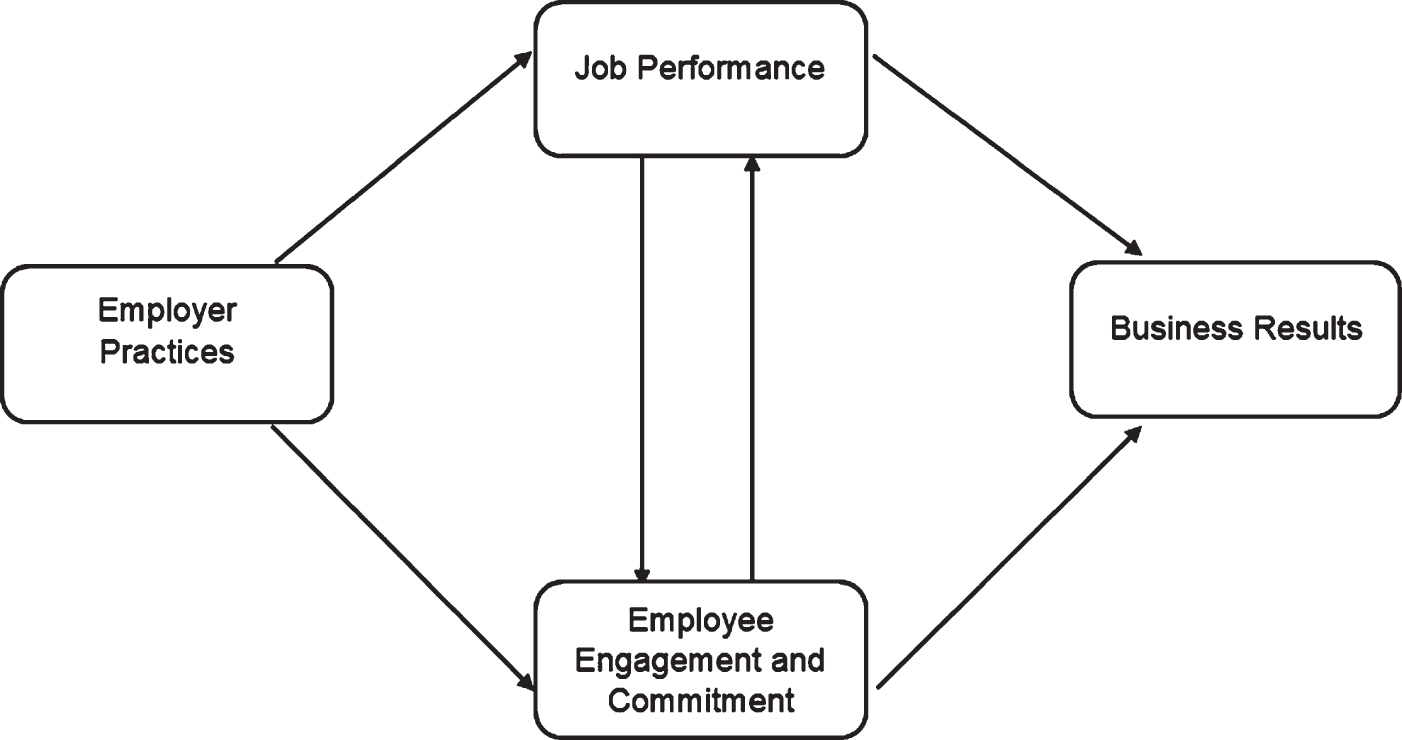
Figure 1.2 shows “DDI’s engagement value proposition”, which includes four sequential components, that are engagement drivers, work environment, engaged employees and organizational success. The engagement drivers focus on hiring the right employee with the right skills for the relevant job and provide support to the employees through a strong system and strategies. This dimension will lead to the formation of an engaging work environment, once created, this engaging work environment will change the employee’s attitude and behaviour in a positive direction, consequently employees will be more loyal to the organization which will lead to organizational success.
Fig. 1.2
DDI’s Engagement Value Proposition.
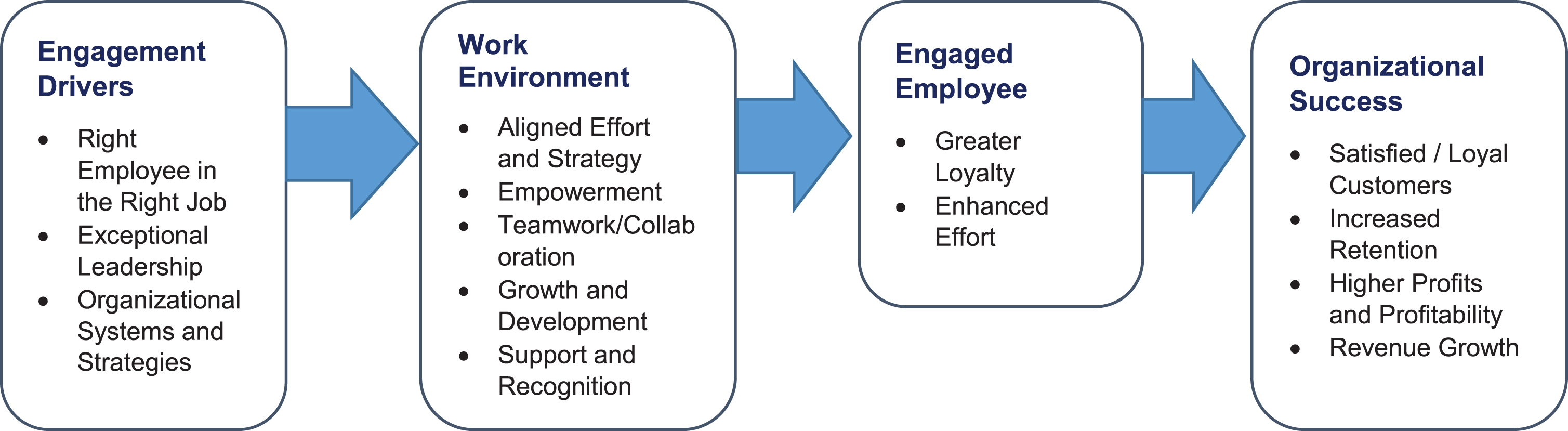
Fig. 1.3
Research Model.
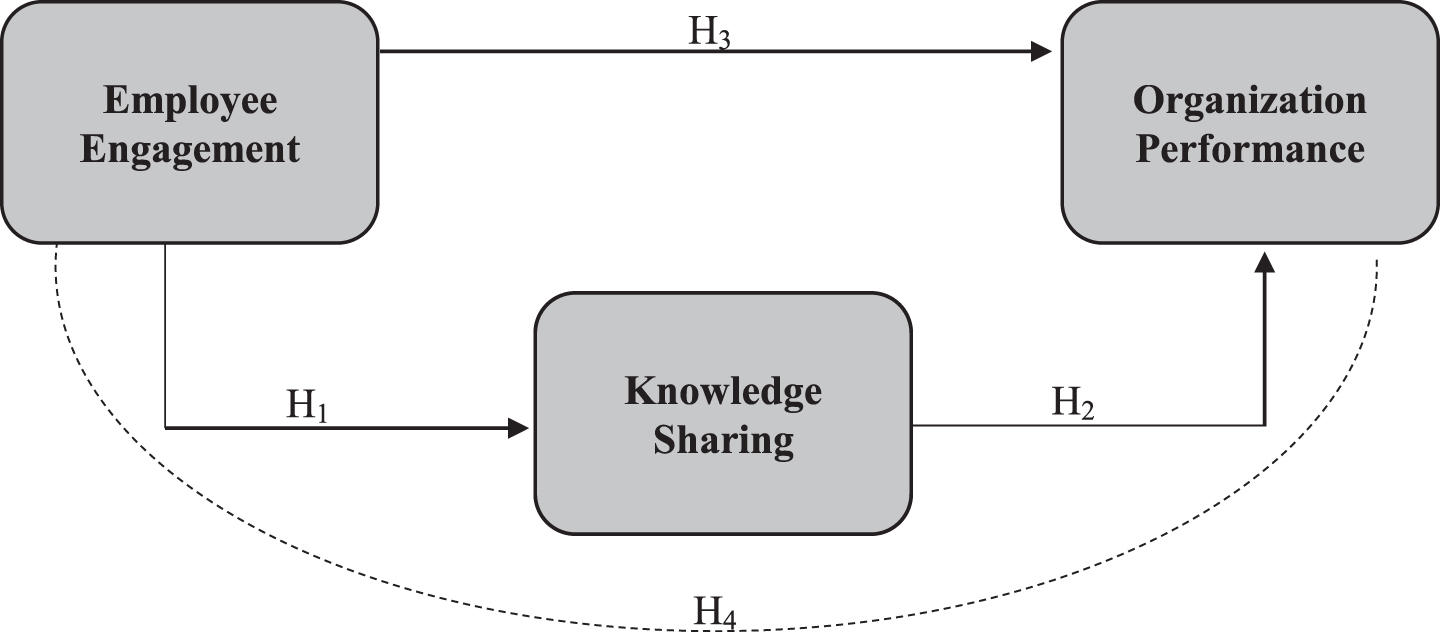
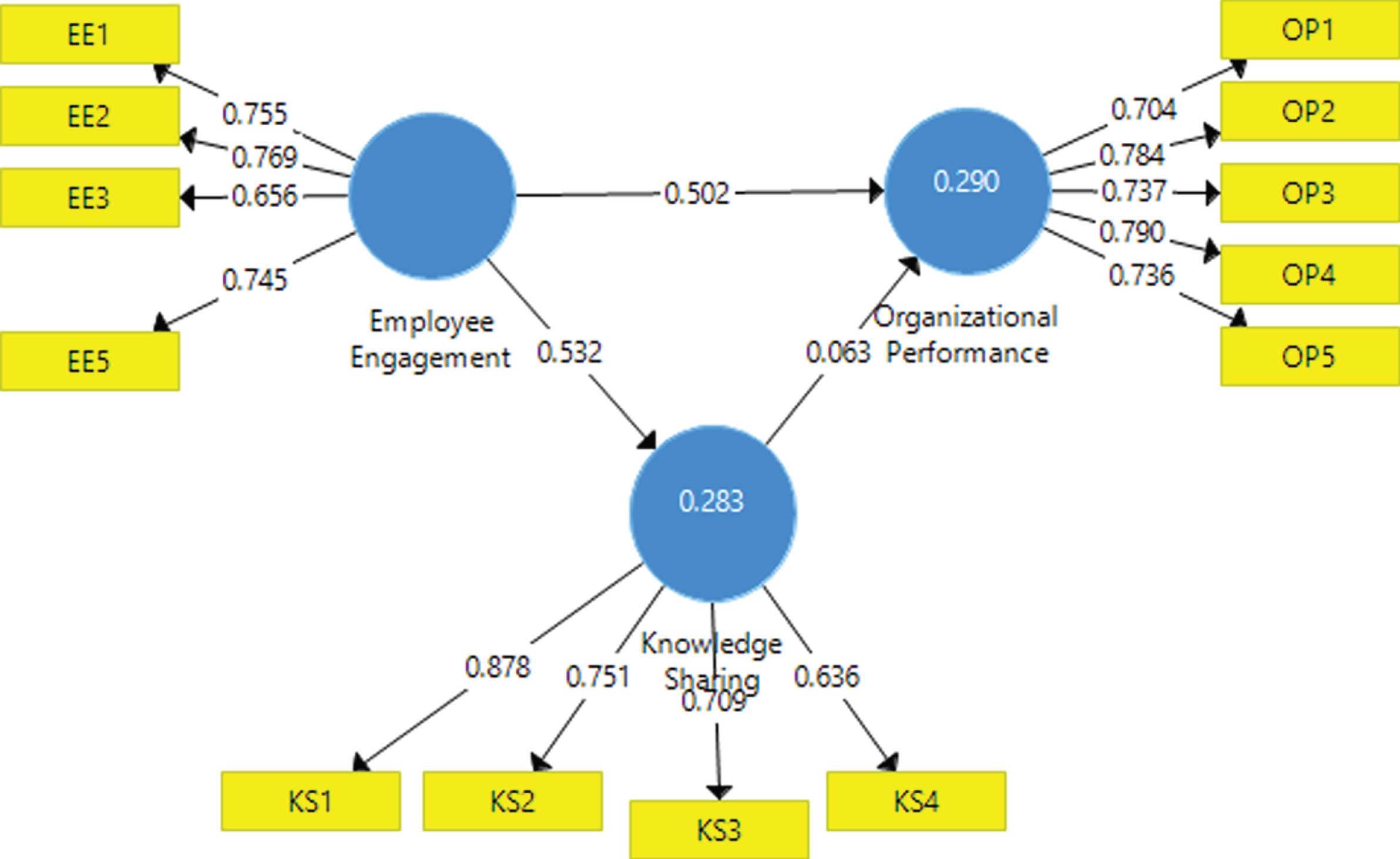
Fig. 4.1
Structural Model Results.
1.2Problem statement
The idea of studying employee engagement from a business stance and its relationship with organizational performance may be traced far back in 2002 [7]. It has been recognized that employee engagement stages correlate with the level of involvement and commitment employees devote to their organization, values and beliefs [8]. According to Ilyasa et al., (2018) [9] employee engagement and knowledge sharing have a direct and positive impact on employee work innovation. However, the amount of such collaborative and knowledge sharing activities remains limited in higher education [54]. Employee engagement and organization performance is widely discussed in the literature, but studies on measuring the relationship between employee engagement and the organization’s performance with knowledge sharing as a mediator variable are rarely available. Practically, this kind of study is not yet tested in the context of higher education in Pakistan.
1.3Research question
This study addresses the following questions:
• What is the impact of employee engagement on knowledge sharing in an organization?
• Does knowledge share affect the organization’s performance?
• What is the impact of employee engagement on the organization’s performance?
• Does knowledge sharing mediate the relationship between employee engagement and organizational performance?
1.4Research objective
• To examine the impact of knowledge sharing on organization performance.
• To study the relationship between knowledge sharing and organizational performance.
• To measure the impact of employee engagement on organizational performance.
• Examine the mediating impact of knowledge sharing between employee engagement and organizational performance.
1.5Research model
1.6Hypothesis
H1: Employee engagement has a positive impact on knowledge sharing
H2: Knowledge sharing has a positive impact on organization performance
H3: Employee engagement has a positive impact on organization performance
H4: Knowledge sharing mediates the relationship between employee engagement and organization performance
2Literature review
2.1Employee engagement
Shuck and Vollard (2010) [10] have defined employee engagement as “the emotional, cognitive and behavioral state of the employee, with an emphasis on the desired organizational outcome”. Employee engagement is defined as a characteristic of the relationship between an organization and its employees. In other words, employee engagement means the intellectual and emotional involvement of employees within the organization [11]. Furthermore, employee engagement is a close conceptualization of the relationship between employees and their work [12]. Greater employee engagement can help in reducing absenteeism, accidents, turnover and also improve employee performance as well as organizational performance [49]. There is a positive relationship between engagement and direct indicators of the effectiveness of the organization, such as productivity, quality, performance, customer satisfaction, profit and business development [13].
Engaged employees have a lot of energy and are excited about their work. Besides, they are often devoted to working and time runs out [13]. Leaders and managers around the globe recognized that engagement and trust under optimism, employee engagement is one of the important factors that impact organizational performance [58]. The continuity of employee engagement drives beyond the old-style concepts of participation, organizational commitment and job satisfaction. The engagement contains the use of emotional, cognitive and behavioral energy in the workplace while performing according to the goals and strategies of the organization [14].
The effectiveness and efficiency of the organization depend on the joint efforts of all employees [15]. Committed employees must share, support, collaborate, create a positive common work environment, and whether they have psychological, social or organizational positive emotions while ensuring sustainable compliance in the workplace. Engagement is characterized by positive concentration and absorption at work when the time has passed and it is difficult to leave working [16]. The theory of employee involvement is considered to be one of the most influential theories of business literature. It is derived from the concepts of job satisfaction, organizational participation, and public action, but is much broader than the thoughts of “motivation” and “involvement” in the management literature. Employee engagement is generally recognized as the mutual interaction between employees and the organization [17]. Employee engagement is an important issue in the human resource department as it is very critical in achieving organizational success and competitiveness and engaged employees can contribute to organizational performance [18]. Engaged employees put more effort toward their work and are likely to go beyond their required and expected amount of work tasks [19].
2.2Knowledge sharing
Wang and Noe (2010) [20] suggested that sharing knowledge to provide important information and knowledge to help others, solve problems and develop ideas, and to work effectively with others. “Knowledge sharing is related to a set of behaviors which contribute to knowledge and information sharing and helping others to share their knowledge” [55]. Knowledge sharing is an important factor that influences corporate innovation, explicit knowledge directly influences the speed of innovation, and hidden knowledge influences the quality of innovation [21]. Knowledge sharing can be explained as “A culture where an individual can share their knowledge, ideas, views, skills, and experience”. Knowledge sharing can also be defined as “Experience, task-related information and response about any process or any product”. Knowledge sharing can further be explained as “The process of moving the knowledge from one source to another (receiver)” It is a procedure of sharing of knowledge between two parties that redesign and create new knowledge [16]. The definition of knowledge sharing in the academia vary situation to situation, sharing knowledge means exchange or interchange of knowledge between teams and organizations [22–25]. The past literature shows that sharing knowledge provides employees, teams and organization with the opportunity to improve performance at work and create new ideas and innovations [20]. Knowledge sharing is the process of knowledge management that is used to create, collect and maintain business processes. The evolution of knowledge sharing largely depends on the importance and the use of knowledge sharing towards the business. Knowledge sharing is, therefore, the practice of exchanging and disseminating ideas, experiences and knowledge with others to ensure that knowledge is kept, sustained and retained in business [22–26].
Zannah and Sumadhinata (2013) [27] stated that knowledge sharing is the exchange of knowledge among employees and the exchange of information, experience and knowledge to improve the efficiency of the employee as well as the organization. Knowledge is defined as habit, skills, expertise, experience and understanding as a result of the learning and training process, it is a key source of competitive advantage for the organization [28]. The exchange of knowledge is a social process where employees are willing to share their experience, knowledge and valuable information with others. It relates to sharing resources that are rare, inimitable, non-substitutable and valuable, due to sharing of resources that open up new opportunities for individuals and organizations [29]. Study of Son, Phong. & Loan, (2020) [50] concluded that knowledge-sharing behaviours stimulate organizational performance in a positive direction. In today’s competitive business environment, organizations have introduced a knowledge management department, the purpose of this department is to acquire new knowledge through databases with the help of employees, store the knowledge in databases and share it with employees, this kind of activity is very helpful to innovate the services and products. As knowledge is an asset, employees should also give benefit to the organization, they can share their valuable knowledge with the help of proper knowledge management system.
2.3Organizational performance
Markos and Sridevi (2010) [30] have confirmed that engagement is a dual aspect to exchange information between employees and managers and to identify weaknesses in employees that require devotion. Consideration of management to employees, satisfaction lead towards the organization’s performance. Managers and financial personnel concentrate on financial factors to get the results of an organization that processes profits and maintained earnings by calculative the financial advantages of the project operations [31]. Researchers place less importance of satisfaction and employee engagement, which are non-financial factors that play a key role in the organization long-term commitment. Employee engagement is a positive element of an organization’s commitment to performance. Recognizing employee attitudes is a key element of the competition and to promote organizational profitability. Researchers have reported that organizations need to share employee commitments and organizational performance with them and show their strategic planning ideas [32]. “Thoughtful and effective performance and employee engagement can ensure outsize returns for this investment, directly benefitting our communities and stakeholders” [6].
Hromei (2014) [33] reported that human problems are being ignored, but now it is well-known that employees’ satisfaction leads to better performance, creativity, and an organization’s commitment to goals. However, according to the survey, management is facing the task of improving the performance of the organization by lack of knowledge and ability to consider non-financial factors of human capital, which represent the balance of work environment, organization productivity. Employee engagement is another factor related to an organization’s performance. With happiness and dedication, employees at their workplace ensure that their organization gains significant and observable competitive advantage [34]. Employees who are more deeply involved in the organization’s activities will increase retention and reduce absenteeism and turnover [35].
This motivation and perseverance ultimately lead to high-level of organizational performance. Absorption refers to a sense of disinterest from culture, a high degree of concentration at work, and a general lack of awareness of the length of time spent at work [36]. Employees who are experiencing absorption are immersed in their work and find it difficult to separate themselves from the job [37]. Organizations tend to consider the financial factor of their employees to achieve their goals. Organizations have the opportunity and potential to consider both financial and non-financial aspects for their performance [38]. Regardless of the size or type of organization, non-financial factors can have a beneficial effect on the performance of the organization.
2.4Employee engagement and organizational performance
Employee engagement is a key element of employee and organization’s success. It predicts employee performance, organizational success and financial performance of the organization. The impact of employee engagement or disengagement appear on the productivity and efficiency of the organization, outcomes for the organization’s customers, staff retention rates, advocacy and the organization’s culture and also its external image [39] By focusing on your work and not paying attention to the things around you, you can complete your work with minimal confusion and maximum competition. Employees who work passionately and engaged are usually performed well than others and contribute to the success of the organization. In terms of dedication, it’s about inspiration, enthusiasm, and the significant involvement of employees in the workplace [36].
The organization’s performance is based primarily on well-planned, articulated and effective employee engagement strategies. Researchers attempt to develop a variety of tools for employee engagement, impact and the need to refine employee engagement, to understand the complexity of employee engagement [40]. Tejaswi and Raya (2014) [41] propose six areas of work that require special attention. Control, workload, equity, communities, rewards and values. They argue that employee integration is recognized in specific work (self-employment) and engagement through conversation, transfer of thoughts, ideas or opinions (self-expression). Essentially, most studies have focused not only on the factors that influence employee engagement but also on individual and organizational outcomes which are associated with the employee engagement.
2.5Research gap
Rare research is done on finding the mediating impact of knowledge sharing between two variables i.e. employee engagement and organization performance. And how much impact does employee engagement has on the performance of the organization, also how much impact knowledge sharing has on organization performance. Also in Pakistan, there has not been much research done on this topic for the higher education sector. It will help the HR managers and other leaders of the organization to take efficient steps to engage the employees and also important steps to manage the knowledge of the employees to increase the performance of the organization. Employees engagement as a tool for knowledge sharing can be used inside the higher educational institute of Pakistan, by this effort, highly qualified and most knowledgeable faculty members can share their knowledge by knowledge sharing databases, this will enable all faculty members or staff to get knowledge which will lead towards individual and organization high performance.
3Methodology overview
This section explains in detail the methodology implemented for this study. A quantitative research strategy was used in this study, where the positivism research approach was used. Quantitative information accumulation strategies are considerably more organized than qualitative information-gathering method [42]. The population frame of this study was higher education staff of public sector and private sector universities located in Karachi, Pakistan. A Non-Probability approach and convenient sampling technique were used in this study. The questionnaire was adopted from the past published research. Employee engagement and organizational performance were measured with the help of a questionnaire used by Paluku, (2016) [43]. While knowledge sharing was measured through the questionnaire used by Aslam et al., (2013) [44]. For the data collection, an online survey was conducted with the help of google form. Total of 400 faculty members of 9 higher education institutions of Karachi was targeted. The response rate through Google Forms was 16%, therefore, the authors decided to collect the data through a printed questionnaire, another 150 hard copies of the questionnaires were distributed to the faculty members of the 9 private and public sector universities located in Karachi, 91 filled questionnaires were received. The response rate of the distributed questionnaire was 60.6%. Researcher discarded 7 questionnaires because he felt the respondents have followed some pattern in filling the form.
A structural equation modelling technique was used to test the model. Data were examined with the help of statistical software SMART-PLS Version 3. This software is widely used in social sciences [56–57]. The scale reliability was assessed by using internal consistency approach through the Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability (CR). Past literature suggested that if the value of the Cronbach’s alpha is 0.7 then it is acceptable but if it is more than 0.9 it is considered strong reliability [45]. To check the validity, convergent validity and discriminant validity approach was used. The PLS method is a proven method for estimating the path coefficients of structural models. It is increasingly used in social sciences research because of its ability to test the model under non-normality conditions with small to medium samples [46]. The PLS algorithm defines the significant loadings, weighs and path coefficients, and its bootstrap method determines the significance level of the hypothesis and mediation, therefore a two-stage approach was used in this study, in the first stage the measurement model was assessed and in the second stage, the structural model was assessed.
4Results and findings
4.1Reliability and validity
As discussed earlier in the methodology section, this study tested the model in two stages as recommended by Hair et al. (2013) [46], in stage 1, measurement model was assessed through factors, loading, reliability and validity analysis. The recommended value for Average Variance Extracted, Composite Reliability and Factor Loadings should be more than 0.5 and 0.7 respectively [47]. Table 4.1 shows that Average Variance Extracted (AVE), Composite Reliability (CR) of all three variables (Employee Engagement, Knowledge Sharing and Organization Performance) and Factor Loading of all the indicators were more than 0.7. Table 4.1 shows the Cronbach’s Alpha value of all three variables were more than 0.7. The Cronbach’s alpha and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) value of variable Employee Engagement were 0.723 and 0.537 respectively, similarly, the Cronbach’s Alpha and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) of the variable Knowledge Sharing were 0.738 and 0.560 respectively, for variable Organization Performance has 0.817 value of Cronbach’s Alpha was 0.817 and value of Average Variance Extracted (AVE) was 0.563.
Table 4.1
Validity and Reliability for Constructs
| Constructs | Items | Loadings | AVE | CR |
| Employee Engagement (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.723) | EE1 | 0.755 | 0.537 | 0.822 |
| EE2 | 0.769 | |||
| EE3 | 0.654 | |||
| EE4 | 0.746 | |||
| Knowledge Sharing (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.738) | KS1 | 0.878 | 0.560 | 0.834 |
| KS2 | 0.751 | |||
| KS3 | 0.709 | |||
| KS4 | 0.637 | |||
| Organization Performance (Cronbach’s Alpha = 0.817) | OP1 | 0.710 | 0.563 | 0.866 |
| OP2 | 0.786 | |||
| OP3 | 0.743 | |||
| OP4 | 0.781 | |||
| OP5 | 0.730 |
Discriminant validity indicates to the degree to which the measures are not an impression of some other factors’ and it is demonstrated by low relationships between the measure of interest and the measures of other concepts. Table 4.2 displays that the square root of the AVE (diagonal values) of every variable is greater than the matching associated measurements, indicating in the direction of satisfactory discriminant validity [50]. Overall the measurement model displayed a satisfactory convergent validity and also the discriminant validity.
Table 4.2
Discriminant Validity (Fornell-Larcker Criterion)
| Employee Engagement | Knowledge Sharing | Organization Performance | |
| Employee Engagement | 0.732 | ||
| Knowledge Sharing | 0.533 | 0.749 | |
| Organization Performance | 0.535 | 0.336 | 0.751 |
4.2Structural model
In the second stage of model testing, authors used PLS algorithm and bootstrapping method to test the hypothesis significant level and mediation. The bootstrapping process with 5000 iterations was conducted to check the significant level.
Table 4.3 shows the regression model results of organization performance and knowledge sharing. Chin et al. (2008) [47] categorized the dependent variable as large, reasonable, and low, centered on the values of R2 that is 0.67 or higher value for a strong effect, 0.33 or more for moderate and 0.19 for weak effect respectively. The value of R2 for Knowledge Sharing is 0.284 and the adjusted R2 is 0.279 and the value of R2 for Organizational Performance is 0.290 and adjusted R2 value is 0.280. This shows that Knowledge Sharing and Organizational Performance are moderately affected by Employee Engagement, therefore, the significant variance is observed in an endogenous variable.
Table 4.3
Regression
| Endogenous Constructs | R2 | Adjusted R2 |
| Knowledge Sharing | 0.284 | 0.279 |
| Organizational Performance | 0.290 | 0.280 |
Table 4.4 displays the result of the structural model and hypothesis test. Total 4 hypotheses are being tested in this study, and all hypotheses were found significant and positive. Employee engagement has a significant and positive impact on knowledge sharing (β= 0.532, t = 8.805 and p = 0.000), Employee engagement has also a significant and positive impact on organizational performance as (β= 0.502, t = 6.741 and p = 0.000), and this study also found that knowledge sharing has a significant and positive impact on organizational performance as (β= 0.063, t = 6.633 and p = 0.000), 1. Finally, this study also concludes that knowledge sharing also partially mediate the relationship between employee engagement and organizational performance, as, (β= 0.040, t = 5.994 and p = 0.000).
Table 4.4
Hypothesis Testing
| Hypothesis | Original Sample (O) | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P Values | Decision |
| Employee Engagement ->Knowledge Sharing | 0.532 | 8.805 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| Employee Engagement ->Organizational Performance | 0.502 | 6.741 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| Knowledge Sharing ->Organizational Performance | 0.063 | 6.633 | 0.000 | Accepted |
| Employee Engagement ->Knowledge Sharing ->Organizational Performance | 0.040 | 5.994 | 0.000 | Accepted |
P < 0.01 = Significant.
The Effect size f² describes whether an exogenous latent construct has a substantial, moderate or weak effect on an endogenous latent construct as mentioned by Hair et al (2013) [46], Cohen (1988) [51] recommended a magnitude of f² at 0.35 (showing large effects), 0.15 (showing medium effects) and 0.02 (showing small effects). The result of f², as mentioned in appendix B, revealed a range of effect sizes between large effects and medium-size effects within this study. The effect size (f²) of employee engagement on knowledge sharing was 0.396 which is considered as a large effect size, similarly, the effect size of employee engagement on organizational performance was 0.250 which is considered as a medium-size effect, while effect size of knowledge sharing on organizational performance was 0.120 which is slightly a small effect size (see appendix B).
5Discussion and conclusion
5.1Discussion
The literature of the current study has highlighted the importance of employee engagement, this construct is important for the success and sustainability of the organization’s performance. A knowledge-sharing process allows an individual to share his/her knowledge with the team and thus, achieve success for the organization and himself/herself [3].
5.2Research contribution
This study allows others to understand the effects of employee engagement in knowledge sharing and organizational performance, and the mediating effect of knowledge sharing between employee engagement and organizational performance in the education sector. This study contributes to the existing literature of knowledge sharing and employee’s engagement. The impact of employee’s engagement is rarely discussed in past literature with organization performance through a mediating effect of knowledge sharing.
5.3Research implications
This study is based on relevant published research and has established a research model to examine the mediating influence of knowledge sharing between employee engagement and organizational performance. A review of the prevailing literature exposed that similar investigation has not been conducted in the higher education sector in Pakistan. Thus in addition to providing this research for theoretical improvement, higher educational institutions management can take advantage of useful insights generated to develop and implement strategies to improve organizational performance through the concept of knowledge sharing and employee engagement.
5.4Theoretical implications
This research rationalizes and empirically tests the impact of employee’s engagement and knowledge sharing with organization performance. Beyond the previously agreed affiliation between employee engagement and organizational performance. Precisely, the findings enhance the academic indulgent of employee engagement and knowledge sharing as an important foundation for organizational performance.
5.5Practical implications
There are two management implications to this study. First of all, the results of this study will help the management of the higher education institution to understand how the employee engagement of faculty members can improve within the organization. If you want to satisfy your employees and invest in the work they do, management can find tools that can increase the engagement of employees to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization.
Secondly, the results help to explain how the employee engagement level could affect the performance of the higher educational institution in Pakistan. This means that managers who are looking to enhance the employee engagement level will benefit from improved organizational performance. As a result, management should know about having the right procedures, processes, mechanism and structures that can increase the employee engagement and this will lead towards the accomplishment of organizational objectives and goals.
5.6Practical Implication for HR challenges and organizational performance sustainability
Prioritizing employee wellbeing has been a key component by many organizations to the current pandemic, and they have created the workplace into a virtual workplace, also called as work from home. This pandemic increasing challenges for the HR department, especially in recruitment and selection, training and development, layoff because of to low productivity of the organizations. One of the biggest challenges for HR managers is how to engage employees effectively, in the current situation the organization’s productions process and services are also affected by COVID-19 pandemic. Organizations are also thinking to move towards innovation to serve the customer in a better way. Employees are working from home, therefore to engage them in a unique style can increase organization performance, employees are the assets of the organization as they have knowledge, skills and abilities which can make a difference in the current competitive environment.
Pandemic is destroying global economies, but at the same time its bringing different opportunities for organizations also. Now organizations have to think about how to avail the opportunity. Knowledge sharing could be a possible way to engage the employees in the current situation. If employees are sharing the knowledge, and organizations are storing it in databases and visualize through an artificial intelligence system, this could help organizations to bring innovation in services and products. Recently researchers Abukhait et al (2019) [52] concluded that knowledge sharing practices have a strong and positive impact on employee innovative behaviour. Similarly, researcher found a significant and positive association between employee innovative behaviour and organization innovation [53], therefore this study concludes that knowledge sharing inside the organization can create a pool of new ideas which will lead to product and service innovation. Empirical evidence of this study predicted that employee engagement has a significant and positive impact on organizational performance, similarly it is also predicted that employee engagement has also a significant and positive impact on knowledge sharing which further affect organization performance. Therefore, to maintain the high performance of the organization, employee engagement and knowledge sharing could be the best solution to meet the current HR challenges.
A remote workplace cannot only lead towards low productivity of the organization, if HR managers engage employee effectively then remote work would be a future of an effective working system, as employees would be connected to the family and there would be no psychological pressure of their bosses, hence this can lead towards high productivity. The remote workplace is also important for higher education institutes, faculty and staff members could be more productive from home, as they will have no more psychological pressure, staff are more flexible towards their working activities. Hence, the HR department has to play a leadership role inside the organization, there is also need of changing the organizational culture, simply employee’s layoffs policy can’t save the organization from bankruptcy, as after pandemic, the organization might face problem to hire talented employees immediately. The HR department should also focus on online recruitment and selection process, training and development and should focus on employee’s health and safety issues, all these efforts can lead towards organization performance sustainability during the current pandemic.
5.7Limitations
Most of the studies, no matter how good they are, face some limitations. However, these limitations are considered beneficial because they provide a guideline for future research. Limitation of this study is that data were collected from 9 higher educational institutes of Karachi, if the data were collected from the other cities the results might vary from the current study. In this study only three variables were used, two exogenous variables and one endogenous variable, other predictors such as leadership, learning culture and artificial intelligence in knowledge sharing, employee engagement and organizational performance enhancement can be analyzed in future.
5.8Future studies
In this study, the researcher has focused only on the higher educational institutions of Karachi and the results may certainly differ from sector to sector. The people who have taken a part in this study were similarly limited to the faculty members of the universities only. These are the factors that encourage the requirement of additional perfection in this study like a more varied number of participants could have been included in future study and there are chances that the outputs might be changed. It is recommended to take this study into the other cities of Pakistan because employee engagement and knowledge sharing is a very important factor of the employee performance as well as organizational performance.
5.9Conclusion
This research examined and evaluated employee engagement strategies related to the success of the organization. Researchers used quantitative analysis by collecting employee opinions using descriptive and speculative statistics and drawing important conclusions. The organization must give its employees the freedom to create an environment conducive to a dedicated professional life that inspires their work. Employees are an important asset for any organization. If they do not have enough space and time to combine work and pleasure at work, then dis-engagement may found between employees. Organizations and employees trust each other to achieve their goals and objectives. Therefore, employee engagement must be embedded in the corporate culture. Employee involvement must be an ongoing process of learning, action and improvement. Thus, today’s organizations must actively look forward to meeting the expectations of employees, create an impact on the employees’ performance, which directly affects the performance of the organization. Similarly, knowledge sharing is also a significant predictor of organization performance, this study found a positive association between knowledge sharing and organization performance.
5.10Recommendations
In general, organization adopt a more intensive organizational approach, ranging after elevated measures which are the establishment of a board of engagement to training programs on responsiveness and employee participation to enhance employee engagement within the organization. To achieve the full benefits of employee engagement, we need to work hard at all levels, including integrating employee engagement and client satisfaction into employees’ rewards and compensation plans. Management of these universities should focus more on the employee engagement and then on knowledge sharing strategies because results of the study show that employee engagement has a more impact upon the organizational performance that is Beta = 0.502 and on the other hand knowledge sharing has 0.063 impacts on the organizational performance. Employees who are engaged feel a greater connection with their work and the organization. To enhance their organization productivity higher educational institutions should focus on employee engagement strategies to make their employees more involved (physically, mentally and cognitively), more productive and more creative towards their work as the employees who are engaged are happier at their work as well as their personal lives than the ones who are not engaged.
Appendices
Author contributions
CONCEPTION: Tanveer Ahmed and Muhammad Shahid Khan
METHODOLOGY: Duangkamol Thitivesa and Yananda Siraphatthada
DATA COLLECTION: Tanveer Ahmed
INTERPRETATION OR ANALYSIS OF DATA: Muhammad Shahid Khan and Tawat Phumdara
PREPARATION OF THE MANUSCRIPT: Muhammad Shahid Khan
REVISION FOR IMPORTANT INTELLECTUAL CONTENT: All authors
SUPERVISION: Muhammad Shahid Khan
Appendix A: Questionnaire
THE MEDIATING EFFECT OF KNOWLEDGE SHARING ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE
Please indicate the extent of your agreement with the following statement on a 5-point scale. (Please circle your answer)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Strongly Disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly Agree |
| Employee Engagement | ||||||
| 1. | I have a chance to practice my best skills at work every day. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2. | My supervisor and colleagues seem to care about me at work. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 3. | My organization motivates me to go beyond what I would in a similar role elsewhere. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4. | I am proud to work for my organizations. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 5. | Most of the systems and processes here support me getting my work done effectively | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Knowledge Sharing | ||||||
| 6. | When I was face difficulties at work, my colleagues help me out | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 7. | Negative behavior towards Knowledge sharing is always discouraged in my organization. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 8. | Knowledge sharing improves the interpersonal relationships amongst the employees. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 9. | I will open my knowledge to anyone in the organization if it is helpful to the organization. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10. | I will always provide my knowledge at the request of other organizational members. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Organizational Performance | ||||||
| 11. | My organization is flexible, open to new ideas and promotes creativity. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 12. | Employees are not prepared to go an extra mile for the company. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 13. | Employees do not feel special commitment to the organization. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 14. | Absenteeism and turnover in my organization (relative to competition) is very low. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 15. | Reputation of my organization in eyes of the customers has declined. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Appendix B: Effect Size (F—Square)
| Knowledge Sharing | Organizational Performance | |
| Employee Engagement | 0.396 | 0.250 |
| Knowledge Sharing | 0.120 |
Appendix C: Cross Loadings
| Employee Engagement | Knowledge Sharing | Organizational Performance | |
| EE1 | 0.755 | 0.325 | 0.253 |
| EE2 | 0.769 | 0.388 | 0.349 |
| EE3 | 0.654 | 0.166 | 0.432 |
| EE5 | 0.746 | 0.561 | 0.481 |
| KS1 | 0.510 | 0.878 | 0.364 |
| KS2 | 0.351 | 0.751 | 0.219 |
| KS3 | 0.322 | 0.709 | 0.092 |
| KS4 | 0.365 | 0.637 | 0.253 |
| OP1 | 0.507 | 0.352 | 0.710 |
| OP2 | 0.334 | 0.206 | 0.786 |
| OP3 | 0.260 | 0.261 | 0.743 |
| OP4 | 0.488 | 0.251 | 0.781 |
| OP5 | 0.268 | 0.077 | 0.730 |
Appendix D: Collinearity Statistics (VIF)
| Items | VIF |
| EE1 | 1.791 |
| EE2 | 1.811 |
| EE3 | 1.288 |
| EE5 | 1.170 |
| KS1 | 1.935 |
| KS2 | 1.845 |
| KS3 | 1.490 |
| KS4 | 1.301 |
| OP1 | 1.289 |
| OP2 | 2.039 |
| OP3 | 2.808 |
| OP4 | 1.578 |
| OP5 | 2.582 |
References
[1] | Chen Y . Relationships among Service Orientation, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Commitment in the International Tourist Hotel Industry. Journal of American Academy of Business. (2010) ;11: (2):71–82. |
[2] | Albrecht SL . The Influence of Job, Team and Organizational Level Resources on Employee Well-Being, Engagement, Commitment and Extra- Role Performance –Test of a Model. International Journal of Manpower. (2011) ;33: (7):840–53. |
[3] | Bailey AA , Albassami F , Al-Meshal S . The roles of employee job satisfaction and organizational commitment in the internal marketing-employee bank identification relationship. International Journal of Bank Marketing. (2016) ;34: (6):821–40. |
[4] | Chauhan R . Impact of Training and Development On Employee Performance and Productivity with Reference to Indian Banking Sectors. International Journal of Engineering Research & Management Technology. ISSN: 2348-4039, 2018;5(2). |
[5] | Vance RJ . Organizing for customer service. In L. Fogli (Ed.), Customer service delivery: Research and best practices (pp. 22-51). San Francisco, Calif.: Jossey-Bass. 2006. |
[6] | Risley C . Maintaining Performance and Employee Engagement During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Library Administration. (2020) ;60: (6):653–9. |
[7] | Harter JK , Schmidt FL , Hayes TL . Business-unit level relationship between employee satisfaction, employee engagement, and business outcomes: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology. (2002) ;87: :268–79. |
[8] | Abrahma S . Development of Employee Engagement Programme on the Basis of Employee Satisfaction Survey. Journal of Economic Development, Management, Information Technology Finance and Marketing. (2012) ;4: :27–37. |
[9] | Ilyasa M , Mansyur R . The Effect of Organization Culture, Knowledge Sharing and Employee Engagement on Employee Work Innovation. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management (IJSRM). (2018) ;6: (1):57–63. |
[10] | Shuck B , Wollard K . Employee engagement and HRD: A seminal review of the foundations. Human Resource Development Review. (2010) ;9: (1):89–110. |
[11] | Amhalhal A , Anchor J , Dastgir S . The Effectiveness of the Use of Multiple Performance Measures: The Influence of Organizational Contingencies. London: Sage. 2015. |
[12] | Yalabik ZY , Bruce AR , Andriana R . Facets of job satisfaction and work engagement. Evidence based HRM: A Global Forum for Empirical Scholarship. (2017) ;5: (3):248–65. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBHRM-08-2015-0036. |
[13] | Sundaray BK . Employee engagement: A driver of organizational effectiveness. European Journal of Business and Management. (2011) ;3: (8):53–9. |
[14] | Andrew OC , Sofian S . Engaging People Who Drive Execution and Organizational Performance. American Journal of Economics and Business Administration. (2011) ;3: :569–75. |
[15] | Bakker AB , Albrecht SL , Leiter MP . Key questions regarding work engagement. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology. (2011) ;20: :4–28. |
[16] | Blanchard PN , Thacker JW , Ram VA . Effective Training: Systems, Strategies and Practices. Fourth Edition. Noida, UP: Dorling Kindersley. 2012. |
[17] | Nassazi A . Effects of training on Employee performance. Evidence from Uganda (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Vaasa University of Applied Sciences, Vaasa, Finland. 2013. |
[18] | Aktar A , Pangil F . Antecedents and Consequences of Employee Engagement: A Conceptual Study. IOSR Journal of Business and Management. 2017;(Vol. 19). https://doi.org/10.9790/487X-1906065467 |
[19] | Hanaysha J . Testing the Effects of Employee Engagement, Work Environment, and Organizational Learning on Organizational Commitment. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. (2016) ;229: :289–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.07.139 |
[20] | Wang S , Noe RA . Knowledge Sharing: A Review and Directions For Future Research. Human Resource Management Review. (2010) ;20: (2):115–31. |
[21] | Becerra-Fernandez I , Xia W , Gudi A , Rocha J . Task Characteristics, Knowledge Sharing and Integration, And Emergency Management Performance: Research Agenda and Challenges. Paper Presented at The Proceedings of The 5th International ISCRAM Conference Washington, DC, USA. 2010, 88-92. |
[22] | Khan M , Bilal H , Mateen A , Haq Z . The Mediating Effect of Knowledge Management System and Learning Culture on Human Capital Development. International Journal of Management and Applied Science. (2017) ;4: (5):14–7. |
[23] | Khan M , Sentosa I , Salman F . Exploring the role of transformational leadership in human capital effectiveness. World Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management, And Sustainable Development. (2018) ;14: (2):191–204. Doi: 10.1108/wjemsd-10-2017-0075. |
[24] | Khan M , Chongcharoen D , Jankaweekun P . Transformational Leadership, Mediating Effect of Knowledge Management System and Moderating Effect of Training in Human Capital Development: SEM-SMART PLS Approach. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research. (2020) ;9: (4):929–42. |
[25] | Khan MS , Chongcharoen D , Ulhaq Z . The Mediating Effect of Employee Learning between Job Rotation and Employee CareerDevelopment: Empirical Evidence from the Banking Sector of Pakistan. 2019, 66-80. |
[26] | Witherspoon LC , Jason B , Cam C , S. Dan N . Antecedents of businessal knowledge sharing: a meta-analysis and critique. Journal of Knowledge Management. (2013) ;17: (2):250–77. |
[27] | Zannahjuan UN , Yelli ES . Knowledge Sharing Implikasinya terhadap Employee Engagement. Fakultas Bisnis dan Manajemen Universitas Widyatama. 2013. |
[28] | Maldonado-Guzmán G , Lopez-Torres GC , Garza-Reyes JA , Kumar V , Martinez-Covarrubias JL . Knowledge management as intellectual property: evidence from Mexican manufacturing SMEs. Management Research Review. 39: (7):830–50. |
[29] | Pinho JC . Social capital and export performance within exporter-intermediary relationships: the mediated effect of cooperation and commitment. Management Research Review. (2016) ;39: (4):425–48. |
[30] | Markos S . Employee Engagement: The Key to Improving Performance. International Journal of Business and Management. (2010) ;5: (12):89–96. |
[31] | Akter K . The Role of Non-Financial Factors in Measuring Organizational Performance. Proceedings of International Conference on Business Management. (2011) ;8: :245. |
[32] | Shamila VJ . Employee Engagement—An Approach to Organizational Excellence. International Journal of Social Science & Interdisciplinary Research. (2013) ;2: :111–7. |
[33] | Hromei A . Non-Financial Factors That Influence the Success of a Merger Transaction. Economic and Management. 2014;504-11. |
[34] | Tak I . Misleading the Financial Situation Users by Frauds. CCI3 Economy and Management. 2014, 547-56. |
[35] | Nawaz S , Hassan M , Hassan S , Shukat S , Asadullah AM . Impact of Employee Training and Empowerment on Employee Creativity through Employee Engagement: Empirical Evidence from Manufacturing Sector of Pakistan. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research. (2014) ;19: :593–601. |
[36] | Rayton B , Yalabik Z . Work Engagement, Psychological Contract Breach and Job Satisfaction. The International Journal of Human Resource Management. (2014) ;25: (17):2382–400. |
[37] | Shekari H . Evaluating the Three Dimensions of Work Engagement in Social Security Organization of Yazd Province in Iran. Journal of Educational and Management Studies. (2015) ;5: (3):168–74. |
[38] | Questica. The Importance of Measuring Non-Financial Factors. 2015. http://www.questica.com/budgeting-tips-and-tricks/the-importance-of-measuring-nonfinancial-factors |
[39] | Schaufeli WB , Salanova M , Gonzalez-Roma V , Bakker AB . The measurement of engagement and burnout: A two simple confirmatory factor analytic approach. Journal of Happiness Studies. (2009) ;3: :71–92. |
[40] | Karumuri . Employee Engagement: Hotel Industry SCMS Journal of Indian Management, July - September 2016, 2016;120. |
[41] | Tejaswi B , Raya RP . Employee engagement: Key to organizational success. SCMS Journal of Indian Management. (2014) ;11: (4):61–71. |
[42] | DeFranzo SE . What’s the difference between qualitative and quantitative research? (2011, Sep 16). Retrieved from https://www.snapsurveys.com/blog/qualitative-vs-quantitative-research/ |
[43] | Paluku K . Employee Engagement and Organizational Performance of Retails Enterprises. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management. (2016) ;6: :516–25. |
[44] | Aslam MMH , Shahzad K , Syed AR , Ramish A . Social capital and knowledge sharing as determinants of academic performance. Journal of Behavioral and Applied Management. (2013) ;15: (1):25–41. |
[45] | Kline P . The handbook of psychological testing (2nd ed.). London: Routledge, 2000, pp. 13. |
[46] | Hair JF , Hult GTM , Ringle C , Sarstedt M . A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS–SEM). Sage Publications. (2013) . |
[47] | Chin WW , Peterson RA , Brown PS . Structural equation modeling in marketing: Some practical reminders. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice. (2008) ;16: (4):287–98. |
[48] | Lin C , Wu J-C , Yen DC . Exploring barriers to knowledge flow at different knowledge management maturity stages. Information & Management. (2012) ;49: (1):10–23. |
[49] | Juan S , Yao L . Considering university governance: a preliminary investigation of employee engagement in higher educational institutions in Malaysia. In FGIC 1st Conference on Governance & Integrity, 2017 “Innovation & Sustainability Through Governance” 2017, (pp. 224-232). |
[50] | Son TT , Phong LB , Loan BTT . Transformational Leadership and Knowledge Sharing: Determinants of Firm’s Operational and Financial Performance. SAGE Open. (2020) ;10: (2):2158244020927426. |
[51] | Cohen J . Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). New Jersey, USA: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates. 1988. |
[52] | Abukhait RM , Bani-Melhem S , Zeffane R . Empowerment, knowledge sharing and innovative behaviours: Exploring gender differences. International Journal of Innovation Management. (2019) ;23: (01):1950006. |
[53] | Al-Ababneh M . Employees’ Service Innovation Behavior and New Service Development in Four- and Five-Star Hotels. SSRN Electronic Journal. 2014. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3633078. |
[54] | Djikhy S , Moustaghfir K . International faculty, knowledge transfer, and innovation in higher education: A human resource development perspective. Human Systems Management. 2019, 423-31. |
[55] | Ahmadi A , Abzari M , Nasr Isfahani A , Safari A . High-performance, knowledge sharing and ICT skills. Human Systems Management. (2018) ;37: (3):271–80. doi: 10.3233/hsm-17169. |
[56] | Khan MS , Saengon P , Alganad AMN , Chongcharoen D , Farrukh M . Consumer green behaviour: An approach towards environmental sustainability. Sustainable Development. 2020;1-13. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2066 |
[57] | Mansoor A , Farrukh M , Wu Y , Abdul Wahab S . Does inclusive leadership incite innovative work behavior? Human Systems Management. 2020, 1-10. doi:10.3233/hsm-200972. |
[58] | Welch M . The evolution of the employee engagement concept: communication implications’. Corporate Communications: An International Journal. (2011) ;16: :328–46. |



