Energy resolution and neutron flux of the 4SEASONS spectrometer revisited
Abstract
The elastic energy resolution, integrated intensity, and peak intensity of the direct-geometry neutron chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) were re-investigated. This was done with respect to the incident energy and the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper using incoherent scattering of vanadium and simple analytical formulas. The model calculations reproduced the observed values satisfactorily. The present work should be useful for estimating in instrument performance in experiments.
1.Introduction
The time-of-flight direct-geometry chopper spectrometer is one of the typical and powerful neutron scattering spectrometers to measure atomic and magnetic dynamics in materials. This type of instrument uses a rotating chopper to monochromatize the neutron beam incident on a sample, and the energy and momentum transfers to the sample are determined by analyzing the time-of-flight of neutrons and scattering angle of the detector. One of the advantages of this type of instrument is that the energy and momentum ranges and resolution can be flexibly chosen by tuning the rotation phase and speed of the chopper. This high flexibility, however, sometimes makes it difficult to find the best experimental condition in terms of resolution and flux, because high resolution generally results in low flux. Therefore, it is important to understand the relationship between the resolution and flux for the instrument quantitatively and prepare a convenient tool to estimate their values as a function of the incident energy (
In this study, we investigated the energy resolution and flux of the direct-geometry chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) [11]. 4SEASONS, also called SIKI, is one of the four direct-geometry chopper spectrometers installed at the pulsed neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC [13,18]. It was designed for the studies of dynamics using thermal neutrons, and has been used in a variety of research fields such as superconductors, quantum magnets, topological materials, catalysts, and thermoelectric materials. The instrument views the supercritical hydrogen coupled moderator, which is 18 m upstream of the sample. A Fermi chopper, 1.7 m upstream of the sample, is used to monochromatize the incident beam, and
Accordingly, we re-investigated the energy resolution and intensity of the elastic scattering using incoherent scattering of vanadium. The integrated intensity of the elastic scattering peak is the value directly related to the neutron flux on the sample. On the other hand, if the excitation to be observed is intrinsically sharp, the peak intensity, rather than the integrated intensity, is essential to determine the data quality. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the integrated intensity and the peak intensity. By comparing the observed data with simple analytical model, we developed empirical formulas which are useful to calculate the energy resolution and intensities.
2.Experiment
To study the scattering intensity as a function of
3.Calculations
3.1.Energy resolution
The energy resolution (FWHM) of the energy spectrum relative to the incident energy (
3.2.Intensity
The neutron flux at the sample is described as follows [9,25]:
Now we are interested in the
4.Results and discussions
The
Fig. 1.
(a) The energy resolution, (b) integrated intensity, and (c, d) peak intensity at 4SEASONS as a function of the incident neutron energy for different Fermi chopper rotation speeds. Symbols denote the observed values. The values of the integrated intensities in (b) were converted to the neutron flux per MW at the sample. In (a) and (b), the broken lines and solid lines are calculated values with
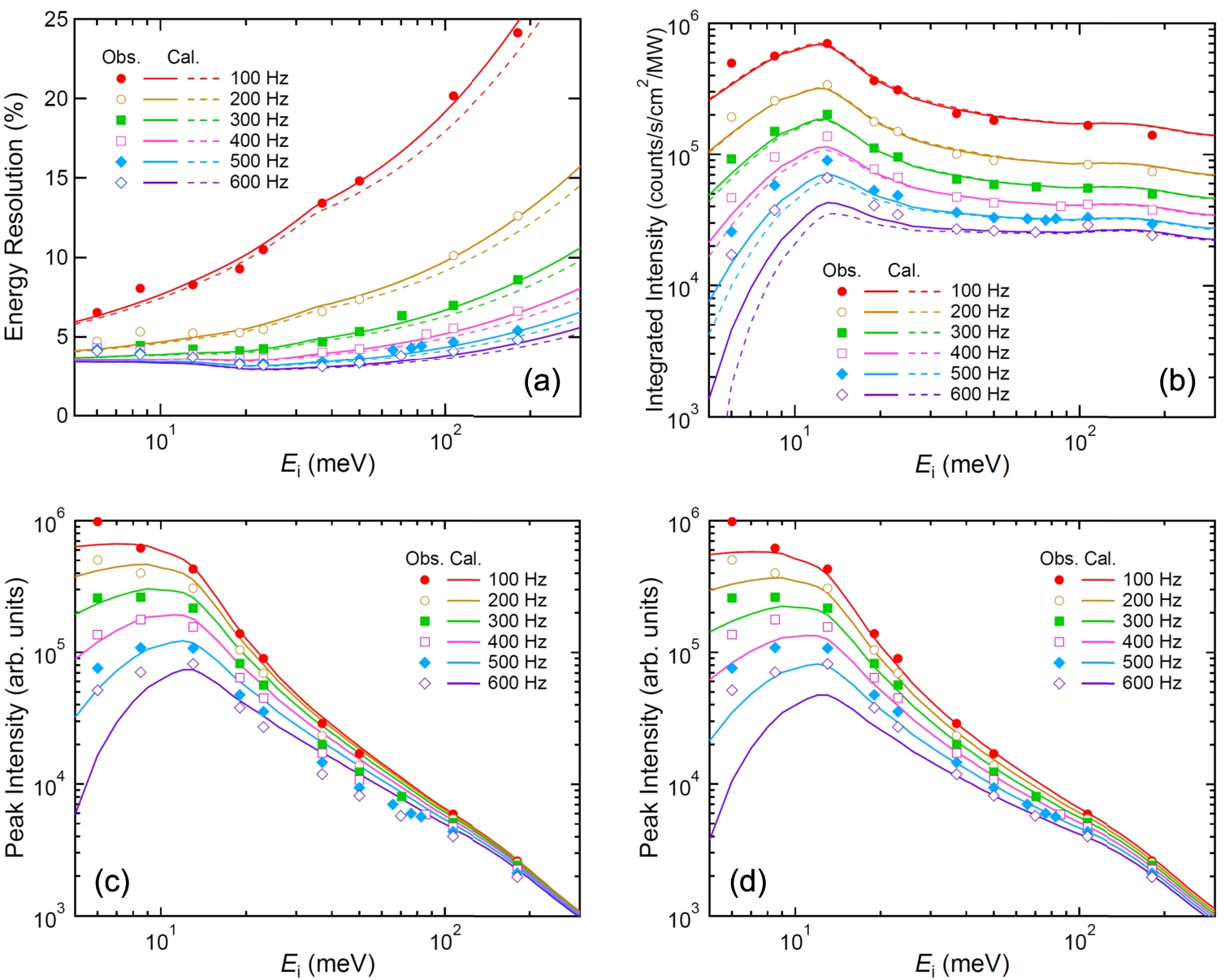
As the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper increased, the energy resolution improved [Fig. 1(a)]. However, it became saturated as f increased, as shown later in detail. The value of energy resolution decreased as
The symbols shown in Figs. 1(c) and 1(d) show the observed peak intensities as a function of
Fig. 2.
(a) The integrated intensity, (b) energy resolution, and (c) peak intensity at 4SEASONS as a function of the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper. Symbols denote the observed values, while solid lines denote the values calculated by using Eqs. (1), (6), and (7). The observed and calculated values are normalized so that the values at 100 Hz are unities. In (a) and (b), the function of
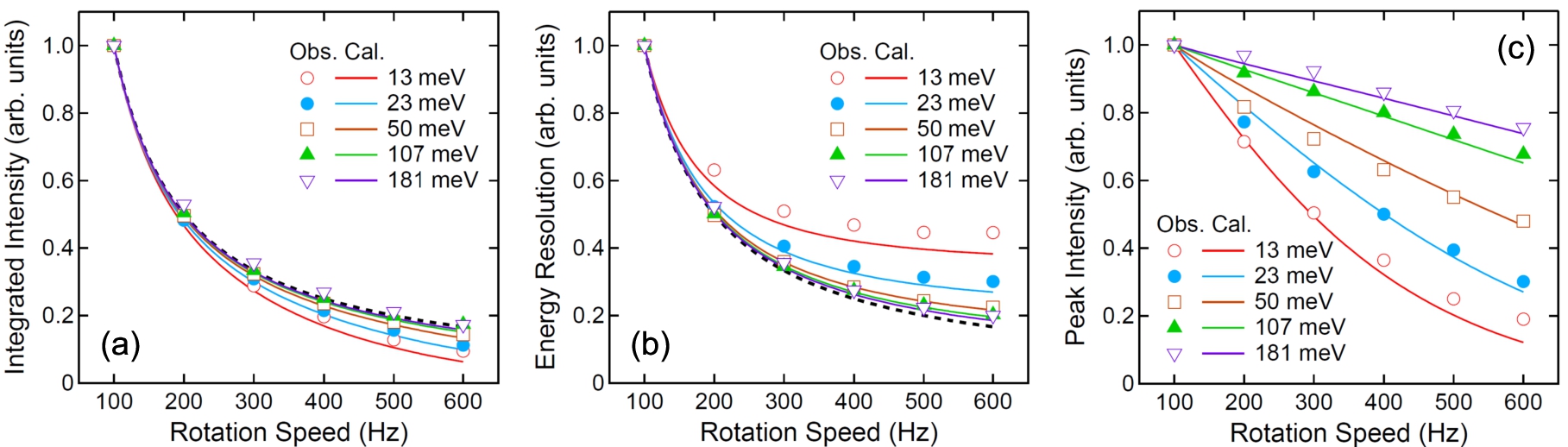
The observed and calculated energy resolutions, integrated intensities, and peak intensities for selected
Fig. 3.
The calculated energy resolutions of 4SEASONS as a function of the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper for (a)
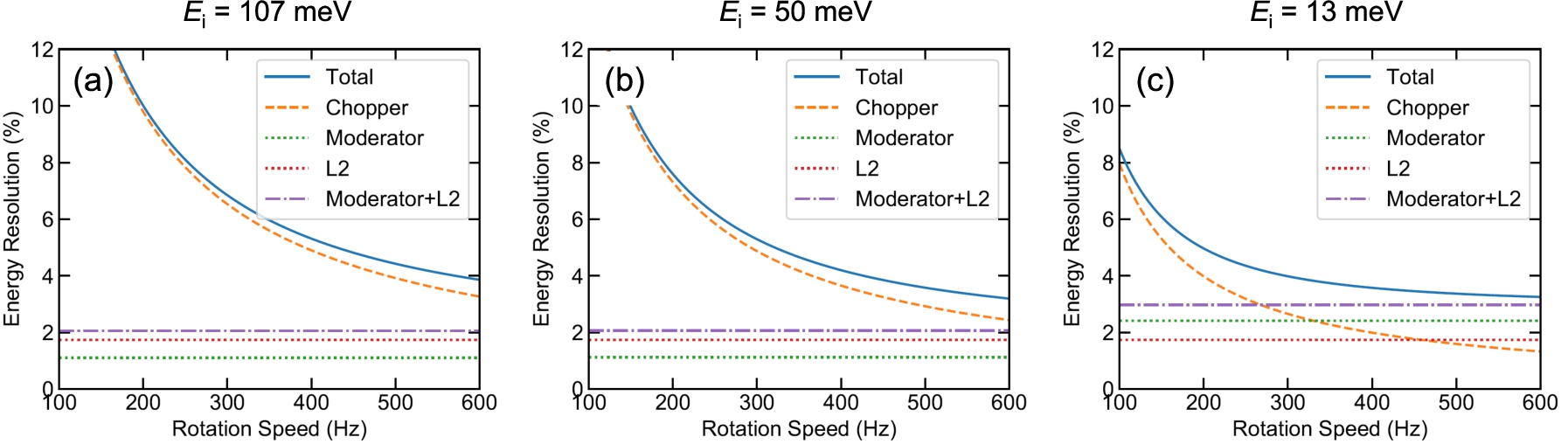
As seen above, the saturation of the energy resolution at low
Having established practical formulas to calculate the energy resolution, integrated intensity, and peak intensity easily, we can take advantage of this knowledge to find the best combination of
Fig. 4.
Outputs of computing tools to calculate (a) the energy resolution and (b) the integrated and peak intensities for 4SEASONS.
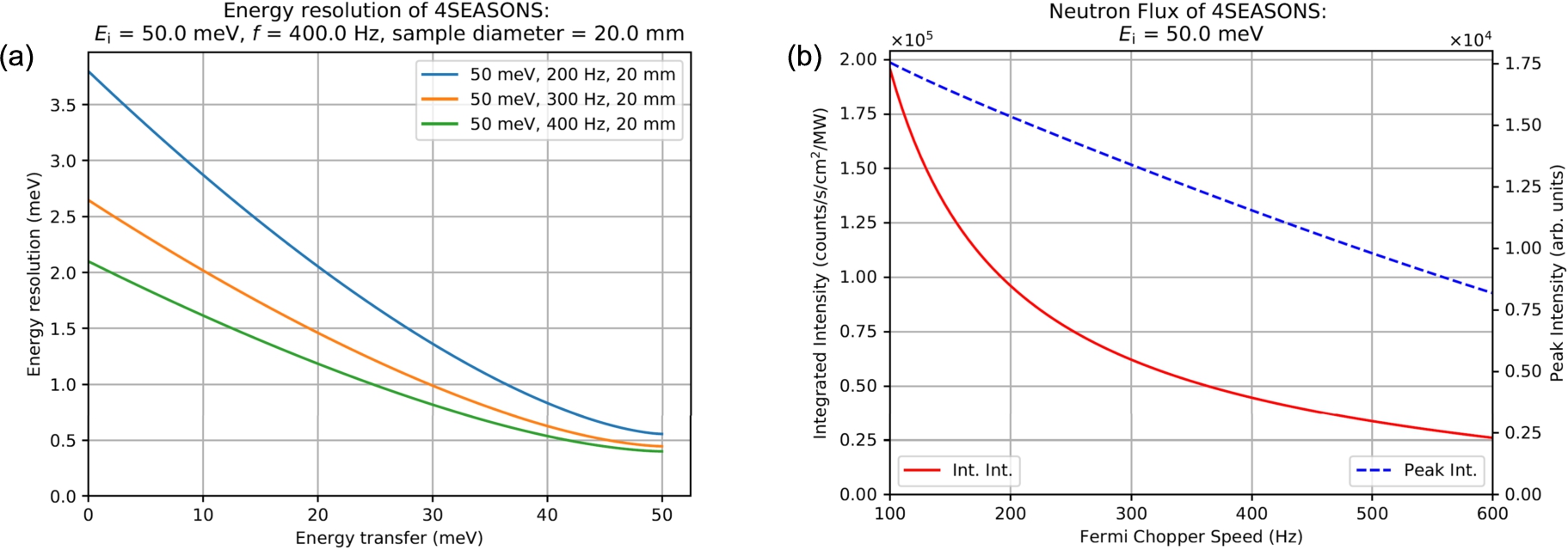
5.Summary
The elastic energy resolution as well as the integrated and peak intensities of the direct-geometry neutron chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC were re-investigated with respect to the incident energy and the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper using incoherent scattering of vanadium. The model calculation based on formulas sufficiently reproduced the observed energy resolution and integrated intensity, but the agreement was improved by assuming a 10% larger slit width in the Fermi chopper. The naive division of the integrated intensity by the peak width failed to reproduce the observed peak intensity probably due to the asymmetric line shapes of the energy spectra, which became significant at low incident energies and high rotation speeds. We introduced an empirical scaling function, which practically described the observed peak intensity. The inverse of the rotation speed of the Fermi chopper is an adequate measure of the rotation speed dependence of the energy resolution and integrated intensity at high incident energies. However, they deviated from the
Acknowledgement
The neutron scattering experiment at MLF of J-PARC was performed under the user program no. 2019I0001.
References
[1] | http://j-parc.jp/researcher/MatLife/en/instrumentation/ns3.html. |
[2] | D.L. Abernathy, M.B. Stone, M.J. Loguillo, M.S. Lucas, O. Delaire, X. Tang, J.Y.Y. Lin and B. Fultz, Design and operation of the wide angular-range chopper spectrometer ARCS at the Spallation Neutron Source, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83: ((2012) ), 015114. doi:10.1063/1.3680104. |
[3] | M. Arai, R. Kajimoto, M. Nakamura, Y. Inamura, K. Nakajima, K. Shibata, N. Takahashi, J. Suzuki, S. Takata, T. Yamada and S. Itoh, Recent developments of instruments in a spallation neutron source at J-PARC and those prospects in the future, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 82: ((2013) ), SA024. doi:10.7566/JPSJS.82SA.SA024. |
[4] | G. Ehlers, A.A. Podlesnyak, J.L. Niedziela, E.B. Iverson and P.E. Sokol, The new cold neutron chopper spectrometer at the Spallation Neutron Source: Design and performance, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82: ((2011) ), 085108. doi:10.1063/1.3626935. |
[5] | G.E. Granroth and S.E. Hahn, Monte Carlo simulation of the resolution volume for the SEQUOIA spectrometer, EPJ Web Conf. 83: ((2015) ), 03006. doi:10.1051/epjconf/20158303006. |
[6] | K. Iida, K. Ikeuchi, M. Ishikado, J. Suzuki, R. Kajimoto, M. Nakamura, Y. Inamura and M. Arai, Energy- and Q-resolution investigations of a chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC, JPS Conf. Proc. 1: ((2014) ), 014016. doi:10.7566/JPSCP.1.014016. |
[7] | S. Ikeda and J.M. Carpenter, Wide-energy-range, high-resolution measurements of neutron pulse shapes of polyethylene moderators, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 239: ((1985) ), 536–544. doi:10.1016/0168-9002(85)90033-6. |
[8] | K. Ikeuchi, M. Nakamura, R. Kajimoto and M. Arai, Optimization of a Fermi chopper for an inelastic neutron spectrometer with focusing guide, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 82: ((2013) ), SA038. doi:10.7566/JPSJS.82SA.SA038. |
[9] | S. Itoh, T. Yokoo, S. Satoh, S. Yano, D. Kawana, J. Suzuki and T.J. Sato, High Resolution Chopper spectrometer (HRC) at J-PARC, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 631: ((2011) ), 90–97. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.11.107. |
[10] | R. Kajimoto, M. Nakamura, Y. Inamura, K. Kamazawa, K. Ikeuchi, K. Iida, M. Ishikado, N. Murai, H. Kira, T. Nakatani, S. Ohira-Kawamura, R. Takahashi, N. Kubo, W. Kambara, K. Nakajima and K. Aizawa, Status report of the chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1021: ((2018) ), 012030. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1021/1/012030. |
[11] | R. Kajimoto, M. Nakamura, Y. Inamura, F. Mizuno, K. Nakajima, S. Ohira-Kawamura, T. Yokoo, T. Nakatani, R. Maruyama, K. Soyama, K. Shibata, K. Suzuya, S. Sato, K. Aizawa, M. Arai, S. Wakimoto, M. Ishikado, S. Shamoto, M. Fujita, H. Hiraka, K. Ohoyama, K. Yamada and C.-H. Lee, The Fermi chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS at J-PARC, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80: ((2011) ), SB025. doi:10.1143/JPSJS.80SB.SB025. |
[12] | R. Kajimoto, K. Sato, Y. Inamura and M. Fujita, Instrumental resolution of the chopper spectrometer 4SEASONS evaluated by Monte Carlo simulation, AIP Conf. Proc. 1969: ((2018) ), 050004. doi:10.1063/1.5039301. |
[13] | R. Kajimoto, T. Yokoo, M. Nakamura, Y. Kawakita, M. Matsuura, H. Endo, H. Seto, S. Itoh, K. Nakajima and S. Ohira-Kawamura, Status of neutron spectrometers at J-PARC, Physica B 562: ((2019) ), 148–154. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2018.11.061. |
[14] | K. Lefmann and K. Nielsen, McStas, a general software package for neutron ray-tracing simulations, Neutron News 10: (3) ((1999) ), 20–23. doi:10.1080/10448639908233684. |
[15] | J.Y.Y. Lin, A. Banerjee, F. Islam, M.D. Le and D.L. Abernathy, Energy dependence of the flux and elastic resolution for the ARCS neutron spectrometer, Physica B 562: ((2019) ), 26–30. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2018.11.027. |
[16] | J.Y.Y. Lin, H.L. Smith, G.E. Granroth, D.L. Abernathy, M.D. Lumsden, B. Winn, A.A. Aczel, M. Aivazis and B. Fultz, MCViNE – an object oriented Monte Carlo neutron ray tracing simulation package, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 810: ((2016) ), 86–99. doi:10.1016/j.nima.2015.11.118. |
[17] | D.F.R. Mildner and R.N. Sinclair, Considerations for a cold moderator on a pulsed neutron source, Ann. Nucl. Energy 6: ((1979) ), 225–237. doi:10.1016/0306-4549(79)90076-8. |
[18] | K. Nakajima, Y. Kawakita, S. Itoh, J. Abe, K. Aizawa, H. Aoki, H. Endo, M. Fujita, K. Funakoshi, W. Gong, M. Harada, S. Harjo, T. Hattori, M. Hino, T. Honda, A. Hoshikawa, K. Ikeda, T. Ino, T. Ishigaki, Y. Ishikawa, H. Iwase, T. Kai, R. Kajimoto, T. Kamiyama, N. Kaneko, D. Kawana, S. Ohira-Kawamura, T. Kawasaki, A. Kimura, R. Kiyanagi, K. Kojima, K. Kusaka, S. Lee, S. Machida, T. Masuda, K. Mishima, K. Mitamura, M. Nakamura, S. Nakamura, A. Nakao, T. Oda, T. Ohhara, K. Ohishi, H. Ohshita, K. Oikawa, T. Otomo, A. Sano-Furukawa, K. Shibata, T. Shinohara, K. Soyama, J. Suzuki, K. Suzuya, A. Takahara, S. Takata, M. Takeda, Y. Toh, S. Torii, N. Torikai, N.L. Yamada, T. Yamada, D. Yamazaki, T. Yokoo, M. Yonemura and H. Yoshizawa, Materials and life science experimental facility (MLF) at the Japan proton accelerator research complex II: Neutron scattering instruments, Quantum Beam Sci. 1: ((2017) ), 9. doi:10.3390/qubs1030009. |
[19] | M. Nakamura and R. Kajimoto, General formulae for the optimized design of Fermi chopper spectrometer, JPS Conf. Proc. 1: ((2014) ), 014018. doi:10.7566/JPSCP.1.014018. |
[20] | H. Takada, K. Haga, M. Teshigawara, T. Aso, S. Meigo, H. Kogawa, T. Naoe, T. Wakui, M. Ooi, M. Harada and M. Futakawa, Materials and life science experimental facility at the Japan proton accelerator research complex I: Pulsed spallation neutron source, Quantum Beam Sci. 1: ((2017) ), 8. doi:10.3390/qubs1020008. |
[21] | A. Vickery, L. Udby, N. Violini, J. Voigt, P.P. Deen and K. Lefmann, A Monte Carlo simulation of neutron instrument resolution functions, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 82: ((2013) ), SA037. doi:10.7566/JPSJS.82SA.SA037. |
[22] | P. Willendrup, E. Farhi, E. Knudsen, U. Filges and K. Lefmann, McStas: Past, present and future, J. Neutron Res. 17: ((2014) ), 35–43. doi:10.3233/JNR-130004. |
[23] | P. Willendrup, E. Farhi and K. Lefmann, McStas 1.7 – a new version of the flexible Monte Carlo neutron scattering package, Physica B 350: ((2004) ), E735–E737. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2004.03.193. |
[24] | P.K. Willendrup and K. Lefmann, McStas (i): Introduction, use, and basic principles for ray-tracing simulations, J. Neutron Res. (in press). doi:10.3233/JNR-190108. |
[25] | C.G. Windsor, Pulsed Neutron Scattering, Taylor & Francis Ltd., London, (1981) . |




