Proprioceptive based training or modified constraint-induced movement therapy on upper extremity motor functions in chronic stroke patients: A randomized controlled study
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
The Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (mCIMT) method is a unilateral training that respectively avoids and activates less affected and affected sides of upper extremities; however, the selected options are not typically ideal. Proprioceptive based training (PT) includes bilateral training methods and influencing proprioceptive receptors.
OBJECTIVE:
The primary purpose was to determine if conventional therapy and PT or conventional therapy and mCIMT therapy show similar improvement in patients with chronic stroke. The secondary purpose was to investigate the effectiveness of conventional therapy and PT or mCIMT therapy in patients with chronic stroke and to compare which of the two interventions is more effective.
METHODS:
Forty patients with chronic stroke were randomly allocated to only conventional therapy (PTR, n = 14), conventional therapy plus proprioception training (PTR-PT, n = 13), and mCIMT (PTR-mCIMT, n = 13) groups. Evaluations were assessed before and 6 weeks after treatment.
RESULTS:
Intragroup evaluations revealeda significant improvement in the all scores in the PTR-PT and PTR-mCMIT groups (p = 0.006 < 0.001). Intergroup comparisons demonstrated that the PTR-mCIMT group had a significant improvement in spasticity and motor function scores compared to the PTR (p < 0.001) and the PTR-PT groups (p = 0.006–0.015).
CONCLUSIONS:
PT and mCMIT applied in addition to conventional therapy in patients with chronic stroke were more effective than only conventional therapy. Additionally, mCMIT showed greater improvement in spasticity and motor function scales than PT.
1Introduction
According to the World Health Organization, stroke is the leading cause of disability and mortality among neurological diseases (World Health Organization, 2020). Approximately 13.7 million people experience a stroke anually worldwide, of which 5.5 million people die. Five million people experience permanent activity limitations during their lifetime after a stroke (Johnson et al., 2019). In Turkey, 22.4% of total deaths in 2018 were reportedly caused by cerebrovascular events, and one-third of the stroke survivors in Turkey become dependent in their activities of daily living (İnme, 2018).
Studies have reported that 67% stroke survivors continue to experience disability in the upper extremity and cannot use the affected upper extremity (Broeks, Lankhorst, Rumping, & Prevo, 1999; Siebers et al., 2010). Despite the importance of the condition of upper extremities, rehabilitation often focuses on improving balance, gait, and general mobilization because of the inadequacies of rehabilitation resources, time constraints, and insufficient early motor recovery in upper extremities (Ward & Cohen, 2004). Futhermore, it is unclear which dose (frequency, duration, or intensity) of upper limb rehabilitation and which rehabilitation interventions are most effective; furthermore, the patient characteristics that would be benefitted the most remain unclear (Cho & Li, 2021; Kwakkel et al., 2004). Therefore, it is important to compare the techniques and determine which of them improve functional outcomes and limitations and the effect on function. In addition, Whitall claimed that exploring the relative effects of different research supported by training programs is important to design and develop efficient and effective rehabilitation programs for patients with stroke (Whitall et al., 2011).
Proprioception is the capacity of the central nervous system to determine where all body parts will be placed statically or dynamically. Formation or preservation of somatosensory integrity, and proprioceptive integrity in particular, is considered crucial for motor control and learning ((Bornstein, Konstantin, Alessandro, Tresch, & Zelzer, 2021; Vidoni, 2008). Proprioceptive based training (PT) is based on motor learning principles, such as the use of concurrent feedback and repetition of tasks; it is one of the bilateral arm training methods. PT is reported to be beneficial as it performs simultaneous movements with both the unaffected and the affected arm to promote motor recovery through some reciprocal connections of the interhemispheric and transcallosal pathway. PT in the upper hemiplegic extremity is supported by a physiotherapist with the aim to retrain movement and spatial location/position/movement awareness (Bolognini, Russo, & Edwards, 2016; Vidoni, 2008, Kiper, Baba, Agostini, & Turolla, 2015). Recognition of the position of both limbs, therefore, is always requested. The advantage of the proposed approach relies on the possibility of application since the early acute phase after stroke, when several therapeutic modalities— such as Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy— cannot be provided because of the absence of residual voluntary muscular activation (Kiper, Baba, Agostini, & Turolla, 2015).
Proprioceptive deficits have reportedly been negatively associated with initial motor function, independence during hospitalization, and upper extremity functional recovery, (Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020; Meyer, Karttunen, Thijs, Feys, & Verheyden, 2014). Although, in recent years, the importance of proprioceptive therapy targeting the somatic sensation has been increasing (Rand, 2018; Kiper et al., 2015; Smania, Montagnana, Faccioli, Fiaschi, & Aglioti, 2003; Ocal et al., 2020), studies examining the role of post-stroke proprioceptive rehabilitation are rather limited (Rand, 2018; Kiper, Baba, Agostini, & Turolla, 2015; Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020; Meyer, Karttunen, Thijs, Feys, & Verheyden, 2014; Smania, Montagnana, Faccioli, Fiaschi, & Aglioti, 2003; Yozbatiran, Donmez, Kayak, & Bozan, 2006; Findlater & Dukelow, 2017). Therefore, the field of proprioceptive rehabilitation is relatively new and well-designed studies are needed in this area particularly those pertaining to upper extremity rehabilitation (Findlater & Dukelow, 2017).
The Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) method aims to increase the functional use of the affected extremity by restricting the less affected side extremity (Rocha et al. 2021; Wolf, 2007). Unsuccessful use of the affected upper extremity in stroke patients may cause “learned nonuse phenomenon,” in which patients habitually rely on their less affected upper extremity to accomplish daily activities. CIMT has been effective for overcoming learned nonuse. The three major components of CIMT include the following: [1] restraint of the less affected arm; [2] repetitive, structured, practice intensive therapy in the more affected arm; and [3] application of a package of behavioral techniques that transfers gains from the clinical setting to the real world (i.e. making it functional, shaping practice, and task specific training). Studies with CIMT have shown that patients with chronic stroke improve functional use of the upper limbs by 20% – 25% (Yadav, Sharma, Borah, & Kothari, 2016; Page, Sisto, Levine, & McGrath, 2004; Pauli et al., 2020; Fleet, Page, MacKay-Lyons, & Boe, 2014; Shi, Tian, Yang, & Zhao, 2011; Cho & Li, 2021). The CIMT approach, with its high evidence value, is recognized as an important therapeutic method in the treatment of patients with stroke (Pauli et al., 2020). The original CIMT approach required the use of restrictive gloves for 90% of the wake time and approximately 6 hours of goal-directed training per day in a 2-week period (Rocha et al. 2021; Page, Sisto, Levine, & McGrath, 2004). However, the difficulty of applying this method has been reported by patients, families, and physiotherapists. Many patients with stroke have reported that they would not want to participate in CIMT, but would prefer a longer treatment protocol with shorter activity sessions and/or wearing restrictive devices for fewer hours (Page, Levine, Sisto, Bond, & Johnston, 2002; Pauli et al. 2020). More than 60% of responding therapists also noted that patients were extremely unlikely to comply with CIMT (Pauli et al., 2020). Therefore, a modified version of CIMT has been created. The modified CIMT (mCIMT) application varies between 30 minutes and 6 hours of goal-directed training per day and 2–7 sessions per week (total treatment duration 2–12 weeks). Specifically, in comparison to the original CIMT, meta-analytic evidence suggests that mCIMT is similar functional recovery of an affected limb post-stroke (Yadav, Sharma, Borah, & Kothari, 2016; Page, Sisto, Levine, & McGrath, 2004; Pauli et al., 2020; Fleet, Page, MacKay-Lyons, & Boe, 2014; Shi, Tian, Yang, & Zhao, 2011; Cho & Li, 2021).
In recent years, the question of whether unilateral or bilateral training is better for improving upper extremity function in chronic stroke patients has received more attention in the literature. PT includes bilateral training methods as well as influencing proprioceptive receptors (Sethy et al., 2016). The mCIMT method is a unilateral training strategy that avoids the less affected side of the upper extremity and activates the affected side of the upper extremity (Sethy, Bajpai, Kujur, Mohakud, & Sahoo, 2016; Cho & Li, 2021). To the best of our knowledge, there is no study in the literature regarding their superiority over each other. Therefore, we hypothesized that PT— because it restores proprioception deficits and sensory integrity, as well as being a bilateral education— will show similar or more beneficial functional improvements as mCIMT in patients with chronic stroke and PT could be used for patients who could not adapt to CMIT or mCMIT. In the present study, we attempted to investigate the effectiveness of conventional therapy and PT or mCIMT therapy in patients with chronic stroke and to compare which of the two interventions showed more or smilar effectiveness in terms of recovery of upper extremity function in patients with chronic stroke.
2Methods
2.1Study design and patients
This study used a prospective three-arms randomized controlled trial. The study was approved by Acıbadem University and Acıbadem Healthcare Institutions Clinical Research Ethics Committee (reference no. 2020-24/05) and registered on ClinicalTrials.gov from the U.S. National Library of Medicine (registration no. NCT04873908), and performed in accordance with the 2010CONSORT statement. The participants for the study were patients who applied for private home care (May 2021–September 2021), were aged 40–80 years, and had a stroke at least 6 months ago. Verbal and written consent was obtained from the patients for the study in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The inclusion criteria were (Wolf, 2007; Page, Sisto, Levine, & McGrath, 2004):
• Patients who were diagnosed with stroke according to the World Health Organization criteria;
• One-sided hemiparesis;
• According to Brunnstrom the upper extremity value at a minimum of 3;
• At least 10° active extension in the wrist, at least 10° active abduction in the thumb, any 2 of the metacarpophalangeal joints have at least 10° of active extension;
• According to the Standardized Mini Mental State Examination, scoring a minimum of 24 points;
• Upper extremity spasticity score of < 3 according to Modified Ashworth Scale were included from the study.
The exclusion criteria were (Yadav, Sharma, Borah, & Kothari, 2016; Page, Sisto, Levine, & McGrath, 2004):
• Severe heart disease with upper extremity pain [score ≥4 according to the visual pain scale (0–10 cm)];
• Minimal nonuse upper extremity (Motor Activity Diary score > 2.5);
• Major neurological or rheumatological disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system other than stroke;
• Impaired cognitive functions;
• Significant vision or hearing impairment;
• For safety reasons patients who had balance problems in the less affected side upper extremity restrictions were excluded from the study.
After the end of the study, the most effective rehabilitation program (according to results of our study) was applied to the control group in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The study power was calculated using the G*Power V.3.1.7 (Kiel University, Kiel, Germany) program. A total of 45 patients were needed to achieve the power ratio of the study as 80% (effect size = 0.45 according to the Fugl-Meyer Upper Extremity Motor Rating Scale [FM]) with an error margin of 0.05 at a confidence level of 95% (Page, Sisto, Levine, & McGrath, 2004; Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020). A random allocation software program was used to randomly allocate the participants into three groups using the block randomization method, and the allocation was concealed. The recruitment process is reported as per the CONSORT (Fig. 1) and whose results could be analyzed after the completion of their treatment in groups as follows (n = 40):
Fig. 1
CONSORT flowchart of the study process.
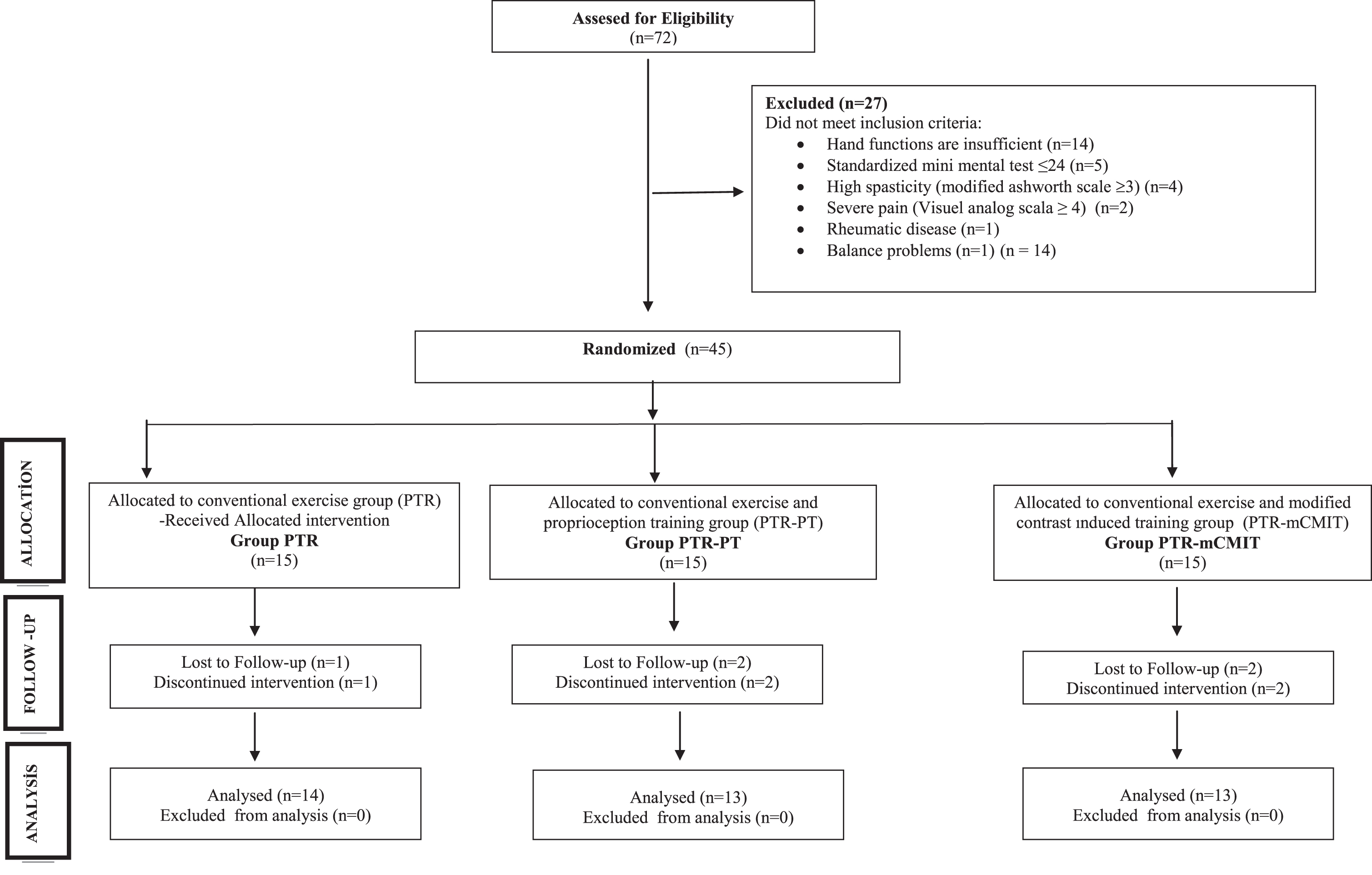
i. Conventional therapy training group (PTR, n = 14);
ii. Conventional therapy and proprioceptive based training group (PTR-PT, n = 13);
iii. Conventional therapy and Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy group (PTR-mCIMT, n = 13).
2.2Rehabilitation programs
Conventional therapy consisted of passive/active/active assistive range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises specifically targeting antispastic muscles (triceps, wrist extensors), electrical stimulation (70–100 hz, 150μs, 6-second contraction, and 10- second relaxation for 15 minutes was applied in particular to the triceps muscle and wrist extensors), and a rehabilitation program containing recommendations and compensation methods to prevent complications were applied for 45 minutes. Appropriate upper extremity passive/active/active assistive range of motion exercises, especially strengthening exercises targeting antispastic muscles, were prescribed to the patient as an additional home program that was applied 5 times a week for 30 minutes per day for a total of 1 hour a day (Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020). This program was held 5 days a week for 6 weeks.
Conventional therapy and PT group was delivered 30 minutes per session. The PT training was delivered as per the program by Partin, Stone, Ryan III, Lueken, & Timm (1994). In the first stage, the physiotherapist moved the patient’s upper extremity on the less affected side passively in various positions within the range of motion. The patient was asked to repeat this position with the hemiplegic upper extremity, first with eyes open and then closed. In the second stage, the hemiplegic upper extremity was passively moved to a position within the current range of motion and returned to a resting position. The patient was asked to repeat this with both arms, first with eyes opens and then closed. In the third stage (a rhythmic stabilization technique), the physiotherapist asked the patient to perform an isometric contraction after placing the patient’s upper extremity, and this resistance was not high enough to break the isometric contraction. As the patient progressed, the rhythmic stabilization time was increased, the resistance provided by the physiotherapist was increased, and the contact area between the hands of the physiotherapist and the patient’s upper extremity was reduced, thereby providing less stability. All these exercises were performed first with the eyes open and then closed (positions ranging 5–10) for 10–20 repetitions. Appropriate proprioceptive education taught to the patient and the patient’s relatives was additionally given as a home program; this was applied 5 times a week for 30 minutes, twice a day for a total of 1 hour per day. Exercises were applied to the group of patients 5 times a week for 6 weeks.
In the conventional therapy and mCMIT group, the patient’s less affected side arm was splinted for 30 minutes a day, and an exercise program for fine motor skills was applied to the affected extremity by a physiotherapist. The exercise program for fine motor and sensory included functional activities, such as reaching forward to hold a glass and drinking from it, taking a comb and combing the hair, turning a light switch on and off, buttoning and unbuttoning clothes, and writing with a pencil. Appropriate fine skill training taught to the patient was administered as a home program, the patient’s less affected side upper extremity was splinted and the exercises were applied 5 times a week for 30 minutes twice a day, for a total of 1 hour per day (Cao & Li, 2021). This program was conducted 5 days a week for 6 weeks.
2.3Evaluation procedures
The participants were assessed before the treatment and 6 weeks after treatment. The primary outcome assessments evaluated motor function and activity scales (FM, Action Research Arm Test and Motor Activity [ARAT] Log-28). Secondary outcome assessments evaluated spasticity (Modified Ashworth Scale [MAS]) and proprioception (Thumb Localization Test [TLT]). Rehabilitation programs and evaluations were conducted by two researchers (NA, NÖ) who are not blinded. MAS and FM are considered to assess the body function; ARAT and MAL are considered to assess the activity according to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) (Santisteban et al., 2016).
2.3.1Assessment of spasticity
The MAS was developed by Bohannon & Smith (1987) to measure muscle tonus, and it is among the most commonly used scales for clinical and research purposes. The resistance against passive movement is evaluated on a scale of 4 points. In the current study, biceps muscle was assessed with MAS. The test was performed with each patient placed in a supine position. While holding the forearm distally (close to the wrist), it was ensured that the patient quickly brought the elbow from the maximum possible flexion position to the maximum possible extension, passively, within approximately 1 second. The forearm was in a neutral and supination position. Resistance to the passive motion was evaluated as follows: 0 points, no increase in tone; 1-point, slight increase in muscle tone, and when the affected part is brought to flexion or extension, minimal resistance is felt at the end of the movement or there is a grasp-release feeling. With a score of 1+, pulling sensation is felt during movement, resistance is felt in less than half of the joint movement; 2 points, resistance is felt in most joint movement, but the affected part is easy to move; 3 points, passive movement during ROM is difficult; and 4 points, the affected part is rigid in flexion or extension (Bohannon & Smith, 1987).
2.3.2Assessment of proprioception
Proprioception was evaluated using the TLT. The patient’s arm with hemiplegia was moved by the physiotherapist to four different locations in the air, and each time the patient is asked to find and grasp the affected thumb with the less affected side hand with his/her eyes closed. Scoring for each of the four attempts is based on the estimated distance that the patient distinguished between the less affected side hand and the affected thumb that the patient has missed in the air; 0 points; full (thumb grips fully), 1 point; defined as mild (indicates ability to locate the thumb via locating the wrist), 2 points, medium (can find the arm and use the arm to find the thumb), and 3 points severe (cannot find the thumb) (Hirayama, 2011; Otaka et al., 2020).
2.3.3Evaluation of upper extremity motor function
FM is a disease-specific, objective motor impairment scale designed specifically for the evaluation of recovery in post-stroke hemiplegic patients. It includes subsections that evaluate joint movements, coordination, and reflex activities related to the shoulder, elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand. Although the highest score that can be obtained from this evaluation is 66, the lowest score is zero. It consists of 9 parameters under the categories of sitting position, wrist assessment, hand assessment, coordination, and speed assessment. In the sitting position; reflex activity, flexor and extensor synergies, combined synergistic movements, non-synergistic movements, and normal reflex activities are evaluated. In wrist evaluation; the shoulder at 0° abduction and elbow flexion at 90° extension, dorsiflexion, shoulder flexion at 30° and while the elbow is in extension, wrist stability and wrist flexion–extension with the shoulder at 0° abduction and elbow flexion at 90° when in flexion, wrist circumference is evaluated in forearm pronation. In hand evaluation, the flexion–extension of the fingers and the types of grip are evaluated. In coordination and speed assessment; the finger nose test is performed rapidly 5 times in repetition to check tremor, dysmetria, and speed. The score of the patient is determined according to the state of performing—unable to perform— and partially performing to the abilities in different items (0: Unable to perform, 1: Partially performing, 2: completely performing). FM has been tested extensively, and is found to have excellent psychometric properties (Sullivan et al., 2011).
Functional ability of the upper extremity was also evaluated with the ARAT. It consists of 4 subsections which are, grasp, grip, pinch, and gross movements. It performs functional tasks to collect and transfer objects of different sizes. Total scores range from 0 (non-functional hand) to 57 (fully functional hand) (Lyle, 1981).
2.3.4Evaluation of activities of daily life of the upper extremity
Daily use of the affected upper limb will be assessed using the Motor Activity Log-28 (MAL-28) Quality of Movement (QOM) scale and Amount of Use (AOU) scale. It is a scale that questions how often the patient uses the upper extremity of the affected side for each activity during daily activities (turning on the electric switch, opening the door, etc.). High scores indicate a good frequency of use and quality of action (Hüseyinsinoğlu et al., 2011)
2.4Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted in SPSS 21.00 package program. Normality evaluations were made using the “Shapiro–Wilks Test.” Mean±standard deviation was used to show parametric data, and median (minimum-maximum) was used to show non-parametric evaluations. Chi-square test was used for comparing categorical data. For the evaluation of intra-group change, Paired-samples T Test was used for parametric data and Wilcoxon Signed-rank Test was used for non-parametric evaluations. Demographic comparisons of the groups were conducted using a Chi-square analysis for categorical variables and one-way ANOVA for continuous variables. Comparisons of within-group score change in FM, ARAT and MAL values were analyzed using an one-way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test (HSD) for intergroup comparisons. Mean difference data were used as mean±standard deviation or median 95% Confidence Interval (95% CI, lower-upper). A value of P less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant for a two-tailed test, using Bonferroni equality. Effect size (ES) was interpreted as described by Cohen: < 0.20 a small effect, 0.20–0.50 a moderate effect, > 0.80 large effect (Cohen, 2013).
3Results
The sociodemographic characteristics of the groups and the initial scores of the evaluations that were performed are shown in Table 1. The intergroup comparisons demonstrated that the baseline scores of the groups were not statistically significant (P = 0.217–0.965, Table 1).
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of patients and the difference in baseline evaluations between groups
| Parameters | Group PTR | Group PTR-PT | Group PTR-mCIMT | P |
| (n = 14) | (n = 13) | (n = 13) | ||
| Mean±standard deviation or median | ||||
| (min–max) or n (frequency%) | ||||
| Age | 71.10±13.40 | 63.90±14.30 | 67.70±9.31 | 0.217a |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 5 (35.71%) | 6 (46.15%) | 5 (42.85%) | 0.860b |
| Male | 9 (64.28%) | 7 (53.85%) | 8 (57.14%) | |
| Affected side | ||||
| Dominant | 12 (85.71%) | 11 (84.62%) | 10 (76.92%) | 0.986b |
| Non-dominant | 2 (14.28%) | 2 (15.38%) | 3 (23.02%) | |
| Time since stroke (months) | 9 (7–35) | 10.50 (7–34) | 11 (7–34) | 0.390c |
| Standardized Mini Mental Test – Baseline | 24 (24–29) | 25 (24–29) | 25 (24–29) | 0.775c |
| Modified Ashworth Scale – Baseline | ||||
| 0 | 2 (14.28%) | 4 (30.77%) | 2 (14.28%) | 0.743b |
| 1 | 6 (42.86%) | 3 (23.08%) | 5 (38.46%) | |
| 2 | 6 (42.86%) | 6 (42.86%) | 6 (42.86%) | |
| Thumb Localization Test – Baseline | ||||
| 0 | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (7.69%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0.757b |
| 1 | 8 (57.14%) | 7 (53.85%) | 6 (46.15%) | |
| 2 | 5 (35.71%) | 5 (38.46%) | 6 (46.15%) | |
| 3 | 1 (7.14%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (7.69%) | |
| Fugl-Meyer Upper Extremity Motor Rating Scale – Baseline | 28 (21–57) | 32.50 (18–48) | 37 (14–52) | 0.604c |
| Action Research Arm Test – Baseline | 25.77±11.69 | 28.50±9.20 | 28.17±9.87 | 0.965a |
| Upper Extremity Motor Activity Log – 28-Quality of Movement – Baseline | 1.43±0.90 | 2.01±0.99 | 1.86±0.81 | 0.681a |
| Upper Extremity Motor Activity Log – 28-Amount of Use – Baseline | 1.52±0.88 | 2.12±0.90 | 1.92±0.89 | 0.721a |
PTR, Conventional therapy training group; PTR-PT, Conventional therapy, and proprioceptive based training group; PTR-mCIMT, Conventional therapy, and Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy group; aOne-Way ANAVO; bChi-square Test; cThe Kruskal–Wallis Test.
Spasticity and TLT evaluations were conducted to analyze a Chi-square. In spasticity evaluation before and after the treatment; no change was observed in the PTR (P = 1.000, Table 2) and PTR-PT group (P = 0.165, Table 2). In the PTR-mCIMT group, there was a statistically significant decrease in spasticity in the in-group evaluation (P = 0.031, Table 2). In the comparison of the groups with each other, the PTR-mCMIT group decreased spasticity more significantly than both the PTR (P < 0.001, Table 2) and the PTR-PT group (P = 0.006, Table 2).
Table 2
Comparison of patients’ spasticity and proprioception post-intervention evaluations
| Parameters | Group PTR | Group | Group | P | ||
| (n = 14) | PTR-PT | PTR-mCIMT | Intergroup difference | |||
| (n = 13) | (n = 13) | |||||
| n (frequency%) | PTR vs | PTR vs | PTR-PT vs | |||
| PTR-PT | PTR-mCIMT | PTR-mCIMT | ||||
| Modified Ashworth Scale – Baseline | ||||||
| 0 | 2 (14.28%) | 4 (30.77%) | 2 (14.28%) | |||
| 1 | 6 (42.86%) | 3 (23.08%) | 5 (38.46%) | |||
| 2 | 6 (42.86%) | 6 (42.86%) | 6 (42.86%) | |||
| Modified Ashworth Scale – Post-intervention | ||||||
| 0 | 2 (14.28%) | 4 (30.77%) | 6 (46.15%) | 0.513 | < 0.001 | 0.006 |
| 1 | 6 (42.86%) | 5 (38.46%) | 5 (38.46%) | |||
| 2 | 6 (42.86%) | 4 (30.77%) | 2 (15.38%) | |||
| p (within-group) | 1.000 | 0.165 | 0.031 | |||
| Thumb Localization Test – Baseline | ||||||
| 0 | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (7.69%) | 0 (0.00%) | |||
| 1 | 8 (57.14%) | 7 (53.85%) | 6 (46.15%) | |||
| 2 | 5 (35.71%) | 5 (38.46%) | 6 (46.15%) | |||
| 3 | 1 (7.14%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (7.69%) | |||
| Thumb Localization Test – Post-intervention | ||||||
| 0 | 0 (0.00%) | 6 (46.15%) | 7 (53.85%) | 0.020 | < 0.001 | 0.008 |
| 1 | 8 (57.14%) | 5 (38.46%) | 6 (46.15%) | |||
| 2 | 5 (35.71%) | 2 (15.38%) | 0 (0.00%) | |||
| 3 | 1 (7.14%) | 0 (0.00%) | 0 (0.00%) | |||
| p (within-group) | 1.000 | 0.001 | 0.002 | |||
PTR, Conventional therapy training group; PTR-PT, Conventional therapy, and proprioceptive based training group; PTR-mCIMT, Conventional therapy and Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy group; Chi-square.
In determining the intra-group differences in TLT evaluations, compared with the pre-treatment there was no difference in the PTR group (P = 1.000, Table 2), while there was a significant decrease in the PTR-PT group (P = 0.001, Table 2) and the PTR-mCIMT group (P = 0.002, Table 2). Among the groups, the PTR-PT group showed a significant decrease compared to the PTR group (P = 0.020, Table 2), while the PTR-mCIMT group compared to both the PTR (P < 0.001, Table 2) and the PTR-PT group (P = 0.008) decreased more significantly (Table 2).
In the in-group evaluation of FM, ARAT, and MAL-28-QOM and MAL-28-AOU tests; while there was no significant increase in the PTR group (P = 0.088, P = 0.082, P = 0.061, P = 0.058, respectively, Table 3), with the PTR-PT (P = 0.002, P < 0.001, P = 0.006, P = 0.005 respectively, Table 3) and PTR-mCMIT (P = 0.002, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, respectively, Table 3) groups there was a statistically significant increase compared to the pre-treatment.
Table 3
Evaluation of upper extremity motor function and comparison of patients’ activities of daily living
| Assessment | Group | Baseline | Post- | Within-group | Effect | P within- | Pc | ||
| intervention | difference | size | group | Intergroup difference | |||||
| Mean±SD or | Mean±SD or median | PTR vs | PTR vs | PTR-PT vs | |||||
| median (min–max) | [95% CI (lower-upper)] | PTR-PT | PTR-mCIMT | PTR-mCIMT | |||||
| Fugl-Meyer Upper Extremity Motor Rating Scale | PTR | 28 (21–57) | 30 (21–60) | –0.61 (–1.09–0.07) | 0.51 | 0.088a | 0.070 | < 0.001 | 0.011 |
| PTR-PT | 32.50 (18–48) | 38 (20–48) | 5.50 (–8.00–2.50) | 1.27 | 0.002a | ||||
| PTR-mCIMT | 37 (14–52) | 52 (18–60) | 10 (15.00–6.00) | 1.69 | 0.002a | ||||
| Action Research Arm Test | PTR | 25.77±11.69 | 26.23±12.21 | 0.46±0.24 | 0.52 | 0.082b | 0.062 | < 0.001 | 0.015 |
| PTR-PT | 28.50±9.20 | 32.86±10.93 | 4.29±0.80 | 1.43 | < 0.001b | ||||
| PTR-mCIMT | 28.17±9.87 | 36.33±12.04 | 8.16±1.45 | 1.63 | < 0.001b | ||||
| Upper Extremity Motor Activity Log-28-Quality of Movement | PTR | 1.43±0.90 | 1.47±0.95 | 0.04±0.01 | 0.57 | 0.061b | 0.035 | 0.004 | 0,623 |
| PTR-PT | 2.01±0.99 | 2.30±0.96 | 0.29±0.08 | 0.87 | 0.006b | ||||
| PTR-mCIMT | 1.86±0.81 | 2.25±0.92 | 0.39±0.08 | 1.33 | < 0.001b | ||||
| Upper Extremity Motor Activity Log-28-Amount of Use | PTR | 1.52±0.88 | 1.56±0.97 | 0.04±0.09 | 0.45 | 0.058b | |||
| PTR-PT | 2.12±0.90 | 2.40±0.96 | 0.28±0.06 | 0.82 | 0.005b | 0.041 | 0.005 | 0,688 | |
| PTR-mCIMT | 1.92±0.89 | 2.31±0.94 | 0.39±0.05 | 1.30 | < 0.001b | ||||
PTR, Conventional therapy training group; PTR-PT, Conventional therapy, and proprioceptive based training group; PTR-mCMIT, Conventional therapy, and Modified Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy group; Mean±SD, Mean±standard deviation; median [95% CI (lower-upper)], median [95% Confidence Interval (lower-upper)]; aWilcoxon Signed-rank Test, bpaired-samples t test, cone-way ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey < 0.20 a small effect, 0.20–0.50 a medium effect, > 0.80 a large effect. Bold values indicate statistical significance within the group or between groups.
An one-way ANOVA revealed that there was a statistically significant difference in FM (F (2, 36) =[14.485], P < 0.001), ARAT (F (2, 36) = [14.004], P < 0.001) and MAL (F (2, 36) = [6,690], P = 0.03) between three groups. Tukey’s HSD Test for multiple comparisons found that FM was significantly different between PTR (95% C.I. = [–1.09–0.07]) and PTR-mCMIT (95% C.I. = [–8.00–2.50], p < 0.001), PTR-PT (95% C.I. = 15.00–6.00]) and PTR-mCMIT (P = 0.011, Table 3) groups. FM test, the PTR-PT group did not show a significant difference compared to the PTR group (P = 0.070, Table 3). ARAT score was significantly different between PTR (95% C.I. = [–0.19–2.05]) and PTR-mCMIT (P < 0.001, 95% C.I. = [4.97–11.35], Table 3), PTR-PT (95% C.I. = [2.26–5.90]) and PTR-mCMIT (P = 0.015, Table 3) groups but the PTR-PT group did not show a significant difference compared to the PTR group (p = 0.062, Table 3). MAL-28-QOM was significantly different between PTR (95% C.I. = [0.01–0.08]) and PTR-PT (P = 0.035, 95% C.I. = [0.09–0.050], Table 3), PTR and PTR-mCMIT groups (P = 0.004, 95% C.I. = [0.20–0.58], Table 3). MAL-28- AOU was significantly different between PTR (95% C.I. = [0.01–0.09]) and PTR-PT (P = 0.041, 95% C.I. = [0.09–0.065], Table 3), PTR and PTR-mCMIT groups (P = 0.005, 95% C.I. = [0.20–0.60], Table 3). MAL-28-QOM and MAL-28-AOU scores, the PTR-PT group did not show a significant difference compared to the PTR-mCMIT group (P = 0.623, P = 0.688, respectively, Table 3).
In the effect value results, the PTR-PT group (ES = 0.87–1.43, Table 3) showed a higher effect value than the PTR group (ES = 0.51–0.57, Table 3) in the FM, ARAT, and MAL evaluations. The PTR-mCIMT group showed a higher effect value than the other groups (ES = 1.33–1.69, Table 3).
4Discussion
The present study aimed to compare the effect of PT therapy or mCMIT applied in addition to conventional therapy on upper extremity motor functions in patients with chronic stroke. It was determined that both PT and mCMIT helped improve posttreatment proprioception, motor function, and activities of daily life. The only group where these improvements were not observed was the conventional therapy group. In addition, the group in which mCMIT was applied, compared to the other groups, showed further improvements in spasticity, and motor function.
Various studies in both animals and humans show that the central nervous system is rearranged differently at molecular and synaptic connectivity levels depending on the type of behavioral interaction with the external environment, that is, it develops plasticity. Therefore, conventional therapy methods used to regulate upper extremity motor functions are insufficient (due to low intensity and less repetitions) and techniques with intense stimulation (repetitive and task-oriented movement) including motor learning strategies may be more beneficial (Alıpsatıcı, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020; Barreca, Wolf, Fasoli, & Bohannon, 2003; Krakauer, 2005; Pauli et al, 2020; Dimyan & Cohen, 2011). Similar to previous review articles (Barreca, Wolf, Fasoli, & Bohannon, 2003; Krakauer, 2005; Pauli et al, 2020; Dimyan & Cohen, 2011), probably due to the abovementioned reasons, the current study demonstrated that PT and mCMIT improved upper limb functions, while these improvements were not observed was the only conventional therapy group.
Proprioception training is a bilateral training besides improving proprioception, whereas mCMIT is a unilateral training method. Studies have reported that bilateral training is superior to unilateral training (Kelly, Borstad, Kline, & Gauthier, 2018; Lin, Chen, Chen, Wu, & Chang, 2010; Van der Lee, 1999) while there were studies reporting no difference (Morris, van Wijck, Joice, Ogston, Cole, & MacWalter, 2008; Morris & Van Wijck, 2012; Whitall et al., 2011). Although the neural mechanisms remain unclear, it is speculated that bilateral administration may facilitate co-activation and interhemispheric activation and thus a possible change in the contralesional cortical network. Additionally, cortical motor area damage directly affects 15%–20% of uncrossed corticospinal fibers and provides ipsilateral control of unilateral movements. After stroke, the undamaged primary motor cortex receives reduced interhemispheric inhibition from the lesioned hemisphere. These conditions cause ipsilesional dysfunction with normative motor control. For these reasons, bilateral training suggests that training may cause beneficial changes not only in the ipsilesional brain area but also in the contralesional brain area (the entrainment effect). Another important aspect of bilateral arm training is repetition, a well-established motor learning principle, and recent animal studies have shown that forced use involving a motor task rather than restrictive use alone can best improve central nervous system flexibility (Sethy, Bajpai, Kujur, Mohakud, & Sahoo, 2016; Lin, Chen, Chen, Wu, & Chang, 2010; Van der Lee, 1999; Morris & Van Wijck, 2012; van Delden et al., 2013; Chen, Abel, Janecek, Chen, Zheng, & Cramer, 2019, Yu et al., 2017). On the other hand, CIMT and mCIMT; provide positive reinforcement with the use of the paretic extremity, overcoming learned nonuse with practice through cortical reorganization and strengthening of neural connections, greatly increasing the use of the paretic extremity, improving mobility, and supporting its use in activities of daily living. Neuroimaging studies have shown that stroke patients participating in CIMT and mCIMT undergo neuroplastic changes in brain function and structure. Several cortical areas, such as the primary motor cortex, dorsal premotor cortex, and supplementary motor area, show increased electrical and metabolic neuronal activity during CIMT and mCIMT (Szaflarski, Page, Kissela, Lee, Levine, & Strakowski, 2006; Yadav, Sharma, Borah, & Kothari, 2016; Lucas et al., 2013).
CIMT and mCMIT were more effective in improving motor functions than the Bobath technique, bilateral training, mirror therapy, and other treatment methods especially in evaluations of hand functions and daily life (Huseyinsinoglu, Ozdincler, & Krespi, 2012; Brunner, Skouen, & Strand, 2012; Sethy, Bajpai, Kujur, Mohakud, & Sahoo, 2016; Ju & Yoon, 2018). Although it is a bilateral training method, the number of studies on PT is limited (Rand, 2018; Kiper, Baba, Agostini, & Turolla, 2015, 2015; Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020; Samania et al., 2003; Meyer, Karttunen, Thijs, Feys, & Verheyden, 2014; Yozbatiran, Donmez, Kayak, & Bozan, 2006; Findlater & Dukelow, 2017) and there are very few studies on its divergence from other methods (Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020). In a pilot study conducted by Kiper, Baba, Agostini, & Turolla (2015) with six patients with subacute stroke, they stated that 3 weeks of proprioception-based training had a positive effect on spasticity but a difference was not observed in the FM test. Smania, Montagnana, Faccioli, Fiaschi, & Aglioti, (2003) conducted 30 treatment sessions, similar to the present study, they evaluated the effects of a training program targeting somatic sensory and sensory deficits in motor control in a chronic stroke patient. During the 6-month follow-up, they observed that this treatment provided significant improvements. In addition, the authors’ study published in 2020 (Ocal, Alaca, & Canbora, 2020) compared conventional therapy and the additional PT model in chronic stroke patients. It was observed that upper extremity PT yielded better results in patients with chronic hemiplegia developed after stroke than conventional therapy in increasing the frequency and quality of movement in upper extremity similar to our study.
In the present study, mCIMT in the spasticity, FM, and ARAT evaluations, showed better results than PT and our hypothesis that both treatments might show similar effects was not confirmed. As the reasons for these consequences; it was our understanding that one of the causes for inclusion — in accordance with the working principles of mCMIT— in our study is a moderate lack of proprioception, which occured owing to the need to have slightly improved hand functions. It is unclear whether a patient with severe proprioception deficit will benefit from these therapies. The assessors were not blinded to group allocation, which is a major limitation. Futhermore, the sample size was not large and the long-term follow-up assessment of our patients. We could not be evaluated and the limited external generalisability of the findings, which was a very stringent inclusion criteria. These situtations constitute limitations of our study. In the future, more studies with high sample numbers, long-term results, with suitable masking, patient with different propriocepsion deficits are needed to show the superiority of both treatments more clearly.
5Conclusion
This study demonstrated it was determined that PT and mCMIT applied in addition to conventional therapy in patients with chronic stroke had therapeutic effects on proprioception, motor function, and activities of daily living when compared to only the conventional treatment. In addition, mCMIT showed greater improvement in spasticity and motor functional outcomes than PT.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the numerous professionals (physiotherapists Ihsan Alaca and Sukru Tekeli), patients and families who participated in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
References
1 | Alıpsatıcı, Ç. , Alaca, N. , & Canbora, M. K. ((2020) ). Comparison of the effects of treadmill trainings on walking and balance functions by increasing the speed and incline in chronic patients with stroke. Turkish Journal of Neurology, 26: , 316–321. |
2 | Andrabi, M. , Taub, E. , Mckay Bishop, S. , Morris, D. , & Uswatte, G. ((2021) ). Acceptability of constraint induced movement therapy: Influence of perceived difficulty and expected treatment outcome. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation, 1–9. |
3 | Barreca, S. , Wolf, S. L. , Fasoli, S. , & Bohannon, R. ((2003) ). Treatment interventions for the paretic upper limb of stroke survivors: A critical review. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 17: , 220–226. |
4 | Bohannon, R. W. , & Smith, M. B. ((1987) ). Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Physical Therapy, 67: , 206–207. |
5 | Bolognini, N. , Russo, C. , & Edwards, D. J. ((2016) ). The sensory side of post-stroke motor rehabilitation. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 34: , 571–586. |
6 | Bornstein, B. , Konstantin, N. , Alessandro, C. , Tresch, M. C. , & Zelzer, E. ((2021) ). More than movement: The proprioceptive system as a new regulator of musculoskeletal biology. Current Opinion in Physiology, 20: , 77–89. |
7 | Broeks, J. G. , Lankhorst, G. J. , Rumping, K. , & Prevo, A. J. ((1999) ). The long-term outcome of arm function after stroke: Results of a follow-up study. Disability and Rehabilitation, 21: , 357–364. |
8 | Brunner, I. C. , Skouen, J. S. , & Strand, L. I. ((2012) ). Is modified constraint-induced movement therapy more effective than bimanual training in improving arm motor function in the subacute phase post stroke? A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation, 26: (12), 1078–1086. |
9 | Chen, Y. , Abel, K. T. , Janecek, J. T. , Chen, Y. , Zheng, K. , & Cramer, S. C. ((2019) ). Home-based technologies for stroke rehabilitation: A systematic review. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 123: , 11–22. |
10 | Cao, M. , & Li, X. ((2021) ). Effectiveness of modified constraint-induced movement therapy for upper limb function intervention following stroke: A brief review. Sports Medicine and Health Science, 3: , 134–137. |
11 | Cohen, J. ((1977) ). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Academic Press. |
12 | Dımyan, M. A. , & Cohen, L. G. ((2011) ). Neuroplasticity in the context of motor rehabilitation after stroke. Nature Reviews. Neurology, 7: , 76–85. |
13 | Findlater, S. E. , & Dukelow, S. P. ((2017) ). Upper extremity proprioception after stroke: Bridging the gap between neuroscience and rehabilitation. Journal of Motor Behavior, 49: , 27–34. |
14 | Fleet, A. , Page, S. J. , MacKay-Lyons, M. , & Boe, S. G. ((2014) ). Modified constraint-induced movement therapy for upper extremity recovery post stroke: What is the evidence? Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation, 21: , 319–331. |
15 | Johnson, C. O. , Nguyen, M. , Roth, G. A. , Nichols, E. , Alam, T. , Abate, D. ..., & Miller, T. R. ((2019) ). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Neurology, 18: (5), 439–458. |
16 | Ju, Y. , & Yoon, I. J. ((2018) ). The effects of modified constraint-induced movement therapy and mirror therapy on upper extremity function and its influence on activities of daily living. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 30: (1), 77–81. |
17 | Hirayama, K. ((2011) ). Thumb/big-toe localizing test: Examination for deficit of proprioception through the posterior column-medial lemniscal system. Brain and Nerve, 63: , 851–860. |
18 | Huseyinsinoglu, B. E. , Ozdincler, A. R. , & Krespi, Y. ((2012) ). Bobath Concept versus constraint-induced movement therapy to improve arm functional recovery in stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation, 26: (8), 705–715. |
19 | Hüseyinsinoğlu E. B. , Razak Özdinçler, A. , Erkan Oğul, Ö. , & Krespi, Y. ((2011) ). Reliability and validity of Turkish version of Motor Activity Log-28. Turkish Journal of Neurology, 17: , 83–89. |
20 | Inme, K. Y. ((2018) ). Epidemiology and risk factors. Turkiye Klinikleri J Neurol-Special Topics, 11: , 1–19. |
21 | Kelly, K. M. , Borstad, A. L. , Kline, D. , & Gauthier, L. V. ((2018) ). Improved quality of life following constraint-induced movement therapy is associated with gains in arm use, but not motor improvement. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation, 25: , 467–474. |
22 | Kiper, P. , Baba, A. , Agostini, M. , & Turolla, A. ((2015) ). Proprioceptive Based Training for stroke recovery. Proposal of new treatment modality for rehabilitation of upper limb in neurological diseases. Archiv für die Physiologie, 5: , 1–6. |
23 | Krakauer, J. W. ((2005) December). Arm function after stroke: From physiology to recovery. Seminars in Neurology, 25: , 384–395. |
24 | Kwakkel, G. , van Peppen, R. , Wagenaar, R. C. , Wood Dauphinee, S. , Richards, C. , Ashburn, A. , Miller, K. , Lincoln, N. , Partridge, C. , Wellwood, I. , & Langhorne, P. ((2004) ). Effects of augmented exercise therapy time after stroke: A meta-analysis. Stroke, 35: , 2529–2539. |
25 | Lin, K. C. , Chen, Y. A. , Chen, C. L. , Wu, C. Y. , & Chang, Y. F. ((2010) ). The effects of bilateral arm training on motor control and functional performance in chronic stroke: a randomized controlled study. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 24: (1), 42–51. |
26 | Lucas, M. , Ribeiro, P. , Cagy, M. , Teixeira, S. , Chaves, F. , Carvalho, D. , & Piedade, R. ((2013) ). Neurorestorative effects of constraint-induced movement therapy after stroke: An Integrative Review. NM, 4: , 253–262. |
27 | Lyle, R. C. ((1981) ). A performance test for assessment of upper limb function in physical rehabilitation treatment and research. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research. Internationale Zeitschrift Fur Rehabilitationsforschung. Revue Internationale de Recherches de Readaptation, 4: , 483–492. |
28 | Meyer, S. , Karttunen, A. H. , Thijs, V. , Feys, H. , & Verheyden, G. ((2014) ). How do somatosensory deficits in the arm and hand relate to upper limb impairment, activity, and participation problems after stroke? A systematic review. Physical Therapy, 94: , 1220–1231. |
29 | Morris, J. H. , van Wijck, F. , Joice, S. , Ogston, S. A. , Cole, I. , & MacWalter, R. S. ((2008) ). A comparison of bilateral and unilateral upper-limb task training in early poststroke rehabilitation: A randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 89: , 1237–1245. |
30 | Morris, J. H. , & Van Wijck, F. ((2012) ). Responses of the less affected arm to bilateral upper limb task training in early rehabilitation after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 93: , 1129–1137. |
31 | Ocal, N. M. , Alaca, N. , & Canbora, M. K. ((2020) ). Does upper extremity proprioceptive training have an impact on functional outcomes in chronic stroke patients? Medeniyet Medical Journal, 35: , 91–98. |
32 | Otaka, E. , Otaka, Y. , Kasuga, S. , Nishimoto, A. , Yamazaki, K. , Kawakami, M. , Ushiba, J. , & Liu, M. ((2020) ). Reliability of the thumb localizing test and its validity against quantitative measures with a robotic device in patients with hemiparetic stroke. PLOS ONE, 15: , e0236437. |
33 | Page, S. J. , Sisto, S. , Levine, P. , & McGrath, R. E. ((2004) ). Efficacy of modified constraint-induced movement therapy in chronic stroke: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 85: , 14–18. |
34 | Page, S. J. , Levine, P. , Sisto, S. , Bond, Q. , & Johnston, M. V. ((2002) ). Stroke patients’ and therapists’ opinions of constraint-induced movement therapy. Clinical Rehabilitation, 16: , 55–60. |
35 | Partin, N. B. , Stone, J. A. , Ryan E. J. III, , Lueken, J. S. , & Timm, K. E. ((1994) ). Upper extremity proprioceptive training. Journal of Athletic Training, 29: , 15–18. |
36 | Pauli, G. , Iruthayarajah, J. , & Mirkowski, M. , et al. ((2020) ). Upper extremity motor rehabilitation interventions. EBSR. https://www.ebrsr.com/sites/default/files/Ch.%2010%20Upper%20Extremity%20Motor%20Interventions_v20.pdf |
37 | Rand, D. ((2018) ). Proprioception deficits in chronic stroke upper extremity function and daily living. PLOS ONE, 13: , e0195043. |
38 | Rocha, L. S. O. , Gama, G. C. B. , Rocha, R. S. B. , Rocha, L. B. , Dias, C. P. , Santos, L. L. S. , Santos, M. C. S. , Montebelo, M. I. L. , & Teodori, R. M. ((2021) ). Constraint induced movement therapy increases functionality and quality of life after stroke. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 30: , 105774. |
39 | Santisteban, L. , Térémetz, M. , Bleton, J. P. , Baron, J. C. , Maier, M. A. , & Lindberg, P. G. ((2016) ). Upper limb outcome measures used in stroke rehabilitation studies: A systematic literature review. PLOS ONE, 11: , e0154792. |
40 | Sethy, D. , Bajpai, P. , Kujur, E. S. , Mohakud, K. , & Sahoo, S. ((2016) ). Effectiveness of modified constraint induced movement therapy and bilateral arm training on upper extremity function after chronic stroke: A comparative study. Open Journal of Therapy and Rehabilitation, 4: , 1–9. |
41 | Shi, Y. X. , Tian, J. H. , Yang, K. H. , & Zhao, Y. ((2011) ). Modified constraint-induced movement therapy versus traditional rehabilitation in patients with upper-extremity dysfunction after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 92: , 972–982. |
42 | Siebers, A. , Oberg, U. , & Skargren, E. ((2010) ). The effect of modified constraint-induced movement therapy on spasticity and motor function of the affected arm in patients with chronic stroke. Physiotherapy Canada. Physiotherapie Canada, 62: , 388–396. |
43 | Smania, N. , Montagnana, B. , Faccioli, S. , Fiaschi, A. , & Aglioti, S. M. ((2003) ). Rehabilitation of somatic sensation and related deficit of motor control in patients with pure sensory stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 84: , 1692–1702. |
44 | Sullivan, K. J. , Tilson, J. K. , Cen, S. Y. , Rose, D. K. , Hershberg, J. , Correa, A. , Gallichio, J. , McLeod, M. , Moore, C. , Wu, S. S. , & Duncan, P. W. ((2011) ). Fugl-Meyer assessment of sensorimotor function after stroke: Standardized training procedure for clinical practice and clinical trials. Stroke, 42: , 427–432. |
45 | Szaflarski, J. P. , Page, S. J. , Kissela, B. M. , Lee, J. H. , Levine, P. , & Strakowski, S. M. ((2006) ). Cortical reorganization following modified constraint-induced movement therapy: a study of patients with chronic stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 87: (8), 1052–1058. |
46 | Van der Lee, J. H. , Wagenaar, R. C. , Lankhorst, G. J. , Vogelaar, T. W. , Devillé, W. L. , & Bouter, L. M. ((1999) ). Forced use of the upper extremity in chronic stroke patients: Results from a single-blind randomized clinical trial. Stroke, 30: , 2369–2375. |
47 | Vidoni, E. D. ((2008) ). Proprioception is ‘central’ to motor learning: Different consequences of peripheral and central proprioceptive disruption to sequence learning (Doctoral dissertation, University of Kansas). |
48 | Ward, N. S. , & Cohen, L. G. ((2004) ). Mechanisms underlying recovery of motor function after stroke. Archives of Neurology, 61: , 1844–1848. |
49 | Whitall, J. , Waller, S. M. , Sorkin, J. D. , Forrester, L. W. , Macko, R. F. , Hanley, D. F. , Goldberg, A. P. , & Luft, A. ((2011) ). Bilateral and unilateral arm training improve motor function through differing neuroplastic mechanisms: A single blinded randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 25: , 118–129. |
50 | Wolf, S. L. ((2007) ). Revisiting constraint-induced movement therapy: Are we too smitten with the mitten? Is all nonuse “learned”? and other quandaries. Physical Therapy, 87: , 1212–1223. |
51 | World Health Organization. ((2020) ). Progress on the health-related sustainable development Goals and targets in the eastern Mediterranean Region. https://www.emro.who.int/entity/statistics/statistics.html. Retrieved April 4, 2022. |
52 | Yadav, R. K. , Sharma, R. , Borah, D. , & Kothari, S. Y. ((2016) ). Efficacy of modified constraint induced movement therapy in the treatment of hemiparetic upper limb in stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 10: , YC01–YC05. |
53 | Yu, C. , Wang, W. , Zhang, Y. , Wang, Y. , Hou, W. , Liu, S. ..., & Wu, J. ((2017) ). The effects of modified constraint-induced movement therapy in acute subcortical cerebral infarction. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11: , 265. |
54 | Yozbatiran, N. , Donmez, B. , Kayak, N. , & Bozan, O. ((2006) ). Electrical stimulation of wrist and fingers for sensory and functional recovery in acute hemiplegia. Clinical Rehabilitation, 20: , 4–11. |




