Research on influence factors and application effects of professional ability building for college counselors from PDCA cycle perspectives
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
With the increasing demand for professionalism and specialization in college counselors (CCs), it is especially important to implement comprehensive professional ability building (PAB) of CCs.
OBJECTIVE:
This paper proposes to provide institutional support for CCs’ PAB by establishing a sound CC career development system and improving the CC salary system, in order to better support college education.
METHODS:
Through research interviews, literature research and expert consultation, a questionnaire survey outline is set up from subjective, objective, and institutional factors. A random sampling method is adopted to conduct a questionnaire survey on CCs and school students. Questionnaire results are analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively in terms of reliability, validity and so on, and the influence factors of PAB for CCs are discussed. The research hypothesis is put forward, and the current situation of PAB is further summarized.
RESULTS:
It is found that CCs have a strong subjective willingness to build their PA, and the potential motivation of objective factors is sufficient. However, the existing system is not perfect, and job burnout such as diminished enthusiasm for work has appeared.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on the existing research results, this paper combines PDCA Cycle theory with ideological and political education theory from the perspective of management science. Classical management methods are applied to the PAB system of CCs, and specific implementation countermeasures are presented according to the workflow construction model from decision-making to implementation, monitoring, and improvement.

Hongxia Yan, female, from Wuhan, Hubei. Master’s degree. She is currently a lecturer at Southeast University Chengxian College. Her research direction is ideological and political education. Hongxia Yan is interested in the analysis of the professional capacity building path of college counsellors based on PDCA cycle management.
1Introduction
The full name of college counselor (CC) is an ideological and political counselor for college students, which undertakes three major functions of education, management and service [1–5]. In addition, they are responsible for the fundamental task of fostering morality and cultivating people. They are not only the backbone of the ideological and political work team in colleges and universities, but also the direct implementers and organizers of college students’ ideological and political works. With the promotion of professionalization and specialization of counselors, the professional ability building (PAB) has become one of the most important standards for measuring CC’s PA levels [6–8]. CC’s PAB requires not only the value discussion at theoretical levels, but also the operability strengthening at practical levels. Meanwhile, it is supported by scientific and technical methods [9–11].
Improving CC’s PA is the primary premise and key link to enhancing the affinity of ideological and political education in colleges, and improving the business ability of CC is the core of improving the pertinence of ideological and political education in colleges [12–14]. Improving CC’s PA and doing a good job in students’ ideological and political work is related to the overall development of national education, which is of self-evident significance. Only by continuously improving the PA of CC, enhancing the role and influence of CC in students’ ideological and political education, and ensuring the effectiveness of ideological and political education, can CC realize professional identity. While promoting CC to work more actively and creatively, CC’s healthy and positive working attitude can also imperceptibly drive students to develop an optimistic attitude and form a good sense of professional responsibility.
At present, the research on PAs in CC mainly involves PA standards and classifications, difficulties and suggestions for PA promotion, professional quality requirements, job responsibilities, management models, training and development, and so on. These research perspectives have their own emphases and have guiding value for reference. However, there is less work on analysis from the perspective of influence factors. In particular, there are few reports on the guidance of CC’s PAB based on PDCA, and there is no detailed work on building a related model framework. This paper combines PA Standards for CCs (Temporary) [15–17] to carry out in-depth research, based on the theories of competence, motivation and environmental influence. On the basis of referring to previous research, the most important three factors are summarized, and the elements and connotation of PAB of CC are determined. Meanwhile, the application of the PDCA Cycle in the education field is sorted out, so as to apply PDCA Cycle theory to guide the construction of CC’s PAB system. In addition, after introducing quality management thinking and PDCA Cycle theory into PAB, countermeasures are put forward from the perspective of quality management to explore new paths and methods for CC team building in theory and practice. This is of great significance for perfecting and standardizing the existing PAB system, enriching the theoretical basis of PDCA Cycle and expanding its application field.
2Connotation and functional advantages of PDCA cycle theory
PDCA Cycle management is a classic management method in management science [18–22]. It was first proposed by an American quality management expert named Walter A.Shewhart, and then promoted and developed by his disciple Dr. Deming, so this cycle is also called Deming Cycle. PDCA Cycle is a closed management system composed of a series of links such as Plan (planning), DO (execution), Check (check), Action (processing) and so on (see Fig. 1). Through the closed-loop operation of a series of PDCA links, it continuously optimizes the management process and solves the problems of product quality and enterprise benefit improvement. Effective quality management for projects is carried out, through the combination of successful experience and standards. The application of PDCA Cycle theory is quite extensive and its effect is remarkable in quality management fields [23, 24].
Fig. 1
A step-up model of the PDCA Cycle.
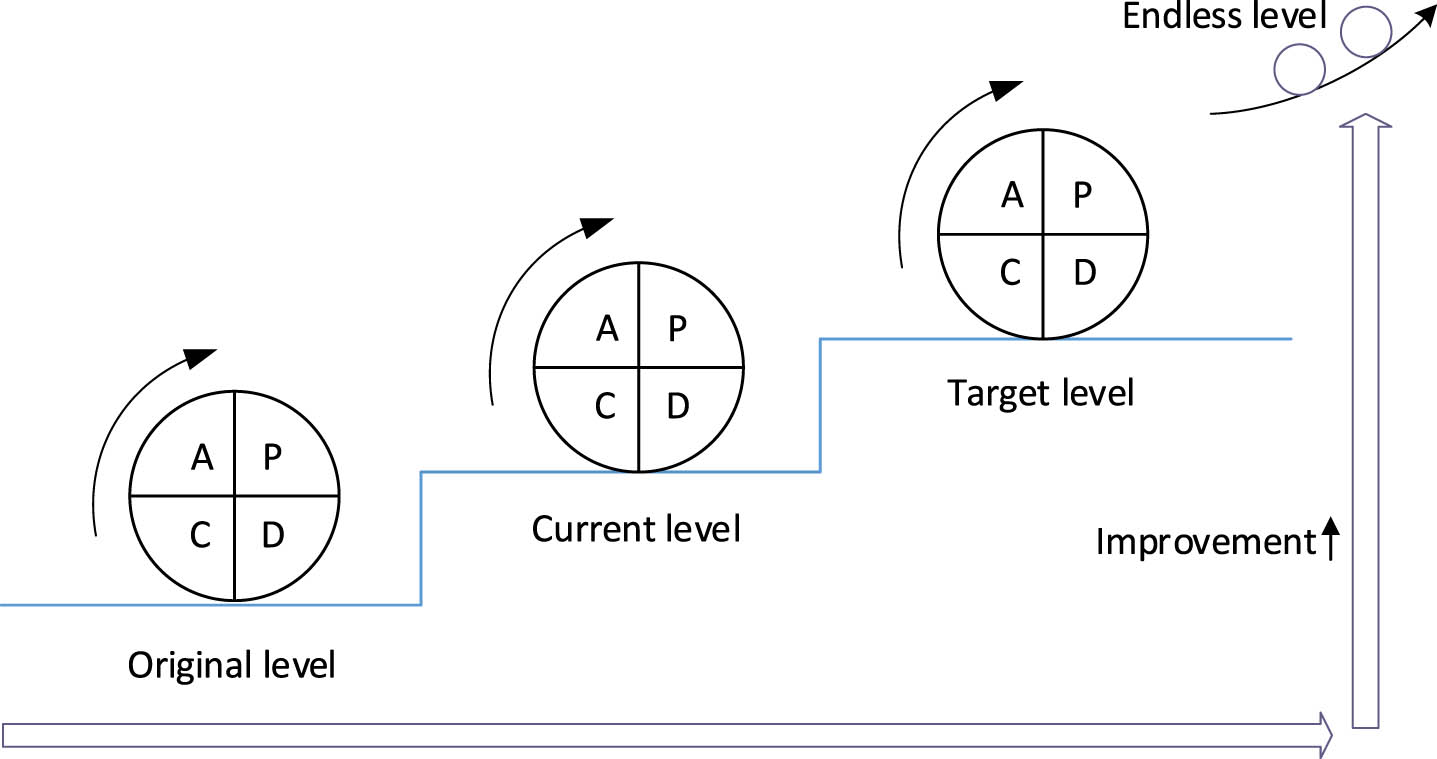
The model shown in Fig. 1 starts from the P stage, passes through the D stage, the C stage, and finally enters the A stage, from operating mechanism perspectives. Problems that can be solved are directly solved, while problems that cannot be solved enter the next stage. These four stages are not carried out in a one-way chain but in a circular manner. After execution, the remaining unresolved problems and new problems enter the cycle’s second round. This approach effectively promotes the continuous optimization of management processes and work quality, through continuous self-circulation.
Also, this type of spiral in function orientation needs to be noted. During the cycle, unresolved problems enter the next cycle. The four cycles of PDCA are interlocking and restrict each other. The cycle of the next level is based on the cycle of the previous level, and it is also the implementation and development of the previous level’s cycle. Each cycle can solve some problems, illustrating a stepwise upward trend (see Fig. 1).
3Current situation survey for CC’s PAB
Many factors affect CC’s PA improvement. Before launching the survey in the form of a questionnaire, a large number of individual interviews are conducted, and the questionnaire is further improved by combining the information obtained from the interviews.
3.1Survey questionnaire settings
3.1.1Survey purpose
According to PA Standards for CCs (Temporary), in-depth research is carried out based on theories of competency, motivation and environmental influence. The survey outline is determined through expert interviews. Through the survey, the factors that affect CCs’ PAB are discussed in subjective, objective and institutional dimensions. Specifically, before carrying out the questionnaire survey, we conducted researches on PAB of CCs in some colleges and universities in Jiangsu Province, China, and interviewed CCs and 10 experts in related fields to obtain the influence factors of PAB (see Table 1). Further, according to the results of investigation and interviews and literature research, the elements and connotation of CC’s PAB are initially formed. Questionnaires are prepared and conducted on the basic situation of CCs in each college and the factors influencing PA.
Table 1
The influence factors of CC’s PAB
| Type | Content |
| Subjective factor | Strong willingness to train |
| Awareness of career planning | |
| Focus on the improvement of method skills | |
| Look forward to the social recognition of the profession | |
| Actively care about career-related platforms | |
| Pay attention to social hot spots and network dynamics | |
| Carry out ideological and political education through network | |
| Able to intervene in students’ psychological problems | |
| Have experience in CC PA competitions | |
| Have a relevant occupation certificate | |
| Undertake relevant teaching tasks | |
| Have scientific research experience | |
| Objective factor | Student-counselor relationship |
| Students’ role orientation to CCs | |
| Student needs CC help | |
| Student recognition of CC career | |
| Satisfaction with daily ideological and political education work | |
| Satisfaction with the development of student party members and education management | |
| Satisfaction with the selection, training and motivation of student backbones | |
| Satisfaction with guiding the construction of student party branches and class organizations | |
| Satisfaction with using new media platforms to communicate with us | |
| Satisfaction with providing efficient and high-quality employment guidance services | |
| The necessity of CCs strengthening the ability of ideological and political education | |
| Evaluation of CC’s working ability | |
| Institutional factor | Organize school training |
| Participate in training every semester | |
| Build a CC salon | |
| Carry out an academic study or on-the-job study |
3.1.2Survey content
According to the survey purpose, the survey questionnaire questions are set as shown in Table 1.
The survey questionnaire of this research is composed of two sets of questionnaires for college students and counselors, to quantitatively analyze CC’s PA. The college student questionnaire is used to find out students’ satisfaction evaluation of CCs’ PA through a survey of students. This questionnaire mainly focuses on objective factors. It sets questions from students’ cognition of CC’s role and ability, and makes an overall evaluation of CC’s PA. The questionnaire for counselors mainly focuses on subjective factors and institutional factors, and sets questions from the internal driving force, PA foundation, school training and team factors of CC’s PA development. The highest and lowest satisfaction scores are 10 and 0, respectively.
3.1.3Survey objects and methods
In this survey, 200 questionnaires are distributed to some CCs in Jiangsu Province, China, by random sampling method [25–30], and 197 questionnaires are recovered, with an effective recovery rate of 98.8%. The questionnaire consists of demographic variables and factual questions. Among them, the factual questions adopt the form of a 5-level Likert scale to set five levels. Score options from 1 to 5 represent different levels of agreement. Table 2 records the basic information of the surveyed CCs.
Table 2
The basic information of CCs
| Type | Number of people | Proportion (%) | Type | Number of people | Proportion (%) | ||
| Gender | Female | 151 | 76.65% | Title | Assistant | 89 | 45.17% |
| Male | 46 | 23.35% | Lecturer | 96 | 48.73% | ||
| Age | ≤35 | 136 | 69.04% | Associate professor | 12 | 6.09% | |
| 36-45 | 55 | 27.91% | Qualification | Undergraduate | 23 | 11.67% | |
| ≥46 | 6 | 3.05% | Master degree candidate | 170 | 86.29% | ||
| Nature | Full-time | 183 | 92.89% | Doctoral candidate | 4 | 2.03% | |
| Part-time | 14 | 7.10% | |||||
3.2College student questionnaire
This part uses a survey of college students to understand the students’ satisfaction evaluation of CC’s PA. The highest and lowest scores of satisfaction obtained from the overall evaluation of PA are 10 and 0, respectively. A random sampling method is adopted again, and 400 questionnaires are distributed to some students in the school in Jiangsu Province, China. A total of 395 questionnaires are returned (including 218 males, accounting for 55.2%; 177 females, accounting for 44.8%), with an effective recovery rate of 98.75%.
3.3Analysis of survey results
3.3.1Reliability and validity analysis
Cronbach’s α coefficient is one of the most commonly used methods for testing reliability [30–35]. An α above 0.8 demonstrates better questionnaire reliability. Based on the internal consistency results of the scale’s overall data, the coefficients of CC and student questionnaires are 0.838 and 0.833, respectively, indicating an excellent reliability performance of the scale (Table 3).
Table 3
The reliability analysis results
| Questionnaire category | Number of items | Sample size | α |
| CC | 16 | 197 | 0.838 |
| College student | 12 | 396 | 0.833 |
Validity refers to the validity of the scale, indicating the extent to which the measurement tool reflects the true meaning of the concept that the researcher wants to measure. This study first uses the theory of influence factors for analysis, and draws on mature scales from domestic and foreign literature to ensure the comprehension and operability of the questionnaire. A KMO value higher than 0.8 indicates high validity. If this value is between 0.7 and 0.8, it means that the validity is good. If this value is between 0.6 and 0.7, it means that the validity is acceptable. However, if this value is less than 0.6, the validity is poor (if there are only two items, then the KMO value is 0.5 anyway) [37–42]. The validity test results of this study record a KMO value of 0.876, indicating high validity.
3.3.2Result analysis
According to the questionnaire data, among the three factors affecting CC’s PAB, subjective factors have obvious advantages, and objective factors have obvious potential driving forces, but the advantages of institutional factors are still insufficient.
Judging from the questionnaire data, the current situation of CC’s PAB is as follows.
(1) CCs have a high degree of professional identity. 95.2% of CCs think that being a counselor is a very meaningful job, which shows that the counselors have a very clear judgment on the importance and significance of their work. From the subjective factors of CCs, 96.75% of them think that training is necessary, 76.8% of them think that they often need to make career plans for themselves, 87.88% of them care about the social recognition of their careers, and 82.6% of them actively care about career-related development platforms. The demand for the training of CCs reaches 100%. This confirms that CCs have a high degree of recognition of their profession and care about career development. The above point of view is the basis for CCs to carry out ideological and political education of students in depth.
(2) CCs do not have a high sense of job accomplishment and show job burnout. The questionnaire data shows that 70.7% of them are often working overtime. 67.4% of them say that their work pressure is very high, 74.5% of them are satisfied with their job completion, 56.7% of them believe that they are competent for the work of students, and 58.9% of them are dissatisfied with their income. CC’s working hours occupy their time, and the long-term nature of service work leads to energy consumption, coupled with work intensity and pressure, resulting in job burnout. In addition, role conflicts, low social-professional identity, lack of career goals and a sense of accomplishment are also reasons for their burnout.
(3) Professional skills and scientific research ability are not strong. Statistics show that 77.9% of CCs can actively learn the knowledge and skills of students’ work. The survey also shows that CCs who have not participated in scientific research and published theoretical articles in the past three years accounted for 70.6% and 51.8% of the total respectively. Problems such as unsystematic business training, lack of professional skills, and the need to improve scientific research capabilities plague the personal development of CCs.
(4) The assessment and incentive mechanism for CCs needs to be improved. According to the survey results, CCs do not have a high evaluation of the assessment mechanism in their schools. 34.6% of CCs think that the existing mechanism is unreasonable, which is mainly reflected in the unscientific assessment indicators (27.2%), unreasonable assessment content (26.3%), and unreasonable use of assessment results (36.3%). Therefore, building a scientific and reasonable assessment and incentive mechanism is an important measure to improve CC’s PA.
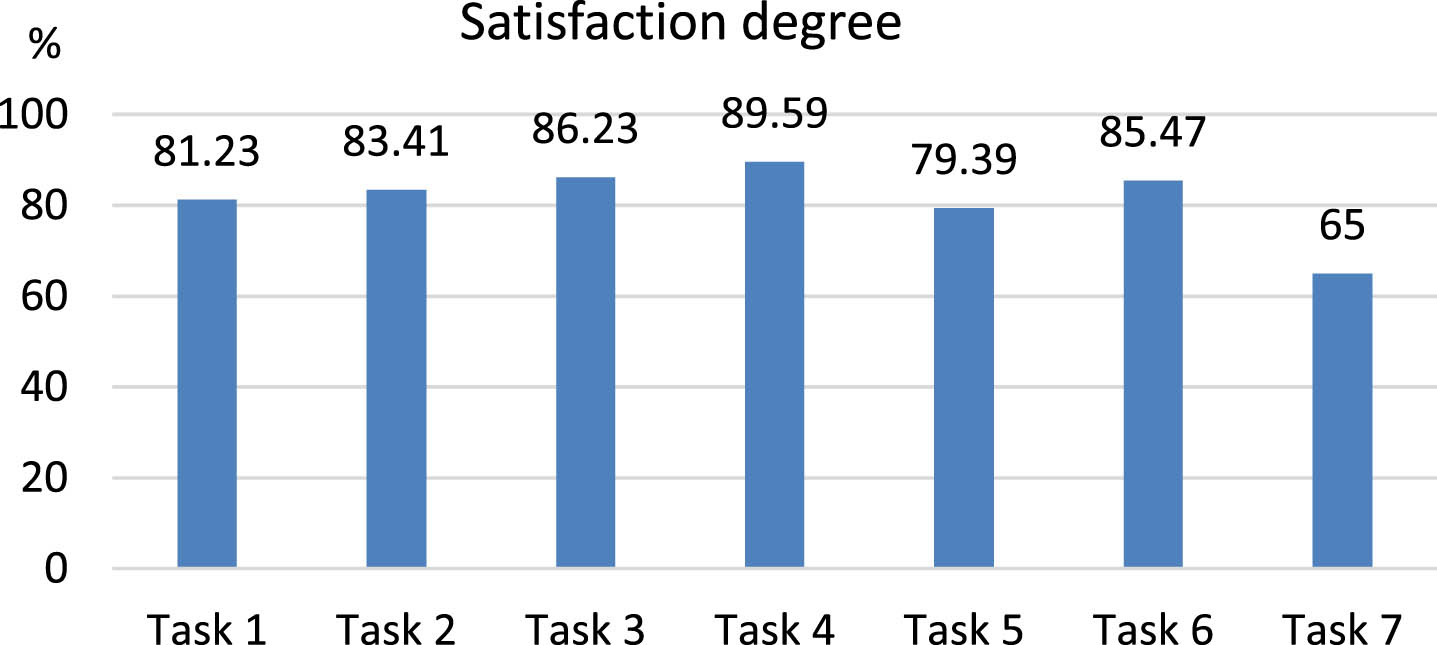
(5) From the perspective of objective factors, the overall evaluation of CC’s various PAs by students is relatively high. See Fig. 2 for students’ satisfaction with various tasks of CCs. Among them, tasks 1 to 7 represent the daily ideological and political education, the development and education of student party members, the cultivation of student cadres, the construction of party and youth organizations, the application ability of new media platforms, employment guidance services, and strong CC’s workability. The objective factors shown in the questionnaire reflect that students and CCs have reached a consensus on the importance of CC’s career and the necessity of improving CC’s PA. 65% of the students think that CCs have strong professional ability, but 7% of the students think that CCs have insufficient professional ability.
(6) Judging from the institutional factors of various colleges and universities, 100% of CCs have participated in the training. The proportion of participants in training per semester is 46% for 1-2 sessions, 25% for 3-4 sessions, and 17% for 5-6 sessions. In addition, 62.58% of colleges and universities have established counselor salon forum activities, and 15% of colleges and universities have provided counselors with on-the-job training opportunities.
Fig. 2
Students’ satisfaction degree with CC’s works.
The level of professionalization, specialization, and expertization for CC team construction has been significantly improved under the full implementation background of the fundamental task of cultivating morals and talents, but there are still some problems. According to the questionnaire analysis, CCs have a high degree of professional recognition, but there are problems such as a low sense of job accomplishment, job burnout, low professional skills and scientific research capabilities, and an imperfect assessment and incentive mechanism system [43–45].
4Framework setting of PDCA Cycle-based CCs’ PAB
According to the analysis of the questionnaire survey, key factors affecting the PA enhancement of CCs include job burnout, professional skills, research ability, performance appraisal, and incentive mechanisms. It is necessary to apply the PDCA Cycle theory in management science to find ways to enhance CCs’ PAs. By optimizing their work process and procedures, a closed-loop model for building the CC team can be well constructed.
4.1Inherent coupling between PDCA cycle and CCs’ PAB
The inherent coupling between PDCA Cycle theory with unique functional advantages and CC’s PAB helps to meet the dual needs of CC’s PAB at theoretical and practical levels. PDCA Cycle is a scientific procedure that total quality management should follow, and it is applicable to all step-by-step management tasks. Such a PAB is not a one-shot process, but a continuous optimization and spiral process. Therefore, exploring the path and method of CC’s PAB has a connection with the attributes of the PDCA Cycle. It is necessary to aim at cultivating and improving CC’s PA. Aiming at the outstanding problems faced by CCs in PAB, through the cycle of decision-making, operation, monitoring and improvement, the four links are repeated to make it run through the immediate feedback of each link [46–48]. Ultimately, the continuous optimization and continuous improvement of CC’s PA are realized.
4.2Construction of PAB system of CCs under PDCA cycle perspectives
As a basic method in the total quality management theory, PDCA Cycle has provided important theoretical guidance for CC’s PAB. As mentioned earlier, this cycle is a closed loop composed of planning, execution, checking, processing and other links. The basic PAB is a process of stimulating improvement awareness of PA. It is urgent to build a PAB system for CCs, and to learn from and use the internal theory and structural mechanism of PDCA Cycle. It is suggested to start from link optimization, design the cycle system of PAB for CCs, find the inner meeting point between PDCA Cycle and PAB, and finally form a cycle system of PAB that can be promoted.
Aiming at the status quo of CC’s PAB, and referring to the PDCA Cycle model, a CC team construction system is constructed to promote professionalization, specialization and expertization. Starting from selection, training, evaluation and motivation, and based on the timely feedback and continuous improvement of the four cycles of PDCA, a system as shown in Fig. 3 is established.
Fig. 3
The proposed cyclic framework for CC’s PAB.
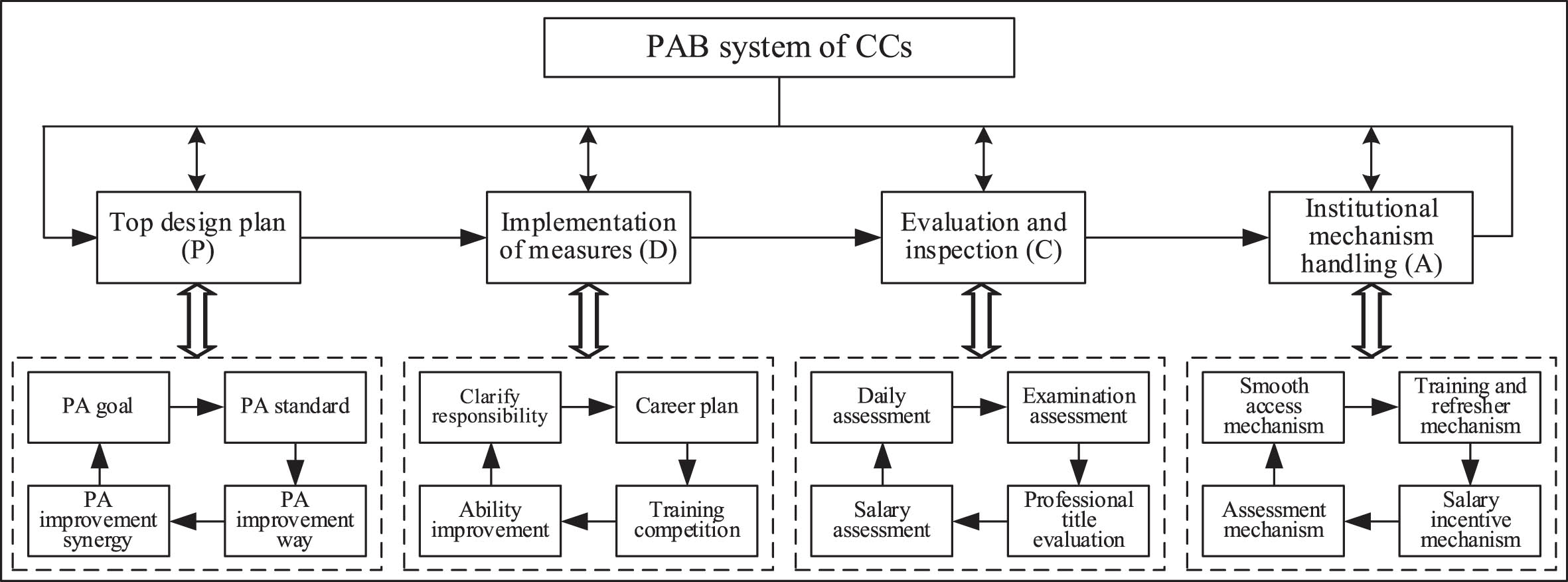
CC’s PAB is not only a process of multi-factor coupling, but also a form of multi-level coordination. After learning from PDCA Cycle, in the process of continuously proposing, analyzing, and solving problems, four power cycles are added around policy formulation, measure implementation, evaluation and inspection, and institutional mechanisms to continuously improve their PAB. This is based on the current situation of CC’s PAB.
4.3Path optimization of CC’s PAB under PDCA cycle perspectives
Under the perspective of the PDCA Cycle, by controlling the process to achieve continuous quality improvement, rationally setting channels and pathways, and building various cycle grid systems, an efficient and scientific path for improving the PA of CCs is finally obtained. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that based on PDCA Cycle, the PAB cycle system of CCs has constructed a top-down, bottom-up feedback-type promotion method from goal to implementation. Focusing on the requirements and standards for the improvement of CC’s PA, problems and gaps are found in the process of promoting the cycle, and feedback is given to each small cycle process. In this way, through the continuous optimization of sub-cycles (orderly advance in the cycle), the high-quality operation of the entire cycle system is realized.
In the path optimization of CCs’ PA improvement, the PDCA cycle constructs the radiation mode from the inside to the outside and the enveloping mode from the outside to the inside. From a subjective point of view, the improvement of CC’s PA is a self-requirement of career planning. From an objective point of view, CC’s PA is continuously upgraded in the practice orientation of college education to form an internal motivation under external influence, thereby promoting the further improvement of CC’s PA.
5Safeguard measures of CC’s PAB under PDCA cycle perspectives
Constructing a scientific security system is a key link in improving CC’s PA. To this end, a guarantee system for CC’s PAB should be constructed through top-level design, implementation of measures, evaluation, and monitoring, and institutional mechanisms.
5.1Planning stage P: Top-level design for improving CC’s PAB
The P stage is the planning stage, and it is also the stage of formulating rules and establishing goals. To strengthen the construction of CCs in the new era, it is necessary to formulate PA improvement goals by PA standards of CCs, and to strengthen the top-level design [49]. In terms of the institutional guarantee, the necessary support for the construction of the CC team needs to be given. In terms of ideology, it is necessary to lead CCs to actively undertake the important task of cultivating socialist builders. In life, CCs need to be cared for more. Meanwhile, it is recommended to establish a generous talent introduction mechanism, implement multi-level teacher training, formulate scientific implementation plans, and discover and solve problems. Finally, by encouraging and attracting high-quality talents to the CC team, a virtuous circle of CC teams can be realized.
First, it is necessary to establish a comprehensive admission evaluation and talent introduction system. The first thing to do is to scientifically formulate the admission standards of counselors and strictly control the entrance. From the survey data, the proportion of CCs from Marxist theory, ideological and political education is 36.9%, with a variety of professional backgrounds. However, they lack systematic and political education professional backgrounds, and there are shortcomings in theoretical basic knowledge. Therefore, in addition to the traditional qualification review, it is recommended to increase the weight of political theory assessment and test lectures in the written test interview session, and select a full-time counselor in accordance with the teacher’s entry threshold.
Second, it is important to unblock the communication system for CCs and full-time teachers. According to the discipline background of CCs, colleges and universities should be selected and cultivated ideological and political counseling. They need to be eligible for lectures by selecting and trial lectures, so as to undertake curriculum teaching tasks and truly realize the teacher status of CCs. At the same time, full-time teachers are encouraged to work as part-time CC to break the communication obstacles between CCs and full-time teachers. This not only creates a dual-teacher full-time teacher team under the two-way communication mechanism, but also meets the growth needs of CCs.
Third, it is advised to optimize the incentive mechanism of CCs and improve the salary system. The first is to optimize the compensation system of CCs. The adjustment of the compensation structure of CCs needs to reflect the differences in working age, workload, work difficulty, and work performance. The second is to improve the promotion system of CCs. Furthermore, CC needs to be given the preferential treatment of double-line promotion. In this case, we can not only evaluate the professional and technical positions of ideological and political education disciplines or other related disciplines by the title review standards of CCs, but also promote the corresponding positions according to CC’s working years and actual performances.
5.2Execution stage D: Measures to strengthen various CCs’ PAB
The execution stage is a stage of designing specific methods and implementing the plan. Based on the overall planning and design, various system measures should be implemented.
First, CCs should clarify their job responsibilities and occupational positioning. According to PA standards of ordinary CCs, CCs need to clarify their scope from ideological value guidance, party group work, student daily management, college student mental health education, vocational planning and employment guidance [50]. Meanwhile, work responsibilities, work authority, workflow, and occupational positioning must be clear, and the functions of service, education, management, and consulting must be fulfilled.
Second, CCs should scientifically plan their career and clarify the direction of career development. They also should formulate scientific career planning by personal career interests, personality characteristics, and ability quality, clarify PA goals, and formulate scientific and reasonable plans. Further, through active practice and timely assessment of feedback, the self-worth of CCs is finally realized.
Third, a multi-level CC training mechanism needs to be established. From the survey data, all CCs have training needs. Among them, 46% participate in 1-2 training per semester, 25% participate in 3-4 training per semester, and 17% participate in 5-6 training per semester. Through organizing CCs to participate in multi-level training, and combining it with various forms such as training, social practice, post-work exercises, and on-the-job degree, a team of ideological and political education with firm politics, professional skills and noble teachers’ ethics is expected to be cultivated.
5.3Check stage C: Strengthening the dynamic monitoring of CCs’ PA
The check stage is also called the summary stage, that is, the inspection and evaluation of the situation after the implementation of stage D, with the effect of inheritance. While promoting development and improvement with evaluation, the evaluation cycle is established (that is, combine daily assessment, examination assessment, professional title evaluation and salary assessment). The daily assessment is mainly aimed at the daily ideological and political work of CCs, focusing on work attitudes. The examination assessment mainly targets the diligence of virtue and focus on work performance. The professional title evaluation is mainly aimed at the work performance for a period of time and the level of scientific research management. Finally, the salary assessment covers basic salary, work performance, welfare benefits, etc. Therefore, a reasonable inspirational salary system is required.
Taking the salary system as an example, according to PA standards of CCs, the feasibility results of the system evaluation indicators are presented (Table 4), based on the results of expert interviews (experts 1 to 10 are abbreviated as E1 to E10). The average score is abbreviated as AS. The indicator scores of ideological and political education (IPE), party group class construction (PGCC), academic style construction (ASC), daily affairs management (DAM), evaluation situation (ES), and addition and subtraction point (ASP) are higher than 8. This is consistent with the actual situation and has high feasibility, so it can be used as a first-level assessment indicator. The rest of the indicators include mental health education (MHE), network thoughts and politics (NTP), crisis response (CR), career planning and entrepreneurial guidance (CPEG), theoretical practice research (TPR), and employment and work (EW). According to the modular work content of CCs, scientific and reasonable and targeted assessment indicators have been established. Work attitude, work ability, work performance, evaluation, and addition and subtraction are listed as first-level indicators. Ideological and political education, party building construction, daily management, and study style construction are set as second-level indicators for performance assessment, and the specific three-level indicators have also been set. In addition, CCs are encouraged to undertake part-time work such as teaching through addition and subtraction projects to cover all aspects of CC’s work, which truly reflects their work effectiveness.
Table 4
Expert opinions on the first-level indicator establishment of CC assessment system
| Indicator | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E5 | E6 | E7 | E8 | E9 | E10 | AS | Feasibility |
| IPE | 10 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 9.8 | High |
| PGCC | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9.2 | High |
| ASC | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 9.6 | High |
| DAM | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8.7 | High |
| MHE | 6 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7.1 | Medium |
| NTP | 6 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6.7 | Medium |
| CR | 6 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 6.7 | Medium |
| CPEG | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6.6 | Medium |
| TPR | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5.9 | Low |
| EW | 4 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5.7 | Low |
| ES | 8 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | High |
| ASP | 8 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8.1 | High |
In the check stage, the whole monitoring system of CCs’ PAB is integrated to give full play to the guidance, promotion and incentive role of evaluation. Finally, monitoring and evaluation are carried out to achieve comprehensive monitoring by integrating all links and elements of CCs’ PAB.
5.4Improvement stage A: Continuous improvement of CCs’ PAB system and mechanism
The processing stage is the feedback to the results of the check stage. In this process, a solution is found so that it is ready for the next cycle. CCs’ PAB is a long-term process. PAB system of CCs needs to be improved, and the access, training, salary incentives and assessment and evaluation mechanisms of CCs need to be continuously perfected. Through multi-party coordination, the enthusiasm of CCs’ PAB is fully mobilized.
Colleges and universities should make overall plans and cooperate with multiple parties to ensure PAB system of CCs. First, we need to set up a scientific and reasonable access mechanism and flow mechanism for CCs. After the communication barrier is broken between CCs and full-time teachers, a two-way communication mechanism is combined to meet the growth needs of CCs. Second, we should establish a multi-level training competition mechanism, and arrange CCs to take turns in stages and in batches for training on various topics at various levels. Third, a reasonable incentive mechanism needs to be established. For those who have improved rapidly on specialization and professionalization paths, they should be given financial policy support and policy preference. Fourth, it is advised to build a scientific evaluation mechanism and a competitive salary system. At the same time, it is necessary to improve the incentive mechanism of CCs and create a good institutional environment to reflect the value of CCs’ work.
The system is an effective guarantee to solve difficult problems. In CCs’ PAB, the core needs of counselors-growth needs are aimed at. It is recommended that CC training should be included in teacher training programs. The career development channel of CCs is unblocked, and career development goals are designed in terms of psychological counseling, career guidance, and entrepreneurship education, making CCs become expert counselors. CCs are supported to participate in academic training and on-the-job training to improve their theoretical literacy and practical ability. After the management position selection policy is perfected, the selected excellent CCs would participate in various exchange studies and training for further study. This provides conditional guarantee for CCs to improve their professional level, scientific research ability and personal development.
6Discussion
A clear goal is a necessary prerequisite for a PDCA Cycle to be effective. Each cycle must point to a clear goal, that is, the problem to be solved. Therefore, in the PA of CCs, the work content such as access smooth mechanism, training and further training mechanism, remuneration and incentive mechanism, and assessment and evaluation mechanism can be broken down into several small problems. This makes it possible to solve some small problems in each cycle, which in turn leads to the solution of big problems. Those left behind and new problems will be put in the next cycle to continue to be solved. After week after week of solving and improving, the set goal is finally achieved [1, 4, 5, 14].
The final processing link in PDCA (i.e. action, named A) is the key step to complete the closed loop, and it is also the link that is easily ignored in the actual improvement work. The neglect of this link leads to the failure of the closed-loop mechanism. Therefore, in the PAB system of CCs, it is necessary to maintain the original pace of work, summarize the experience promptly, and form a standard or system. At the same time, it is necessary to dig deeper into the remaining problems and detect new problems in time, and make them the key issues to be dealt with in the next cycle. Such a cycle of improvement achieves progressive work quality promotion [5, 12, 21].
This study is dedicated to opening up a new perspective for the theoretical research on the construction of teaching staff in colleges and universities from CC’s PAB level. The expansion of the application field of PDCA Cycle theory has important benefits for the construction of the PAB security system [2, 6, 12, 20–24]. As far as CC’s PAB path is concerned, subjective factors are the key, objective factors of students are the driving force, and institutional factors of the country and schools are the guarantees. Combined with the empirical analysis of the questionnaire, PDCA Cycle theory is applied to PAB, and a normalized assessment and evaluation mechanism is established through top-level design, layout planning, optimization of the CC career development system and improvement of the CC salary system, which has a good promotion significance [32, 43–50]. Due to the limited theoretical foundation and imperfect knowledge structure, some viewpoints put forward in this paper still need to be considered. In the future, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research in combination with the actual work of CCs.
CC building is a systematic project. The government, colleges and universities, society, students and their parents, and CCs have all given great inspiration to this research. A lot of rich and valuable support has been provided in many aspects such as CC’s PAB system and paths. In the future, we will focus on deepening the research on PA promotion and the professional development of CC.
7Conclusion
Under the guidance of the current policy, some colleges and universities have issued and implemented the two-way promotion method of CC positions and ranks, which has pointed out the career development direction of CC, and provided a platform and space for their growth, development and social value recognition. Some regions have issued a notice on strengthening the allocation of full-time counselors in colleges. This notice once again reiterates the selection of full-time counselors in colleges, and requires the completion of 1 : 200 allocation by the end of 2020. It is planned that from 2020 to 2022, full-time counselors will be included in the establishment of colleges in batches on an annual basis, and the requirements for the transfer and entry of full-time counselors on the job have also been clarified. Under the guidance of the policy, various colleges have also introduced CC management methods, professional title evaluation methods for college students’ ideological and political education series, CC assessment methods, etc., and established a sound CC career development system under the new situation. The policies provide guarantees for the continuous improvement of these systems and assessment methods.
As a general model in management, PDCA Cycle is to continuously discover problems and formulate improvement measures in practice. It is not only adopted in the quality management system, but also adopted by some colleges that value CC’s PAB. According to the thinking from decision-making to implementation to monitoring and then to improvement, PAB has experienced scientific and reasonable planning, practical and firm execution, real-time monitoring and feedback, dynamic adjustment and optimization and continuous improvement, and finally realized the overall improvement of CC’s professional quality. In this way, CC’s team building has been strengthened to improve the level of ideological and political work in colleges.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Youth Development Fund of Southeast University Chengxian College named Innovation Research on Independent College Counselor Assessment and Incentive Mechanism (Grant No. Y0008).
References
[1] | Guiffrida D , Douglas , Douthit , et al. The African American Student Experience at Predominantly White Colleges: Implications for School and College Counselors. arXiv, 2022. |
[2] | Yang Z , Talha M A coordinated and optimized mechanism of artificial intelligence for student management by college counselors based on big data. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine (2021) ;2021: (6):1–11. DOI: 10.1155/2021/1725490. |
[3] | Newhart S , Travis S , Mullen P R Factors Predicting Attitudes Toward Evidence-Based Practice Among College Counselors. Journal of College Counseling (2021) ;24: (3):194–209. DOI: 10.1002/jocc.12191. |
[4] | Davis E S , Paro C College Counselors’ Perceptions of Working with First-Year Students with Chronic Illnesses. Journal of College Counseling (2020) ;23: (1):15–29. DOI: 10.1002/jocc.12146. |
[5] | Zhao D Research on the Political Leadership of College Counselors under the Background of Collaborative Education. Education Forum (2023) ;1: :33–36. |
[6] | Zhang P Research on the path of improving college counselors’ professional ability under the background of innovation and entrepreneurship. Journal of Contemporary Educational Research. (2020) ;4: (8). DOI: 10.26689/jcer.v4i8.1439 |
[7] | Zhang H On the Training Path of College Counselors’ Professional Ability. The Guide of Science & Education. (2017) . |
[8] | Cui X , Wang H , Chen Y Strengthening the Professional Ability Building of College Counselors in the New Era based on Political Standards. Journal of Beijing City University (2022) ;1: :92–95. |
[9] | Hussain T , Abbas J Impact of Urban Village Disamenity on Neighboring Residential Properties: Empirical Evidence from Nanjing through Hedonic Pricing Model Appraisal. Journal of Urban Planning and Development. (2021) ;147: (1). DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)UP.1943-5444.0000645. |
[10] | Jaffar A , Raza S , Nurunnabi M , Minai M , Bano S The Impact of Entrepreneurial Business Networks on Firms’ Performance Through a Mediating Role of Dynamic Capabilities. Sustainability. (2019) ;11: (11) 3006 DOI: 10.3390/su11113006. |
[11] | AlQudah N F Knowledge sharing and innovation in business organization: A literature review[J]. Human Systems Management (Preprint): (2022) , 1–15). DOI: 10.3233/HSM-220081. |
[12] | Jawad A , Wang L , Ben Belgacem S , Pawar P , Najam H , Abbas J Investment in renewable energy and electricity output: Role of green finance, environmental tax, and geopolitical risk: Empirical evidence from China. Energy. (2023) ;269: 05115. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.126683. |
[13] | Li X , Abbas J , Dongling W , Baig N , Zhang R From Cultural Tourism to Social Entrepreneurship: Role of Social Value Creation for Environmental Sustainability. Front Psychol. (2022) ;13. DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.925768. |
[14] | Macini N , Sengupta A , Caldana A C F , et al. A systematic literature review of the relationship between sustainable human resources management and spiritual leadership[J]. Human Systems Management (Preprint). (2022) ;1–20. DOI: 10.3233/HSM-220099. |
[15] | Li Y Discussing the Professional Category of College Counselors’ Student Party Building Ability in the New Era—Based on the Analysis and Suggestions of College Counselors’ Professional Ability Standards (Provisional). College Fudaoyuan (2021) ;4: :13–17. |
[16] | Li Q , Nie N , Wang J Research on Developmental Countermeasures of Middle-level Counselors Defined in College Counselors’ Professional Ability Standards (Provisional). Research on College Students’ Affairs (2020) ;2: :23–28. |
[17] | Liu H , Fu D Problems and Countermeasures in College Counselors’ Professional Ability Standards (Provisional). Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition). (2019) ;39: (6):53–58. |
[18] | Jiang L , Sun X , Ji C , et al. PDCA cycle theory based avoidance of nursing staff intravenous drug bacterial infection using degree quantitative evaluation model. Results in Physics (2021) ;26: :104377. DOI: 10.1016/j.rin2021.104377. |
[19] | Lei J Research on the mode of innovative talent cultivation in the multi-synergy integrated circuit industry based on the PDCA cycle theory[C] Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing. (2021) ;1744: (3):032107. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/1744/3/032107. |
[20] | Dong Z , An T , Bai J , et al. Construction of PDCA Cycle Education Model for Jewelry E-commerce Talent Training under the New Liberal Arts Concept. Journal of Handan University (2022) ;32: (4):62–67. |
[21] | Song B , Shao Y , Wang X , et al. Application of PDCA Cycle in the Special Review of Personnel Files of Hospital Cadres. Modern Hospitals (2022) ;22: (11):1724–1726. |
[22] | Zheng Y , Zhao Z , Guan L , et al. Application of PDCA to Improve Occupational Disease Diagnosis. Occupational Health and Emergency Rescue (2022) ;40: (6):711–714. |
[23] | Tang R , Peng J , Kong W Application of PDCA in Improving Goods Management in Outpatient Area. Advanced Journal of Nursing (2022) ;2: (4):80–82. |
[24] | Li W , Ding M Clinical Significance of PDCA Cycle Method in the Application of Equipment Management in ENT Operating Room. China Medical Device Information (2022) ;28: (9):172–174. |
[25] | Li Y , Al-Sulaiti K , Dongling W , et al. Tax Avoidance Culture and Employees’ Behavior Affect Sustainable Business Performance: The Moderating Role of Corporate Social Responsibility. Frontiers in Environmental Science. (2022) ;10. DOI: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.964410. |
[26] | Ma C , Chang L , Cui N , et al. Statistical relationships between numerous retired lithium-ion cells and packs with random sampling for echelon utilization. Energy (2022) ;257. |
[27] | Liu Q , Qu X , Wang D , et al. Product Market Competition and Firm Performance: Business Survival Through Innovation and Entrepreneurial Orientation Amid COVID-19 Financial Crisis. Front Psychol. (2021) ;12: :790923. DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.790923. |
[28] | Hussain T , Wei Z , Nurunnabi M The Effect of Sustainable Urban Planning and Slum Disamenity on The Value of Neighboring Residential Property: Application of The Hedonic Pricing Model in Rent Price Appraisal. Sustainability (2019) ;11: (4):1144. |
[29] | Aman J , Abbas J , Shi G , et al. Community Wellbeing Under China-Pakistan Economic Corridor: Role of Social, Economic, Cultural, and Educational Factors in Improving Residents’ Quality of Life. Frontiers in Psychology (2022) ;12: :816592. |
[30] | Fu Q , Abbas J , Sultan S Reset the industry redux through corporate social responsibility: The COVID-19 tourism impact on hospitality firms through business model innovation. Front. Psychol. (2021) ;12: :6686. |
[31] | Peter S , Krispin H , Glueck R , et al. Needs and Experiences in Psychiatric Treatment (NEPT)-Piloting a Collaboratively Generated, Initial Research Tool to Evaluate Cross-Sectoral Mental Health Services. Frontiers in Psychiatry. (2022) . |
[32] | Ge T , Abbas J , Ullah R , et al. Women’s Entrepreneurial Contribution to Family Income: Innovative Technologies Promote Females’ Entrepreneurship Amid COVID-19 Crisis. Front Psychol (2022) ;13: :828040. |
[33] | Schmidt C , Cromwell E , Hill E , et al. The prevalence of onchocerciasis in Africa and Yemen, 2000-2018: a geospatial analysis. BMC Med. (2022) ;20: (1):293. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-022-02486-y. |
[34] | Jiakui C , Abbas J , Najam H , et al. Green technological innovation, green finance, and financial development and their role in green total factor productivity: Empirical insights from China. Journal of Cleaner Production. (2023) ;382: (1):135131. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135131. |
[35] | Hussain T , Abbas J , Li B , et al. Natural Resource Management for the World’s Highest Park: Community Attitudes on Sustainability for Central Karakoram National Park, Pakistan[J]. Sustainability. 972: (2017) ;9: (6). DOI: 10.3390/su9060972. |
[36] | Zafar M , Shi X , Yang H , et al. The Impact of Interpretive Packaged Food Labels on Consumer Purchase Intention: The Comparative Analysis of Efficacy and Inefficiency of Food Labels. Int J Environ Res Public Health (2022) ;19: (22):15098. |
[37] | Yu S , Draghici A , Negulescu O , et al. Social Media Application as a New Paradigm for Business Communication: The Role of COVID-19 Knowledge, Social Distancing, and Preventive Attitudes. Frontiers in Psychology (2022) ;13. DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.903082. |
[38] | Zturk E , Ko Z Turkish validation of the family presence during resuscitation risk-benefit scale. Nursing in Critical Care (2022) ;27: (3):440–449. |
[39] | Su Z , Cheshmehzangi A , Bentley B , et al. Technology-based interventions for health challenges older women face amid COVID-19: a systematic review protocol. Systematic Reviews (2022) ;11: (1):271. DOI: 10.1186/s13643-022-02150-9. |
[40] | Micah A , Bhangdia K , Cogswell I , et al. Global investments in pandemic preparedness and COVID-19: development assistance and domestic spending on health between and The Lancet Global Health (2026) ;19: . DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00007-4. |
[41] | Hafeez A , Dangel W , Ostroff S , et al. The state of health in Pakistan and its provinces and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet Global Health. (2023) ;11: (2). DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)00497-1. |
[42] | Iorember P , Iormom B , Jato T , et al. Understanding the bearable link between ecology and health outcomes: the criticality of human capital development and energy use. Heliyon. (2022) ;8: (12). DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12611. |
[43] | Liu Z , Yang Z Analysis on the Practical Path of High-quality Development of College Counselors in the New Era. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing (Social Sciences Edition) (2023) ;39: (1):44–49. |
[44] | Wang N Analysis on the Path of Integrity Culture Construction of College Counselors in the New Era. Journal of College Advisor. (2022) ;14: (6):24–28. |
[45] | Zhu Z , Wang Y Analysis on the Path of College Counselor Team Construction in the New Era. The Party Building and Ideological Education in Schools. (2022) ;20: :79–81. |
[46] | Balsalobre-Lorente D , He C , Pilar L , et al. Tourism, urbanization and natural resources rents matter for environmental sustainability: The leading role of AI and ICT on sustainable development goals in the digital era. Resources Policy. (2023) ;82: :103445. DOI: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103445. |
[47] | Shah S , Zhang Q , Balsalobre-Lorente D , et al. Technology, Urbanization and Natural Gas Supply Matter for Carbon Neutrality: A New Evidence of Environmental Sustainability under the Prism of COP26. Resources Policy. (2023) ;82: :103465. DOI: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.103465. |
[48] | Zhuang D , Abbas J , Al-Sulaiti K , et al. Land-use and food security in energy transition: Role of food supply. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems. (2022) ;6. DOI: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.1053031. |
[49] | Zhang L , Liu X , Zhao M A Brief Discussion on the Ability Construction of College Counselors in Internet Plus Era. Education Modernization (2020) ;7: (54):80–82. |
[50] | Li H Discussion on the Professional Ability Standards of College Counselors from the Perspective of Psychology. China Standardization (2022) ;20: :205–207. |




