21st anniversary of job embeddedness: A retrospection and future research agenda
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Since the previous decade, researchers and academics have paid close attention to studying job embeddedness (JE), but the bibliometric examination of JE has not yet been explored.
OBJECTIVE:
This study aims to provide general information on the trends of the studies on JE as well as an overall perspective on the development of this topic by utilising a bibliometric analytic approach.
METHOD:
A bibliometric evaluation was conducted in the JE field since the first publication was documented in the Scopus database. The information retrieved examines 1572 JE papers from a variety of perspectives, including citation and publishing metrics.
RESULTS:
The research results pinpoint the most productive countries, universities, journals, authors, and JE articles. The study also classified the most important themes and offered some recommendations for further research.
CONCLUSION:
The study provided a snapshot of JE patterns and trajectories from 1993 to 2020, which can help academics and practitioners figure out the pattern and direction of future research. To the best of our knowledge, no other study examines the bibliographic data on JE and thus this work is one of the first contributions to the literature.
1Introduction
Since the publication of the seminal work by Mitchell et al. [1] in 2001, research on job embeddedness (JE) has grown significantly. Scholars from different fields, such as business management, sociology, and psychology, have become interested in JE due to its interdisciplinary nature. By bringing together theories from these fields, the studies have been endowed with theoretical strength and rigor. There has been an explosion of studies since 2013. This immense increase in research challenges the researchers to understand the past trends and future trajectories. It is expectedly fundamental to categorize and show the patterns of publication in the given area; this will make the JE area trajectory accessible. Thus, to manage the issue of ever-increasing research on JE, this research conducted bibliometric analysis (BA) to answer the following questions:
• What are the latest trends in JE research?
• What countries/regions produce the most papers and citations, and where are the global hotspots?
• Who are the most influential authors?
• What are the conceptual connections between the various authors, countries/regions, and journals?
• What are the most important themes/trends in JE investigation, and when do these patterns develop?
• What are future research avenues?
BA is a quantitative review of the available literatures for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the subject [2]. BA has gained recent popularity in business and management studies [3]. Prior study has explored a vast array of topics, such as publication trends on a certain topic [4–6], the most cited papers [7], journals [8–10] and universities [11]. Farrukh et al. [12], for example, conducted a bibliometric study of pro-environmental behavior to investigate a wide range of issues, including the most cited studies, the most popular topics, leading journals, the most relevant contributors, institutes, and universities.
A recent study by Farrukh et al. [13] used bibliometric research to look at how innovative behavior has evolved over time. Specifically, the analysis focused on the most cited documents, and the most important journals and themes. However, within our ken, there is no bibliometric assessment of JE literatures among contemporary ones. To fill in this vacuum in the academia and contribute to the field of JE, this study utilized the same methodology as Gao et al. [14]. The findings of this research add to the body of knowledge in various ways.
First, our study shows the production and effect trends based on citation counts and the number of publications. Second, it gives an overview of the countries/nations, institutes/universities, publications, contributors/authors, and most cited manuscripts/articles. Third, it presents an overview of the worldwide knowledgeable networks, which may aid individuals to figure out how they are linked. Fourth, and most crucially, the study suggests some future endeavors based on the approach of subject and topic trends, which may aid researchers in selecting future research concepts, the top-cited works to consult, and the journal to submit to for publication. Finally, the research can assist journal editorial groups in deciding which areas of research will be the next ones to develop. This research can also facilitate students in deciding upon the destination and universities for their studies. It can even help policymakers figure out which countries/regions have the optimal JE, and which is the best place for research and development.
1.1Literature review
1.1.1JE
Employment turnover intention costs are difficult to estimate. Researchers have purported that extensive costs are incurred with disruptions when productive employees leave, although scholars have spent a lot of time trying to figure out why they leave [15]. Unfortunately, in this vein, no one has found any single platinum program, golden handcuffs, or magic stone that will help keep the productive employees at their job. A research implication accumulated over decades is that as the employees’ retention rates decrease, the associated costs negatively affect the bottom line of the organization [16]. This implication of research has led to two sides of employee turnover: the reasons why some employees leave the organization (i.e., turnover intention) and the reasons why someone stay in the organization (i.e., retention).
In 2001, Mitchell and colleagues introduced the JE theory which described a combination of attached features that provide a substitute clarification of employee retention. The theoretical foundation of the JE theory is derived from Lewin’s field theory and embedded figures. Lewin’s [17] field theory states that individuals see themselves enmeshed in a web of connections and forces. They may be tightly or loosely attached to the different forces or connections. Witkin’s [18] embedded figures show psychological images embedded in the backgrounds of individuals because these images are attached to, and hardly detachable from, the organization’s background. Similarly, the field theory proposes that individuals have a life perception in which all parts of their life are embodied and interconnected. These relationships may be few or numerous, close, or distant. Using these concepts, Mitchell and his colleagues described JE as a web or net in which someone individual might become stuck.
Redirecting the conceptualized lens from employees’ turnover intention to employees’ retention, Mitchell et al. [1] introduced JE which consists of two dimensions on-and-off the JE akin to conceptually Lewin [17] and Witkin [18]. JE is defined as an all-inclusive collection of ideas that affect one’s choice to stay in the job, functioning like a web or a net which attaches one to the organization and community [1]. JE is further divided into on-and-off the JE in terms of links, fit, and sacrifices related to job and community, respectively. Each of these types of embeddedness has its own set of characteristics: i) the links that an individual has to his/her colleagues and community; ii) the degree to which one is fit within the organization and community, and iii) the sacrifice or the perceived social, material, and psychological paybacks that may be related to one’s leaving job and community [16]. Accordingly, JE forms from both dimensions within the organization and thecommunity.
Over the past decade, scholars have provided little preliminary evidence that JE can describe exceptional disparity in employees’ turnover intention beyond job attitudes and job alternatives [19]. Despite these encouraging findings, scholarly interpretation of the association between JE and turnover-related criteria remains challenging. In this vein, a few insightful reviews in the JE domain have been conducted. Examples include a story of why to stay [20], JE as a multifocal theoretical extension [21], the global measurement of JE construct [22], and a ten-year literature review [23]. Although there are several studies in this field based on the conceptual frameworks and reviews, there is no evidence of a bibliometric review emphasizing JE. Consequently, the objective of this research is to bridge the gap in the literatures by undertaking a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of JE.
2Methods
The JE bibliographic data were obtained from the Scopus database using the search term “JE” Title, abstract, keywords. The Scopus database was selected due to its extensive coverage. It is considered one of the leading repositories for social sciences research. This database also contains all useful bibliographic information for conducting the bibliometric analysis.
2.1Data preparation and tools
The researchers read the title keywords and abstracts of all published papers to ensure that the extracted bibliographic data were credible and applicable to the research topic. The parameters used in the search process are crucial since they can affect the outcome. It is worth noting that only scientific literatures published in the English language were considered for the study. Following the data cleaning, the next step was to choose an indicator for the bibliometric analysis. The literatures used two key types of metrics, science mapping and performance analysis, for the bibliometric study [24]. Science mapping depicted the structure and dynamics of the area, whereas performance analysis assessed production and effect in terms of publications and citations.
The bibliographic data in this report were analyzed using VOSviewer and RStudio. These software tools were selected for their user-friendly interface and the ability to analyze a variety of bibliometric indicators listed above. With a range of analytic capabilities, these software tools may display the intellectual structure and enhance the interpretability of bibliographic data. In an area of study, these graphs may be used to categorize hotspots, developing trends, and knowledgeable networks. In this regard, numerous types of review studies are available, including literature reviews [23], meta-analysis-based reviews [25], and framework-based reviews [26]. Unfortunately, it is evident that there is no systematic literature review on JE literatures that are based on bibliometric analysis. To fill this gap in JE, this study employed bibliometric methodologies to demonstrate the evolution of JE literatures over time, as well as its citation patterns.
3Results
3.1Year wise publication
The findings of the JE research publication trend are shown in Figure 1, which depicts a significant increasing trend in the number of published papers on JE. In 2011, there was a marked increase. Fuelling factors for this rising trend might include the launch of new journals, the relevance of the topic in business research, and Ph.D. degrees in HRM. The rapid increase in publishing indicates that JE is gaining traction in the management field.
Fig. 1
Publications trends.
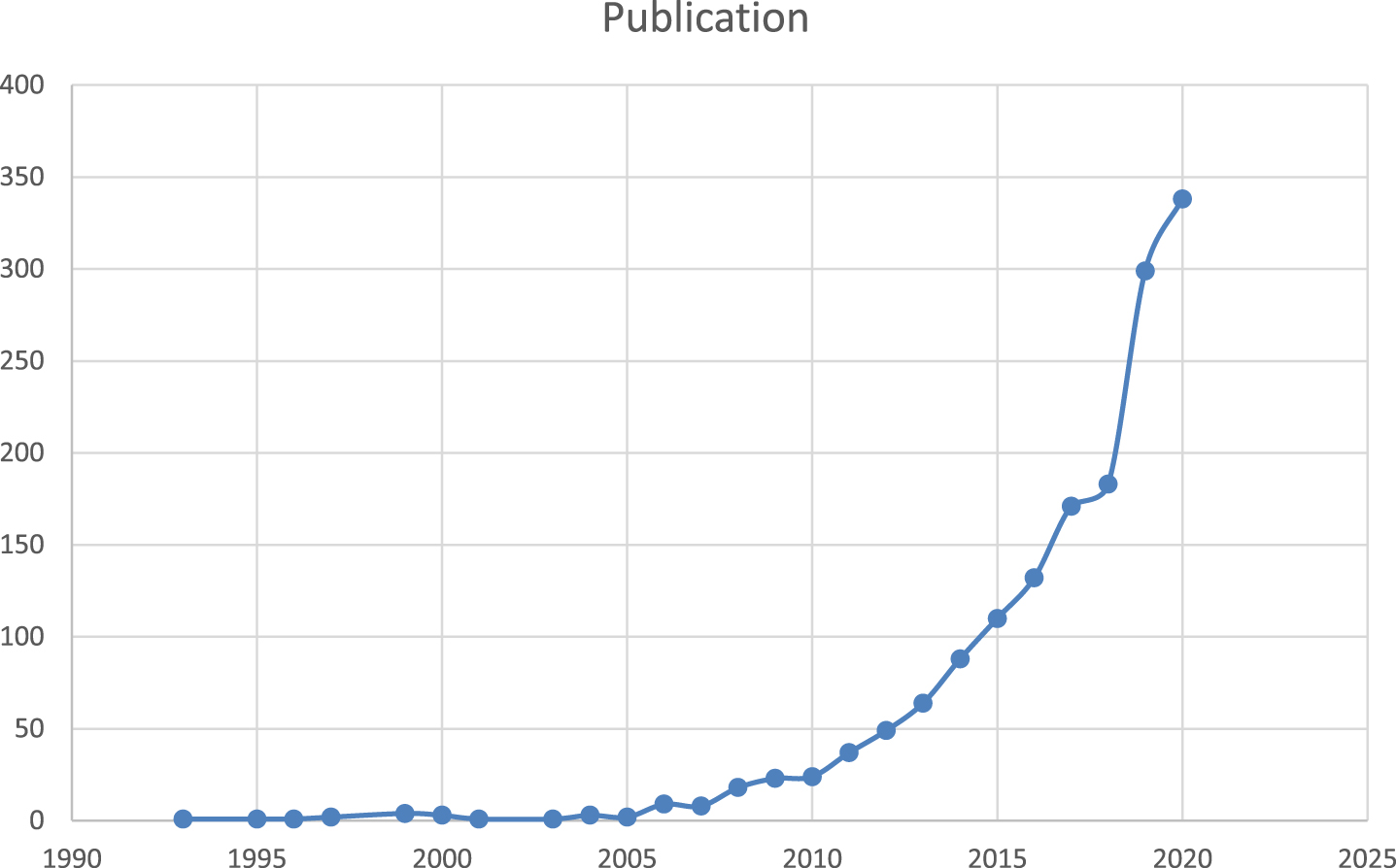
The earliest publication on this subject dates back to 1993, according to Scopus; however, Scopus failed to archive any JE studies for one year, for example, in 1994. After then, beginning in 2010, the number of publications steadily increased year after year. A total of 1572 publications were found in the search results. The results in Fig. 1 are supplemented by Table 1. The most prolific year is 2020, with 338 publications. However, because the data were obtained in early November 2020, it was impossible for us to record the exact total number of publications for the year. As a result, we had the confidence that the publications in 2020 would significantly outnumber those in 2019. The latest increase in publications demonstrates that these themes are becoming increasingly popular among academics for present and future studies. Since JE is gaining traction among scholars and policymakers, more JE investigations are expected in the upcoming years.
Table 1
Publications trends
| Publication | Number of |
| Years | Publications |
| 2020 | 338 |
| 2019 | 299 |
| 2018 | 183 |
| 2017 | 171 |
| 2016 | 132 |
| 2015 | 110 |
| 2014 | 88 |
| 2013 | 64 |
| 2012 | 49 |
| 2011 | 37 |
| 2010 | 24 |
| 2009 | 23 |
| 2008 | 18 |
| 2007 | 8 |
| 2006 | 9 |
| 2005 | 2 |
| 2004 | 3 |
| 2003 | 1 |
| 2002 | 0 |
| 2001 | 1 |
| 2000 | 3 |
| 1999 | 4 |
| 1998 | 0 |
| 1997 | 2 |
| 1996 | 1 |
| 1995 | 1 |
| 1994 | 0 |
| 1993 | 1 |
| Total | 1572 |
3.2Methods and theories
Scholarly JE investigations have adopted qualitative, quantitative, and/or hybrid methodologies. Their focus is placed on quantitative research methods, and most of them rely on surveys. In survey-based investigations, the most common instrument is questionnaire. Most of the preliminary inquiries on JE used a cross-sectional technique to gather information about JE [20]. In contrast, just a few studies employed longitudinal approaches. Several researchers employed a mixed method that incorporated qualitative and quantitative approaches [27], using questionnaires, case studies, and interviews to collect data. However, few academics employed meta-analysis.
In theoretical terms, past research has shown that researchers have used a variety of theories to explain how JE affects job outcomes. Most JE scholars employed motivational theories [28]. In a similar vein, Rubenstein et al. [29] established that embedded individuals are motivated to move forward with a good and positive contribution to the organizational interest. The conservation of resources theory is the most popular of these motivational theories. Others resort to the equity theory and the motivational fit perspective. The conservation of resources theory describes one’s attempt to acquire, guard, and retain such resources as personal attributes, belongings, energy, or situations that are valued [30]. It is understandable that employees need to motivate themselves to stay in their job (i.e., JE) for additional resources. The conservation of resources theory helps them invest their abundance of resources to meet their demands at workplace (i.e., stay embedded in a job). On the other hand, some scholars and academics also employed sociological, leadership-based, and management theories to explain the phenomenonof JE.
In addition, some sociological theories, such as the theories of social exchange, social support resource, social role, social capital, social identity, and social bond, are used in the academia to explain the phenomenon of JE. Among these theories, JE scholars predominantly utilized the social exchange theory. For example, Chan et al. [31] utilized social exchange theory to explain the causes and effects of JE in the workplace. According to the social exchange theory, Blau [32] claimed that individuals who perceived values of the organization were inclined to reciprocate with more positive outcomes at the workplace, (e.g., staying more embedded in their jobs). From the social exchange perspective, Chan and his colleagues established that embedded individuals who work well with their colleagues and are valued by their employers have a great aspiration to produce positive outcomes at the workplace. These positive outcomes also constitute open-ended and long-term transactions characterized by socioemotional investment and mutual commitment.
Still, management theories such as goal orientation, power dependence, reactance theory, and uncertainty management theory are employed in the academia to describe the JE incident. Among them, the uncertainty management theory contended that individuals wish for predictability in their environment and use open interpersonal relations and available information (socializing strategies) to make corollaries about uncertain circumstances. For example, Peltokorpi et al. [33] used the uncertainty management theory to explain the effects of JE among workplace newbies. Furthermore, JE suggested that in groups, employees often pick up on one other’s emotions, which might affect decisions like quitting. JE plays a bridging role between these predictable factors and one’s retention.
Finally, among the leadership-based theories, leader-member exchange and transformational leadership were employed to predict JE. For example, Dechawatanapaisal [34] extended the theoretical underpinning of JE from leader-member exchange perspectives, on which the organizational bond between leader-member exchange and JE was created. The basic assumption of the leader-member exchange theory is that employees’ attitude and behavior at the workplace are dependent on the treatment of the connection between employees and the manager/supervisor. It was further reported that one’s benefits received as the outcome of the trade of resources inherent to the high level of leader-member associations lead to high JE while a lack of leader-member associations leads to low or little JE.
3.3Output by countries/regions
Scientific progress is deemed as a foundation for cultural and economic growths in a country [35]. The need for objective assessment of a country’s scientific efficiency is so essential. Currently, over 100 countries and regions have made important contributions to JE research. The most influential and productive countries/region in the area of JE research were examined in terms of assist students in identifying the regions and universities where they could conduct their JE research, as well as to assist politicians in classifying JE research leaders to figure out which ecosystem would favor their research and development. For productivity, the cumulative and average citations per publication for each country/region, as well as the average citations and total citations per publication, were provided for understanding the influence. Table 2 displays the findings of the top 18 countries/regions that have published studies on JE. The countries/regions are ranked by the number of publications.
Table 2
Ranking list of the highly productive regions/countries in JE
| Rank | Region/Country | Publications | Citations | C/P |
| 1 | United States | 119 | 5835 | 49.03 |
| 2 | China | 49 | 647 | 13.20 |
| 3 | Australia | 31 | 548 | 17.67 |
| 4 | Turkey | 24 | 749 | 31.20 |
| 5 | South Korea | 19 | 50 | 2.63 |
| 6 | Taiwan | 17 | 59 | 3.47 |
| 7 | South Africa | 14 | 105 | 7.50 |
| 8 | Pakistan | 12 | 103 | 8.58 |
| 9 | Indonesia | 11 | 13 | 1.18 |
| 10 | Malaysia | 11 | 20 | 1.81 |
| 11 | United Kingdom | 11 | 235 | 21.36 |
| 12 | India | 10 | 101 | 10.10 |
| 13 | Hong Kong | 7 | 528 | 75.42 |
| 14 | Iran | 7 | 23 | 3.28 |
| 15 | Thailand | 7 | 115 | 16.42 |
| 16 | Germany | 6 | 49 | 8.16 |
| 17 | Japan | 6 | 210 | 35.00 |
| 18 | Cyprus | 5 | 28 | 5.60 |
3.4Authors’ bibliographic coupling (BC)
BC is a metric for measuring the comparability of research sources [36]. It may be used to compare diverse investigative factors, including publications, institutes, and countries/regions. BC is regarded as a critical source for evaluating the relationship between research subjects [37, 38].
BC may also be employed to decide how closely the author’s various areas of research are related. According to Scopus, over 2000 authors contributed to JE studies, with over 150 of them contributing more than three publications. It will be fascinating to analyze the similarities between authors in terms of literature and study. In this study, we utilized authors’ BC to analyze how various authors and their research topics were related. Figure 2 displays the results of a study that focused on each author producing at least 5 documents; only 32 out of 1515 authors satisfy this requirement.
Fig. 2
Authors’ bibliographic coupling.
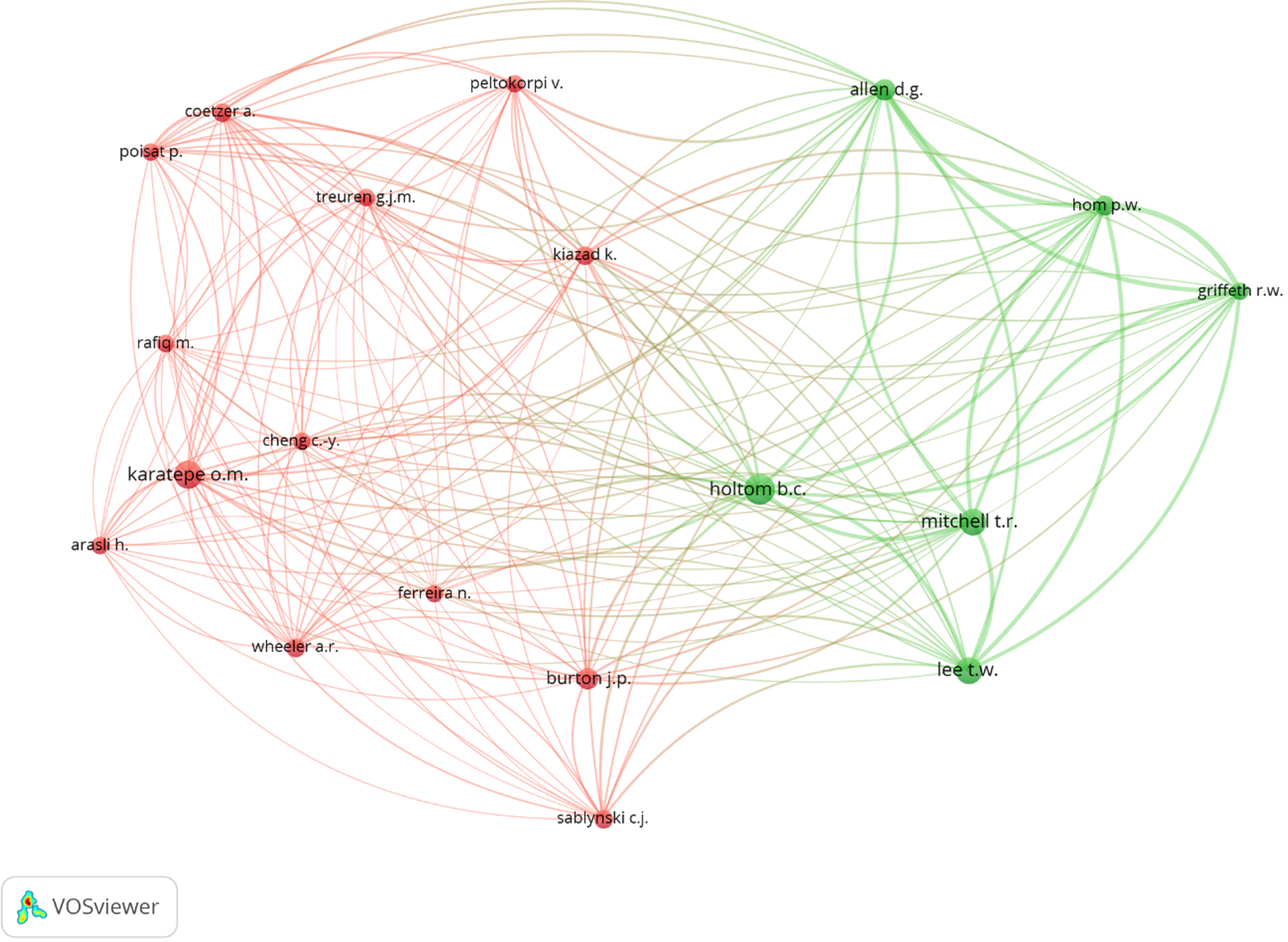
Authors who work in a same or similar field share the same color in the cluster. For example, Arasli, H., Burton, J. P., Cheng C. Y., Coetzer A., Ferreira N., Karatepe O. M., Kiazad K., Peltokorpi V., Poisat P., Rafiq M., Sablynski C. J., Treuren G. M., and Wheeler A. R. are clustered in red, indicating that they frequently do research in a similar field. Likewise, the authors in the green cluster are involved in the same type of studies.
3.5Collaboration among countries and regions
Enjoying a long academic tradition, international research cooperation is a valuable resource for sharing and developing a wider view of research, as well as for exploring conceptually sound research questions. The worldwide research partnership has created a well-organized, systematic approach to complex problems. Nowadays, it has become simpler for scholars to search across the worldwide network of authors with the introduction of computerization.
Co-authorship analysis is one of the most essential methods for evaluating collaboration amongst diverse study participants [39]. Author collaboration is a critical process in research because it gathers individuals with diverse skills to generate research methodologies. In general, research participation gathers disparate groups to generate new information. Co-authorship links may be utilized at the global level, such as institutes and regions, to quantify the collaborative pattern of individuals. This section utilizes the RStudio program to conduct a co-authorship study on how JE researchers from different regions collaborate. Table 3 and Fig. 3 demonstrate the co-authorship system for JE research in terms of the regions involved. Remember that co-authorship allows one to see the total number of publications produced in a country as well as the most important international connections of that region.
Table 3
Interregional and international collaboration
| From | To | Frequency |
| USA | Australia | 6 |
| Australia | South Africa | 5 |
| China | Hong Kong | 4 |
| China | Pakistan | 4 |
| China | USA | 4 |
| United Kingdom | USA | 3 |
| USA | Hong Kong | 3 |
| USA | Japan | 3 |
| Canada | Australia | 2 |
| Germany | Switzerland | 2 |
| Pakistan | Thailand | 2 |
| United Kingdom | Australia | 2 |
| United Kingdom | Canada | 2 |
| USA | Turkey | 2 |
Fig. 3
Interregional Co-authorship.
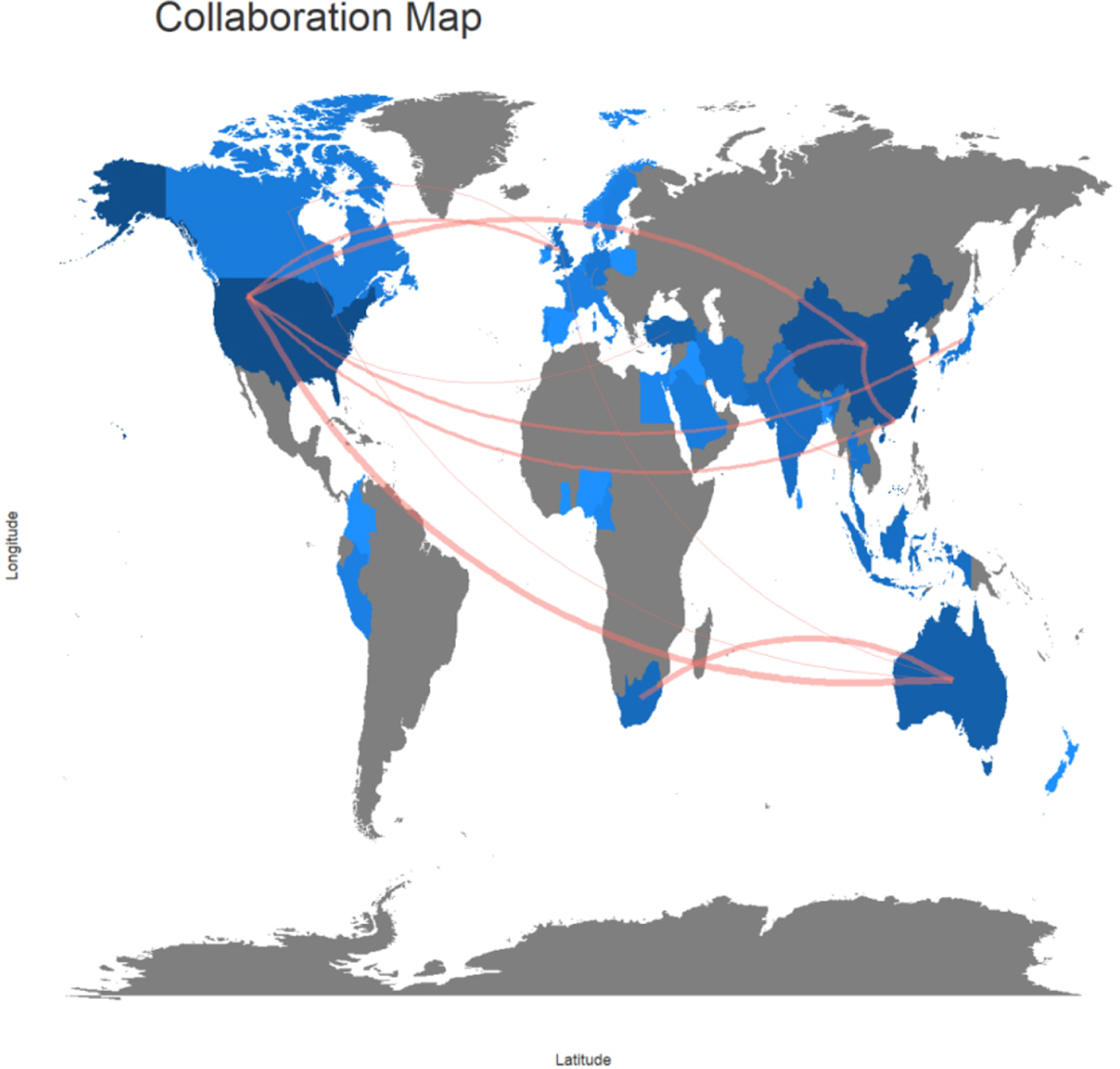
Table 3 reveals that the United States and Australia have the most extensive partnerships, with six documents co-authored by Americans and Australians. Following them, Australian and South African scholars have developed the second most extensive collaborative networks. These findings may indicate that authors of these three countries/regions have close collaboration on sociological issues. This evidence demonstrates a robust social alliance among authors of the three regions. With advancing technology and deepening globalization, the collaboration trend among different regions is strengthening with the availability of improved infrastructures and technological assistances. These kinds of development have influenced the two major activities at the international level including the transfer of knowledge and physical agility of movement. It is now possible for researchers to share and access the diverse data for interconnected complex concerns, and hence, a comparison between past research trends and current knowledge sharing is resulting in more productive and innovative solutions to interconnected complex issues.
Table 4
Ranking list of the most productive Universities
| No. | University/institute | NP |
| 1. | Eastern Mediterranean University | 19 |
| 2. | Georgetown University | 14 |
| 3. | University of Washington | 13 |
| 4. | McDonough School of Business | 13 |
| 5. | Edith Cowan University | 9 |
| 6. | Foster School of Business | 9 |
| 7. | Arizona State University | 8 |
| 8. | University of South Australia | 7 |
| 9. | Ferdowsi University of Mashhad | 6 |
| 10. | University of South Africa | 6 |
| 11. | Northern Illinois University | 6 |
| 12. | Monash University | 6 |
| 13. | University of Central Florida | 6 |
| 14. | Ming Chuan University | 6 |
| 15. | Nelson Mandela University | 5 |
| 16. | Ohio University | 5 |
| 17. | Illinois State University | 5 |
3.6The most productive universities
The most productive and well-known universities and institutes in the JE field would be of great interest to the reader of this manuscript. Table 4 lists all those institutes and universities that produced a minimum of 5 publications on JE. The most productive university in JE research is the Eastern Mediterranean University, one of the oldest universities in Cyprus, with its authors contributing 19 publications on JE. The Eastern Mediterranean University has a long history of producing significant scientific knowledge. The second most productive university is Georgetown University in the USA, with its authors contributing 14 research publications on JE. The University of Washington and McDonough School of Business rank No. 3 and No. 4 respectively in the list with 13 publications each on JE.
3.7Leading journals
Scientific journals are a great way to introduce scientific results, discoveries, innovations, and potential research opportunities to the public. Papers published in peer-reviewed scholarly journals are endorsed by experts in the field, making them reliable tools for scholars, policymakers, and the public. Journals provide a vast collection of scientific papers for scholars to understand and generate ideas for future studies in their area. Ultimately, academic journals facilitate contact among scientists, serve as a foundation for new ideas, and keep track of discoveries in science. Publications in recognized journals enhance the recognition and authority of researchers, as well as their career prospects.
In all walks of life, including research and publishing, the advent of computerization has brought a revolution. For the last few decades, the launch of new journals has expanded exponentially. This exponential growth has challenged researchers to categorize the most important journals in each area of study. This section lists the most prominent and active journals for publications of JE studies. Table 5 displays the leading top journals that collect a minimum of 4 publications. International Journal of Human Resource Management and Journal of Applied Psychology are the top journals with 10 publications each, followed by the Journal of Vocational Behavior with 8 publications on JE. To analyze each journal’s influence, we calculated the average citation per publication of these top journals. With an average of 542.50 citations per publication, Academy of Management Journal is the leading journal, followed by Journal of Applied Psychology (132.80 citations per publication) and International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management (59.80 citations per publication).
Table 5
Top Journals with Publications in JE research
| Rank | Source | Publications | Citations | C/P |
| 1 | Journal of Applied Psychology | 10 | 1328 | 132.80 |
| 2 | International Journal of Human Resource Management | 10 | 270 | 27.00 |
| 3 | Journal of Vocational Behavior | 8 | 405 | 50.62 |
| 4 | Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration | 7 | 12 | 1.71 |
| 5 | International Journal of Hospitality Management | 6 | 100 | 16.66 |
| 6 | Personnel Review | 6 | 95 | 15.83 |
| 7 | International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management | 5 | 299 | 59.80 |
| 8 | Academy of Management Journal | 4 | 2170 | 542.50 |
| 9 | Employee Relations | 4 | 68 | 17.00 |
| 10 | Frontiers in Psychology | 4 | 10 | 2.50 |
| 11 | Management Research Review | 4 | 12 | 3.00 |
| 12 | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 4 | 24 | 6.00 |
The examination of co-citations in these top journals is an intriguing component of the bibliometric analysis. The degree of resemblance between the journals, authors, and documents is determined by co-citation, specifically by citation counts. Co-citation refers to the frequency at which two papers are quoted in a third paper. The more the co-citations shared by two papers, the more closely they are connected. Journal co-citation, author co-citation, and document co-citation are all examples of co-citation types reported in the literatures. This section probes into the co-citation of journals to decide which ones have JE research that is like each other. Based on their interconnectedness, Fig. 4 displays three primary groupings of journals. A substantial co-citation relationship exists between the journals clustered in different colors. A closer look into the green cluster discloses that its articles are more focused on management research, whereas the journals in the red cluster are more focused on human resource and behavioral JE research.
Fig. 4
Co-citations of the Top Ten Journals.
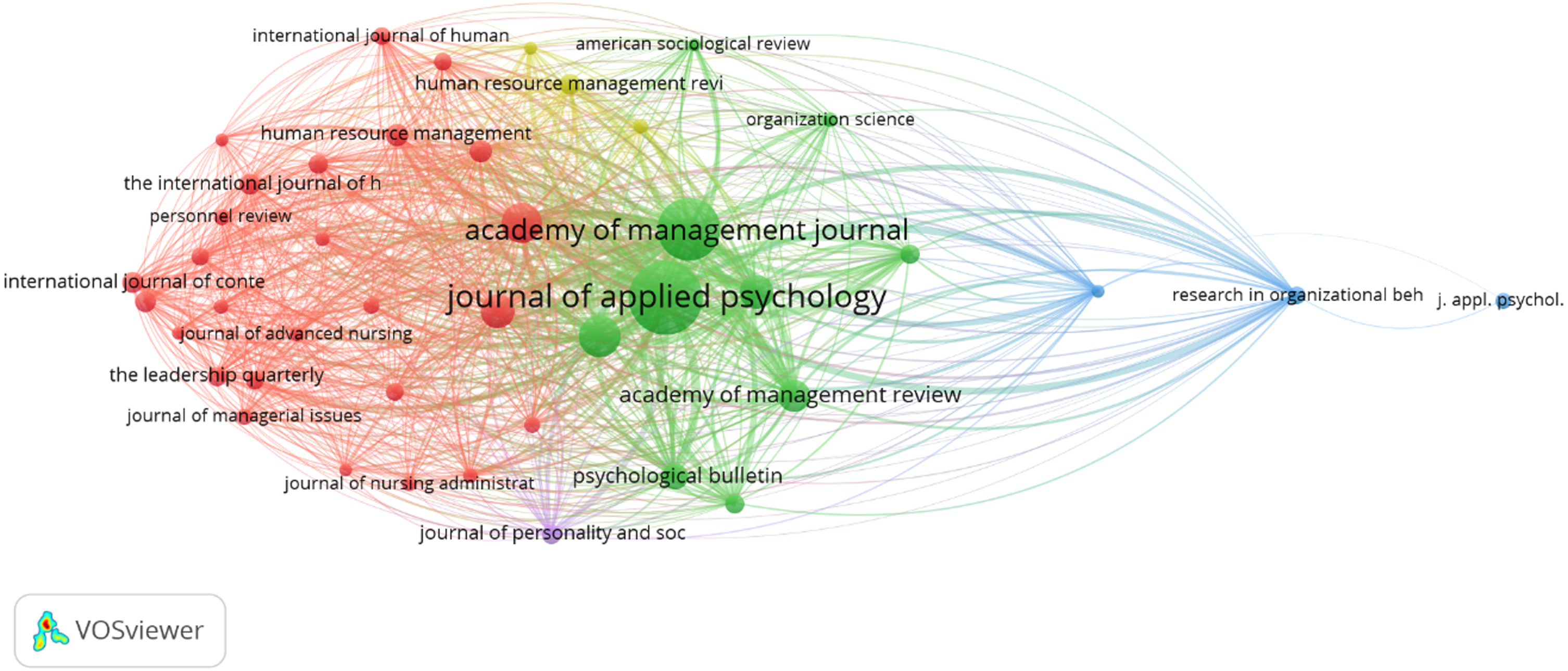
3.8The most productive authors in JE
Before conducting research in a specified academic topic, it is essential to be familiar with the renowned authors in the relevant field in order to acquire basic knowledge and achieve development in the academia. Table 6 lists the top-ranking authors in terms of repetitiveness of their publications on JE. Holtom B. C. is the champion in the list with 16 publications, followed by Karatepe O. M. who published 13 articles. Lee T. W. and Mitchell T. R. rank third and fourth, respectively, with 12 publications each. However, Sablynski C. J. is the most prominent author with a total of 2062 citations in 6 publications in terms of average citation per publication, and Lee T. W. is the most prolific author, with 3043 citations in his 12 publications. All these four authors have nearly half of the JE literature citations, making their works exemplary among JE literatures.
Table 6
Ranking list of the most productive authors in JE research
| Rank | Author | Publications | Citations | C/P |
| 1 | Holtom B. C. | 16 | 2678 | 167.37 |
| 2 | Karatepe O. M. | 13 | 565 | 43.46 |
| 3 | Lee T. W. | 12 | 3043 | 253.58 |
| 4 | Mitchell T. R. | 12 | 2914 | 242.83 |
| 5 | Allen D. G. | 8 | 561 | 70.12 |
| 6 | Burton J. P. | 8 | 838 | 104.75 |
| 7 | Hom P. W. | 7 | 593 | 84.71 |
| 8 | Coetzer A. | 6 | 66 | 11.00 |
| 9 | Kiazad K. | 6 | 206 | 34.33 |
| 10 | Sablynski C. J. | 6 | 2062 | 343.66 |
| 11 | Wheeler A.R. | 6 | 645 | 107.50 |
| 12 | Arasli H. | 5 | 29 | 5.80 |
| 13 | Cheng C. Y. | 5 | 22 | 4.40 |
| 14 | Ferreira N. | 5 | 33 | 6.60 |
| 15 | Griffeth R. W. | 5 | 392 | 78.40 |
| 16 | Peltokorpi V. | 5 | 82 | 16.40 |
| 17 | Poisat P. | 5 | 64 | 12.80 |
| 18 | Rafiq M. | 5 | 32 | 6.40 |
| 19 | Treuren G. J. M. | 5 | 49 | 9.80 |
3.9The most cited publication
According to Bayer and Folger [40], the importance of a work can be weighed by the number of citations to it. From author rankings to journal impact factors, citation counts, and journal impact factors are used in a variety of scenarios. Table 7 shows the publications which have received a minimum of 100 citations. A scrutiny into the publications reveals the multidisciplinary idea of JE research. We analyzed the contents in these most cited papers. The information about the top five most cited papers is shown as follows, based on the Scopus search results:
Table 7
The most cited publications
| Authors | Title | Year | Source title | Cited by |
| Mitchell T.R., Holtom B.C., Lee T.W., Sablynski C.J., Erez M. | Why people stay: Using job embeddedness to predict voluntary turnover | 2001 | Academy of Management Journal | 1273 |
| Lee T.W., Mitchell T.R., Sablynski C.J., Burton J.P., Holtom B.C. | The effects of job embeddedness on organizational citizenship, job performance, volitional absences, and voluntary turnover | 2004 | Academy of Management Journal | 498 |
| Halbesleben J.R.B., Wheeler A.R. | The relative roles of engagement and embeddedness in predicting job performance and intention to leave | 2008 | Work and Stress | 436 |
| Crossley C.D., Bennett R.J., Jex S.M., Burnfield J.L. | Development of a Global Measure of Job Embeddedness and Integration into a Traditional Model of Voluntary Turnover | 2007 | Journal of Applied Psychology | 358 |
| Felps W., Mitchell T., Hekman D., Lee T., Holtom B., Harman W. | Turnover contagion: How coworkers’ job embeddedness and job search behaviors influence quitting | 2009 | Academy of Management Journal | 296 |
| Allen D.G. | Do organizational socialization tactics influence newcomer embeddedness and turnover? | 2006 | Journal of Management | 293 |
| Hom P.W., Mitchell T.R., Lee T.W., Griffeth R.W. | Reviewing employee turnover: Focusing on proximal withdrawal States and an expanded criterion | 2012 | Psychological Bulletin | 253 |
| Mitchell T.R., Lee T.W. | The unfolding model of voluntary turnover and job embeddedness: Foundations for a comprehensive theory of attachment | 2001 | Research in Organizational Behavior | 207 |
| Hom P.W., Tsui A.S., Wu J.B., Lee T.W., Zhang A.Y., Fu P.P., Li L. | Explaining Employment Relationships with Social Exchange and Job Embeddedness | 2009 | Journal of Applied Psychology | 206 |
| Jiang K., Liu D., McKay P.F., Lee T.W., Mitchell T.R. | When and how is job embeddedness predictive of turnover? A meta-analytic investigation | 2012 | Journal of Applied Psychology | 202 |
| Ramesh A., Gelfand M.J. | Will they stay or will they go? The role of job embeddedness in predicting turnover in individualistic and collectivistic cultures | 2010 | Journal of Applied Psychology | 164 |
| Allen D.G., Shanock L.R. | Perceived organizational support and embeddedness as key mechanisms connecting socialization tactics to commitment and turnover among new employees | 2013 | Journal of Organizational Behavior | 162 |
| Holtom B.C., Mitchell T.R., Lee T.W. | Increasing human and social capital by applying job embeddedness theory | 2006 | Organizational Dynamics | 145 |
| Ng T.W.H., Feldman D.C. | Organizational embeddedness and occupational embeddedness across career stages | 2007 | Journal of Vocational Behavior | 136 |
| William Lee T., Burch T.C., Mitchell T.R. | The Story of Why We Stay: A Review of Job Embeddedness | 2014 | Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior | 133 |
| Sekiguchi T., Burton J.P., Sablynski C.J. | The role of job embeddedness on employee performance: The interactive effects with leader-member exchange and organization-based self-esteem | 2008 | Personnel Psychology | 128 |
| Holtom B.C., O’Neill B.S. | Job Embeddedness: A Theoretical Foundation for Developing a Comprehensive Nurse Retention Plan | 2004 | Journal of Nursing Administration | 128 |
| Heavey A.L., Holwerda J.A., Hausknecht J.P. | Causes and consequences of collective turnover: A meta-analytic review | 2013 | Journal of Applied Psychology | 124 |
| Harris K.J., Wheeler A.R., Kacmar K.M. | The mediating role of organizational job embeddedness in the LMX-outcomes relationships | 2011 | Leadership Quarterly | 121 |
| Burton J.P., Holtom B.C., Sablynski C.J., Mitchell T.R., Lee T.W. | The buffering effects of job embeddedness on negative shocks | 2010 | Journal of Vocational Behavior | 112 |
| Karatepe O.M. | The effects of work overload and work-family conflict on job embeddedness and job performance: The mediation of emotional exhaustion | 2013 | International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management | 110 |
| Holtom B.C., Inderrieden E.J. | Integrating the unfolding model and job embeddedness model to better understand voluntary turnover | 2006 | Journal of Managerial Issues | 109 |
| Kraimer M.L., Shaffer M.A., Harrison D.A., Ren H. | No place like home? An identity strain perspective on repatriate turnover | 2012 | Academy of Management Journal | 103 |
| Tanova C., Holtom B.C. | Using job embeddedness factors to explain voluntary turnover in four European countries | 2008 | International Journal of Human Resource Management | 102 |
“Why people stay: Using JE to predict voluntary turnover” has been cited 1273 times and is the article with the highest citation count. In this paper, the authors developed a measure of JE, discussed its reliability and validity, and compared its ability to predict voluntary turnover to other constructs. Furthermore, the study addressed how employers impact embeddedness and hence employee retention or turnover. It also predicted critical outcomes like the desire to quit and voluntary turnover and elucidated considerable additional variances above and beyond employees’ job satisfaction, organizational commitment, job options, and job hunting.
The second most cited paper (498 times) is “The effects of JE on job performance, organizational citizenship, voluntary turnover, and volitional absences”. There were two main goals in this study. First, it aimed to advance JE theories and research by indicating how its key mechanisms (on-and-off the JE) differed in their ability to predict the decision to participate (voluntary turnover and discretionary absences) and the decision to perform (job performance and organizational citizenship). Second, it intended to explain how these JE components might be processed to relate theoretically and empirically to performance and participation decisions.
The third most cited paper (436 times) is “The relative roles of JE and engagement in predicting intention to leave and job performance”. The main research aim of this paper was whether work engagement and JE were different concepts. Using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), the authors discovered that engagement and embeddedness were distinct variables among US individuals from a variety of sectors and occupations (n = 587). Besides, using the usefulness method, the study revealed that each of these variables experienced distinctive variance from quit and in-role performance.
The fourth most cited article (358 times) is “Development of a global measure of JE and integration into a traditional model of voluntary turnover”. The study examined how JE might be incorporated into a typical model/framework of voluntary turnover, extending the line of research (that either on or off the JE aspect can act to link employees to their job). In addition to the original composite measure, this research established and confirmed a global, reflective construct of JE. Beyond job attitudes and core characteristics, JE was originated to be a predictor of voluntary turnover from an unfolding model of turnover as a result of the interaction (with job satisfaction) in this study.
4Discussion: Future trends and suggestions on JE
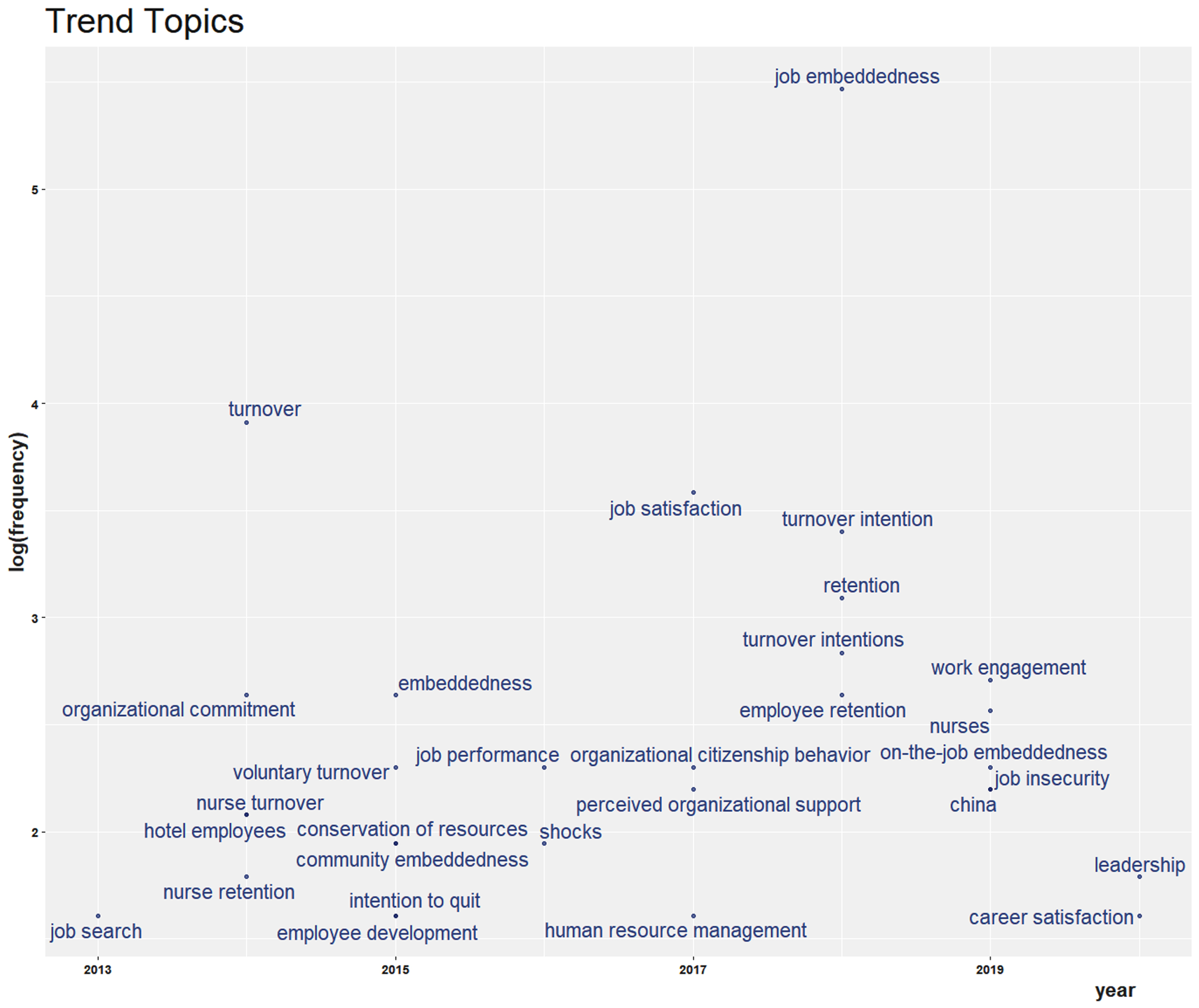
There remain additional topics to the ones highlighted and addressed devotedly and wholeheartedly in previous JE literatures. Figure 5 shows the trends of topics in the journal. With attention to these additional topics, below is a discussion of several future trends and suggestions that seem highly relevant for further advancement in the emerging area of JE.
Fig. 5
Trends of topics in the Journal.
4.1Antecedents of JE
Most of the prior studies emphasize the association between JE and outcomes, but relatively few are focused on the antecedents of JE. JE is enmeshed with different environmental factors, including contextual, organizational, and individual ones, by which it is assumed to be influenced. Therefore, future research is suggested to introduce more antecedent frameworks by considering these influencing factors.
4.2Off-and-on-the-JE
In the preceding section, JE was divided into two dimensions, namely the off and on the JE aspects. Almost all scholars on JE focus on on-the-JE while relatively few emphasize the off-the-JE aspect. Like the off-the-JE aspect, a small number of scholars focus on the separate JE dimensions of fit, link, and sacrifice, and both off and on the job aspects. In this vein, future research is suggested to focus on the separate dimensions of JE across samples and professions.
4.3Research design
Most of the previous literatures on JE predominantly resorted to the quantitative research design rather than the qualitative research design. Furthermore, Hennink et al. [41] argued that this practice adds more details and depth to the findings. They also maintained that quantitative research is necessary to testify to the relationships among constructs, but in the meanwhile qualitative research also provides comprehensive understanding to expand the discourse. Specifically, the inclusion of interviews, critical incidents, and short questions along with the quantitative survey would allow scholars to investigate the issues in more detail, which would ultimately enrich the quantitative findings. It is recommended that future studies employ both qualitative and quantitative studies to understand the JE phenomenon more deeply.
4.4Enriching the theoretical underpinning of JE research
Research on JE has drawn upon a comprehensive collection of theories. Based on the JE literature review, it is concluded that most of the studies resorted to the theories of conservation of resources, social exchange, social role, reactance, goal orientation, uncertainty management, social support resource, leader-member exchange, social information processing, planned behaviour, reason action, social bond, and social capital. Among these theories, the most employed ones are conservation of resources and social exchange (either of which was used in approximately more than 60% of the literatures). However, 25% of the studies reviewed employed no theory at all. It is also suggested here that future research explore the JE phenomenon from other leadership, management, sociological, and contextual theoretical perspectives.
4.5Meta-analysis and systematic review
Limited studies are organized in systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the JE phenomenon. To our knowledge, a single study was conducted along with a meta-analysis on JE [25]. Similar to the meta-analysis, the studies conducted with the systemic review on JE are also limited. Meta-analysis offers the fundamental approach for extracting accurate generalisations from prior literatures in a particular field, so providing an objective and quantitative foundation for future directions. Future JE scholars are suggested to conduct more systematic reviews and meta-analyses, which would turn out particularly instrumental for them.
4.6Cross-cultural expansion
JE is an evolving theory [1]. Expansion and exploration of this theory across diverse cultures can augment scholars’ general indulgence of both individual attitudes and turnover intention. JE is connected not only to the intra-organizational setting but also to the extra-organizational context individuals live in; therefore, the social context, as well as the organizational setting, is profoundly influenced by cultures. Additionally, cultural systems and traditions are entirely different in Western and Eastern countries. Accordingly, individual images, interventional instruments, and the development of influential aspects are supposed to be diverse in \enlargethispage 2ptdifferent backgrounds. It is recommended that future studies focus on different cultural backgrounds.
4.7Limitations
This study has shown an inclusive, highly nuanced, and dynamic set of findings on the JE research over a 20-year period. Nevertheless, this study has limitations, as do many others. The data were obtained from the Scopus database, and the constraints imposed by that database might have made a difference to our research. Hence, it is recommended that future investigations acquire data from various sources such as Google scholar and web of science. Additionally, we admit that a multi-source analysis and retrieval, along with cross-database evaluations, could offer further support of our comprehensive verdicts and implications. Next, this study included only articles from peer-reviewed journals, potentially limiting access to other outcomes, such as books, chapters, and conference proceedings related to JE, which were not included and can be selected in future research. Likewise, in this study, we only looked at quantitative indicators and didn’t look at qualitative ones. As we move forward, adding qualitative indicators can give us new information and new ways to look into research. Consequently, future research can utilise alternative journal performance metrics to circumvent these types of difficulties. Another constraint is the absence of national analysis. Research is done in languages other than English in many countries/regions; however, the majority of these manuscripts were overlooked in the Scopus data collection, and relevant studies were rarely cited, resulting in contradictory conclusions. Lastly, it should be stressed that measuring research is not an easy task because the essence of any research subject may comprise a number of qualities associated with a higher publishing and citation rate. As a result, creating broad expectations is challenging. Despite these limitations, our research has identified a trend in JE and a trajectory for future direction, which may be meritorious.
5Conclusion
In this paper, different bibliometric methods have been used on the publications listed in the Scopus database to provide an overview of the most influential and productive authors, countries/regions, institutes, and sources of JE literatures. From 2001 to 2020, JE research arrived at the following conclusions: (1) The number of published papers has increased, and research topics have become increasingly diversified; (2) the research authors are clearly distributed, and only a small number of them have been found to do on-going, in-depth research on JE-related topics; (3) the USA and Australia have extensive collaboration on JE research in comparison to other countries/regions; (4) the USA is the most productive country in terms of citations; (5) Eastern Mediterranean University does the most research on JE; (6) most of the publications are contributed in the Journal of Applied Psychology; (7) Holtom B. C. is one of the most productive authors in the field of JE; (8) most JE scholars use the motivational theories, most of which are derivatives from the conservation of resources theory, and; (9) Mitchell and his colleagues’ work, which has laid the basis for JE theory or conceptualization, is the most cited paper. We expect that insights inspired by future research and our recommendations will significantly contribute to the increasing and distinctive body of work in the field of JE and promote the success of JE practise.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required due to the nature of the study (bibliometric analysis).
Acknowledgments
None to report.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
References
[1] | Mitchell TR , Holtom BC , Lee TW , Sablynski CJ , Erez M . Why peoplestay: Using job embeddedness to predict voluntary turnover. Acad Manag J. Academy of Management Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510. (2001) ;44: (6):1102–21. |
[2] | Gu Z , Meng F , Farrukh M . Mapping the Research on Knowledge Transfer: A Scientometrics Approach. IEEE Access. (2021) ;9: :34647–59. |
[3] | Yihua W , Meng F , Farrukh M , Raza A , Alam I . Twelve years of research in: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Islam Middle East Financ Manag [Internet]. Emerald Publishing Limited; 2022; ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1108/IMEFM-03-2020-0134. |
[4] | Farrukh M , Raza A , Ansari NY , Bhutta US . A bibliometric reflection on the history of green human resource management research. Manag Res Rev [Internet]. Emerald Publishing Limited; 2021; ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-09-2020-0585. |
[5] | Gao S , Meng F , Gu Z , Liu Z , Farrukh M . Mapping and Clustering Analysis on Environmental, Social and Governance Field a Bibliometric Analysis Using Scopus. Sustainability [Internet]. (2021) ;13: (13). Available from:https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/13/7304. |
[6] | Bhutta U , Martins JN , Mata MN , Raza A , Dantas RM , Correia AB , et al. Intellectual Structure and Evolution of Accounting Conservatism Research: Past Trends and Future Research Suggestions. Int J Financ Stud [Internet]. (2021) ;9: (3). Available from:https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7072/9/3/35. |
[7] | Ritter BA . The 100 Most Cited Articles in Business and Management Education Research. Organ Manag J. Taylor & Francis. (2015) ;12: (3):153–153. |
[8] | Farrukh M , Raza A , Meng F , Wu Y . CMS AT 13: A RETROSPECTIVE OF THE JOURNEY. Chinese Manag Stud. (2020) ;1–29. |
[9] | Farrukh M , Shahzad IA , Meng F , Wu Y , Raza A . Three decades ofresearch in the technology analysis & strategic management: abibliometrics analysis. Technol Anal Strateg Manag [Internet]. Routledge; (2020) ;0: (0):1–17. Available from:https://doi.org/10.1080/09537325.2020.1862413. |
[10] | Imran Ahmed S , Farrukh M , Yihua W , Trunk N . Human systems management: a retrospective of 40 years. Hum Syst Manag. Human Systems Management; (2021) ;41: (1):15–30. |
[11] | Cancino CA , Merigó JM , Coronado FC . A bibliometric analysis of leading universities in innovation research. J Innov Knowl. Elsevier; (2017) ;2: (3):106–24. |
[12] | Farrukh M , Raza A , Mansoor A , Khan MS , Lee JWC . Trends and patterns in pro-environmental behaviour research: a bibliometric review and research agenda. Benchmarking An Int J [Internet]. Emerald Publishing Limited; 2022; ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-10-2020-0521. |
[13] | Farrukh M , Meng F , Raza A , Wu Y . Innovative work behaviour: the what, where, who, how and when. Pers Rev [Internet]. Emerald Publishing Limited; (2022) ; ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). Available from: https://doi.org/10.1108/PR-11-2020-0854. |
[14] | Gao P , Meng F , Mata MN , Martins JM , Iqbal S , Correia AB , et al. Trends and Future Research in Electronic Marketing: A Bibliometric Analysis of Twenty Years. J Theor Appl Electron Commer Res [Internet]. (2021) ;16: (5):1667–79. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/0718-1876/16/5/94. |
[15] | Javed M , Rafiq M , Ahmed M , Khan M . Impact of HR practices on employee job satisfaction in public sector organizations of Pakistan. Interdiscip J Contemp Res Bus. (2012) ;4: (1):348–63. |
[16] | Rafiq M , Shahzad F , Farrukh M , Khan I . The psychological mechanismlinking life satisfaction and turnover intention among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Work. IOS Press; (2022) ;71: :505–14. |
[17] | Lewin K . Resolving social conflicts and field theory in social science. Resolving social conflicts and field theory in social science. Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association; 1997. |
[18] | Witkin HA . Individual differences in ease of perception of embedded figures. Journal of Personality. United Kingdom: Blackwell Publishing; 1950. |
[19] | Rafiq M , Weiwei W . Managerial trust outlook in China and Pakistan. Hum Syst Manag. IOS Press; (2017) ;36: (4):363–8. |
[20] | Rafiq M , Jafar RMS , Ahmad W , Dastane O , Sial MA . Job Embeddedness: Cross-cultural Comparison Between China and Pakistan During COVID-19 Pandemic. Vision [Internet]. SAGE Publications India; Available from:https://doi.org/10.1177/09722629221129980. |
[21] | Rafiq M . The moderating effect of career stage on the relationship between job embeddedness and innovation-related behaviour (IRB). World J Entrep Manag Sustain Dev. Emerald Publishing Limited; 2019. |
[22] | Crossley CD , Bennett RJ , Jex SM , Burnfield JL . Development of a global measure of job embeddedness and integration into a traditional model of voluntary turnover. J Appl Psychol. American Psychological Association; (2007) ;92: (4):1031. |
[23] | Ghosh D , Gurunathan L . Job embeddedness: A ten-year literaturereview and proposed guidelines. Glob Bus Rev. SAGE Publications Sage India: New Delhi, India; (2015) ;16: (5):856–66. |
[24] | Shahzad IA , Fahed AA , Farrukh M , Yasmin N . Twenty five years of the Asian Academy of Management Journal (AAMJ): Intellectual structuremapping and bibliometric review. Asian Acad Manag J 2020. |
[25] | Jiang K , Liu D , McKay PF , Lee TW , Mitchell TR . When and how is job embeddedness predictive of turnover? A meta-analytic investigation. J Appl Psychol. American Psychological Association; (2012) ;97: (5):1077. |
[26] | William Lee T , Burch TC , Mitchell TR The story of why we stay: Areview of job embeddedness. Annu Rev Organ Psychol Organ Behav. Annual Reviews; (2014) ;1: (1):199–216. |
[27] | Hopson M , Petri L , Kufera J . A new perspective on nursing retention: Job embeddedness in acute care nurses. J Nurses Prof Dev. LWW; (2018) ;34: (1):31–7. |
[28] | Wheeler AR , Harris KJ , Sablynski CJ . How do employees investabundant resources? The mediating role of work effort in the job-embeddedness/job-performance relationshi. J Appl Soc Psychol. Wiley Online Library; (2012) ;42: :E244–66. |
[29] | Rubenstein AL , Peltokorpi V , Allen DG . Work-home and home-work conflict and voluntary turnover: A conservation of resourcesexplanation for contrasting moderation effects of on-and off-the-jobembeddedness. J Vocat Behav. Elsevier; (2020) ;119: :103413. |
[30] | Kiazad K , Holtom BC , Hom PW , Newman A . Job embeddedness: a multifoci theoretical extension. J Appl Psychol. American Psychological Association; (2015) ;100: (3):641. |
[31] | Chan WL , Ho JA , Sambasivan M , Ng SI . Antecedents and outcome of job embeddedness: Evidence from four and five-star hotels. Int J Hosp Manag. Elsevier; (2019) ;83: :37–45. |
[32] | Balu P . Exchange and power in social life. New York: Wiley; 1964. |
[33] | Peltokorpi V , Feng J , Pustovit S , Allen DG , Rubenstein AL . The interactive effects of socialization tactics and work locus of control on newcomer work adjustment, job embeddedness, and voluntary turnover. Hum Relations. SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, England; (2022) ;75: (1):177–202. |
[34] | Dechawatanapaisal D . Examining the relationships between HR practices, organizational job embeddedness, job satisfaction, and quit intention: Evidence from Thai accountants. Asia-Pacific J BusAdm. Emerald Publishing Limited; 2018. |
[35] | Farrukh M , Raza A , Javed S , Lee JWC . Twenty years of green innovation research: trends and way forward. World J Entrep Manag Sustain Dev [Internet]. Emerald Publishing Limited; (2021) ; ahead-of-p(ahead-of-print). Available from:https://doi.org/10.1108/WJEMSD-06-2020-0068. |
[36] | Caputo A , Fakhar Manesh M , Farrukh M , Farzipoor Saen R , Randolph-Seng B . Over a Half-Century of Management Decision: A Bibliometric Overview. Manag Decis. Emerald; 2022. |
[37] | Farrukh M , Raza A , Meng F , Wu Y , Gu Z . Shaping social marketing research: a retrospective of the journal of social marketing. J SocMark. Emerald Publishing Limited; 2021. |
[38] | Senadheera SS , Gregory R , Rinklebe J , Farrukh M , Rhee JH , Ok YS . The development of research on environmental, social, and governance (ESG): A bibliometric analysis. Sustain Environ [Internet]. Taylor & Francis; (2022) ;8: (1):2125869. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/27658511.2022.2125869. |
[39] | Farhan M , Iqbal MK . Twenty Years of Sustainable Supply Chain: Past Trends and Future Research suggestions. Int J Bus Psychol. (2021) ;3: (1):1–16. |
[40] | Bayer AE , Folger J . Some correlates of a citation measure of productivity in science. Sociol Educ. JSTOR; (1966) :381–90. |
[41] | Hennink M , Kaiser BN . Sample sizes for saturation in qualitativeresearch: A systematic review of empirical tests. Soc Sci Med. Elsevier; (2022) ;292: :114523. |



