Expanding a love and sex narrative generation mechanism using a coloring technique and conceptual dictionaries
Abstract
Love and sexuality are important themes in the generation of narratives, which is our research objective. In the development of tools to generate narratives, we consider robot-related technology that tells stories as an application of narrative generation. The purpose of this paper is to present prototyping systems that generate narrative expression based on the concepts of love, sex, and sexuality using a technique for narrative generation called “coloring.” The coloring technique in narrative generation is a group of methods through which a certain atmosphere is given to a story by interspersing words and language representations. Although there are various concrete methods in the coloring technique as one of several general narrative generation techniques, this paper proposes three methods related to love, sex, and sexuality: the use of noun, adjective, and adjective-verb conceptual dictionaries. We conducted several experiments using these coloring methods. Additionally, for system implementation, we utilized a narrative generation framework called “story techniques included in a story,” which was developed based on our concept of the automatic narrative generation game, s-expression in the Lisp programming language, and Minsky’s frame theory. In the future, these prototypes will serve as stepping stones for a system that generates narratives based on specific themes.
1.Introduction
In the field of artificial intelligence, story-generation studies have been ongoing for more than 50 years (Gervás, 2013). Gervás mentions the need for narratology in future story generation studies, and is developing story generation systems that aim to integrate the fields of narratology and artificial intelligence. We have likewise continued the study of narrative generation by introducing narratology from the 1990s and systematically collecting the results (Ogata, 2019, 2020). Explanation generation and unchiku (in-depth and unfamiliar knowledge) generation (Ono & Ogata, 2020) in narrative generation that we have conducted in the relationship between love and sexuality has also been conducted as a part of the narrative generation study introducing narratology. Love, sex, or sexuality, which we refer to as important themes in narratives. The themes of love and sex have been dealt with in the narratives of all periods and in all classical literature. In Japan, for example, Genji Monogatari (The Tale of Genji) focused on diverse sexual love between men and women, and Torikahebaya Monogatari (The Changelings) explored the theme of sexual reversal between men and women. Nanshoku Okagami (The Great Mirror of Male Love) boldly described sexual love between men. Thus, various expressions of sexuality exist in narratives. We also considered the relationship between games and narrative generation to develop an automatic narrative generation game. The game system is the background of the system proposed in this study. Because a game is a type of play, we refer to Groos’s (1901) book, which was cited by Natsume (2007a, 2007b) in his essay Bungaku-ron. Groos’s classification of plays considers the courtship behaviors of animals and arts expressing sexual love. Thus, the topics of love and sex have been explored in a wide range of fields.
Although our future plans of the systems proposed in this paper include a combination of robot technologies, the theme of love and sex between robots and humans has also begun to be considered. For instance, Bendel (2020) considered the possibility in areas such as the military, science, and art, where the use of robots for sexual purposes has not been sufficiently studied. The International Congress on Love & Sex with Robots, organized by Levy (2009), discussed themes of social positioning of love and sexuality in ethics, law, and various genres beyond the technological aspects. For instance, McCarthy and Leiman (2021) considered the necessity of laws pertaining to robots designed for sexual acts in the contexts of the care and treatment of functional disorders, assistance of the elderly and handicapped, resolution of anxiety in sexual orientation, and other topics. Thus, the themes of sexuality are important not only in fields of narrative and art but also in a social sense.
This study proposes systems that intersperse sexual information in narratives for robotic applications. We refer to this method of interspersing information into narratives as coloring (Ono, Kawai, & Ogata, 2022). Coloring is a technique that tints a narrative into a certain atmosphere. In this study, we used the technique of coloring a story with an atmosphere of sexuality. In particular, we propose systems that conduct more complex coloring using various methods by applying the abovementioned framework of an automatic narrative generation game.
Section 2 describes the theoretical background of this study. Section 3 explains the overall process of story generation proposed in this study, and Section 4 introduces an overview of the coloring technique and discusses its extension. Section 5 presents the experimental system implementation using the above coloring methods, and Section 6 summarizes the results and discusses future directions of research. Moreover, we discuss the application of the proposed story-generation mechanism to robot technology using coloring and other techniques. Finally, we conclude the paper in Section 7.
2.Theoretical backgrounds
This section shows definition of narrative (Section 2.1) and explains the theoretical background of this study (Section 2.2–2.3). The theoretical background of this study is based on (1) automatic story generation games (Section 2.2), (2) s-expressions in the Lisp programming language (Section 2.3), and (3) frame representations (Section 2.4).
2.1.Narrative, story and explanation
The word narrative has many meanings and Genette (1985) has isolated three meanings for mixed narratives. Here, a narrative is a structured grouping of multiple events. A narrative also has events that took place in it and a structure for telling them. In this paper, the chronological sequence of events in a narrative is called a story. A narrative also includes plots that indicate how the story is told, such as recollections and omissions. In the method proposed here, the temporal flow of the story as perceived by the recipient of the narrative can be disrupted by inserting an explanation that describes the nature of a particular matter. However, since no operation is performed to rearrange the temporal sequence of events, the term story is used in this paper.
2.2.Automatic narrative generation game
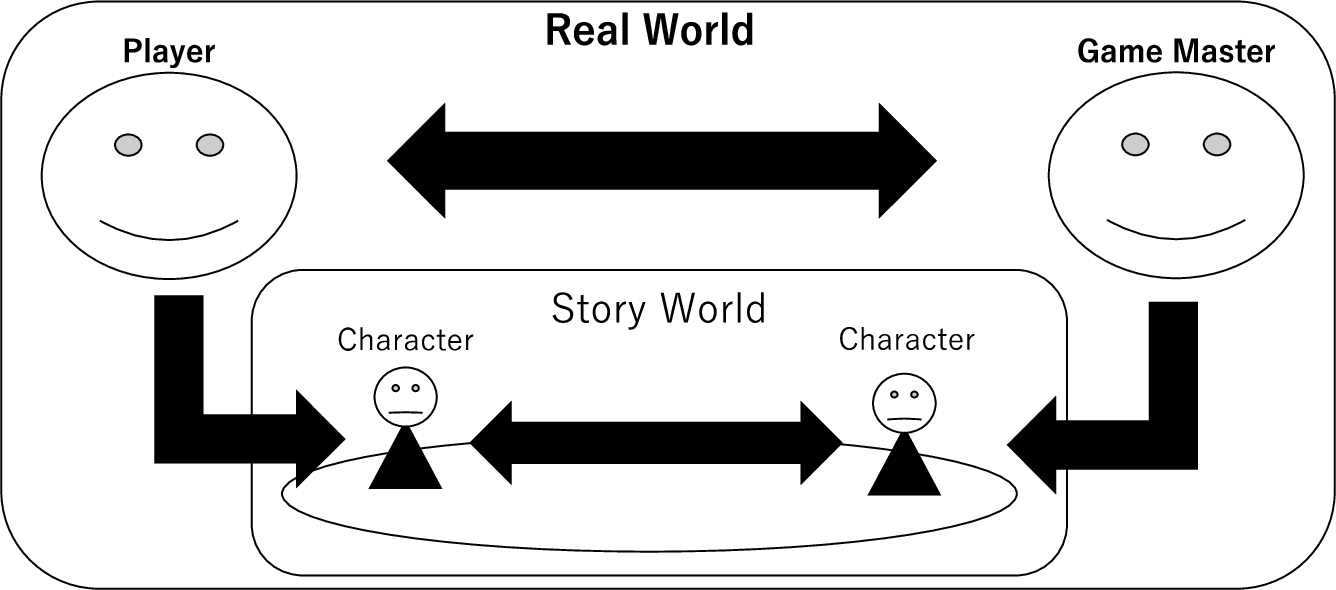
The automatic story generation game was developed by Ono and Ogata (2017, 2018, 2021a) using the Table-talk Role Playing Game (TRPG). The TRPG is an analog game that originated as a role-playing game, a genre of video games. As shown in Fig. 1, this game includes players and a gamemaster. Each player plays the role of a character in a story, and the game is played mainly through dialogue.
The gamemaster prepares a story that progresses according to game’s rules. The prepared story often has gaps in which players can intervene, and their actions can bring surprise to the gamemaster that transforms the story’s framework. Consequently, the gamemaster’s expected outcome may transform to something different through changes that range from trivial to fundamental.
Figure 2 shows the proposed model, focusing on “the story as a generation system” (Ono & Ogata, 2021b, 2021c). The author in this figure is a mechanism located outside the proposed model, and is responsible for extending or editing the tree structure of the story. The characters in this model are data inside the story that extend or edit the tree structure generated by the author, sometimes to the extent of breaking the structure. In addition, when there several characters are present, each has different characteristics, and they may overwrite each other’s generated results.
Fig. 1.
Game structure of a table-top role playing game.
In this model, the story generation mechanism is embedded in the story’s structure. The model is also influenced by the role-playing mechanic and the Lisp s-expressions discussed in the following section. This coloring technique works within the framework of “the story as a generative system.” In other words, this study proposes a method of story generation that embeds coloring techniques to spread sexual terms and representations in the framework of “the story as a generation system.”
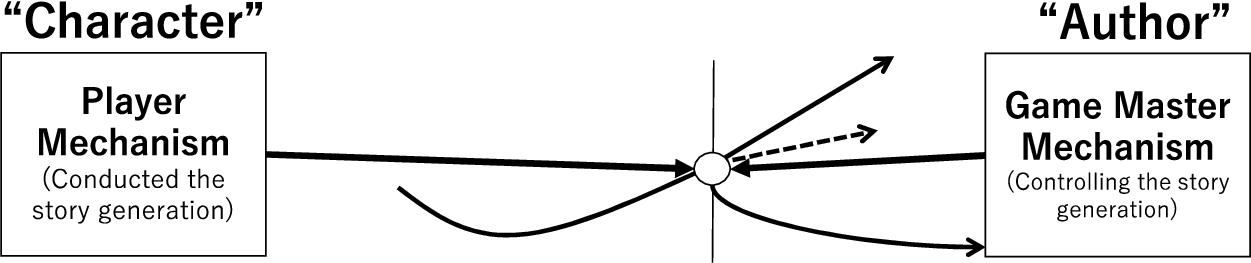
Because the automatic story generation game is a system that models the player and game master in a TRPG, the two types of subjects form key modules, interact with each other, and generate stories. Figure 3 shows a diagram of an automatic story-generation game with the keyword “the story as a generation system.” In the proposed model, the characters correspond to the players and the author is equivalent to the game master.
Fig. 2.
Story generation method using techniques included in a story.
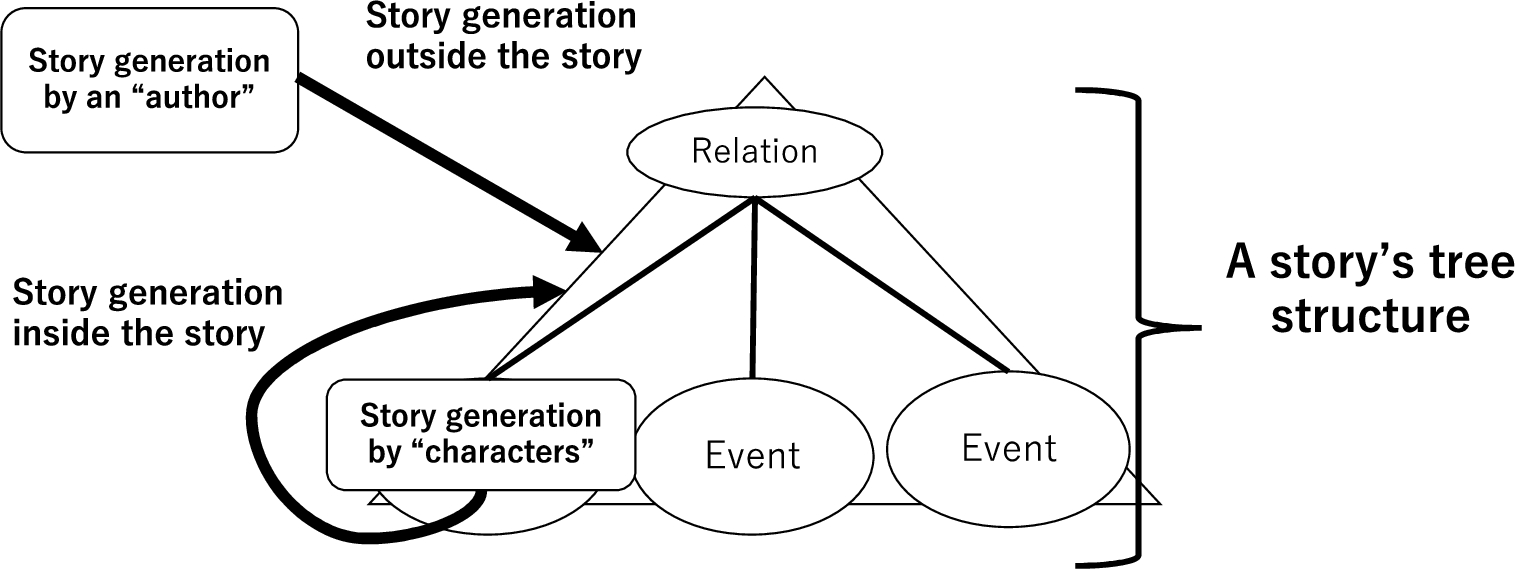
Fig. 3.
Author and characters making a story in an automatic narrative generation game.
2.3.S-expression in Lisp
Lisp is a functional programming language that was developed by John McCarthy in 1958. The common version of Lisp used for system development is an integrated form of the language’s diverse dialects. One major characteristic of Lisp is the s-expression, which is a way of expressing data using a list structure or set of symbols. In most programming languages, data such as values and characters are classified as types according to their categories, whereas functions are treated as procedures, and are not considered a data type. However, as shown in Fig. 4, a list expressed as an S-expression can be treated as a function or datum depending on how it is evaluated. More specifically, as shown in Fig. 5, if the symbol of the first element in the list is associated with a procedure, the expression can be evaluated as a function. The characters represented in the frame representation described in Section 2.3 have procedures related to story generation, whereas the characters function as a story generation system based on certain conditions. This mechanism is useful for representing daemons, which are described in Section 2.4, and in the proposed system the characters are both an element of the story and driven as a story-generating mechanism.
2.4.Frame representation
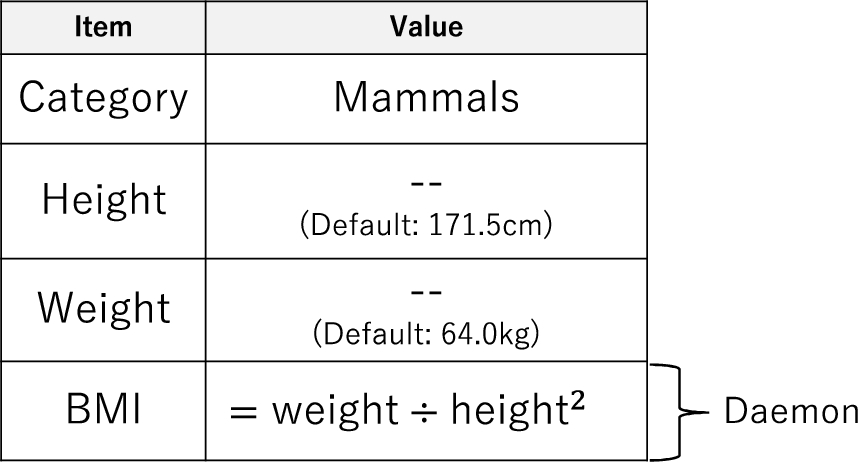
Frame representation is a method of knowledge representation proposed by Minsky (1974) through which general information about an object is described as a framework. Each frame has one or more slots to describe information, with each slot being assigned a concrete value or procedure to obtain a concrete value, called a daemon. As shown in Fig. 6, a concrete value is a property that an object may possess. In contrast, a daemon operates based on certain conditions to assign specific values to slots. For example, when the weight value in Fig. 6 changes, a daemon divides the weight by the square of the height and assigns the result to the BMI slot. In the model proposed in this paper, the characters in a story have attributes that represent their characteristics, and one or more characters have a technique for story generation. The daemon in frame representation is used to express the functions of the player as indicated in Section 2.1.
Fig. 4.
Example of S-expression.
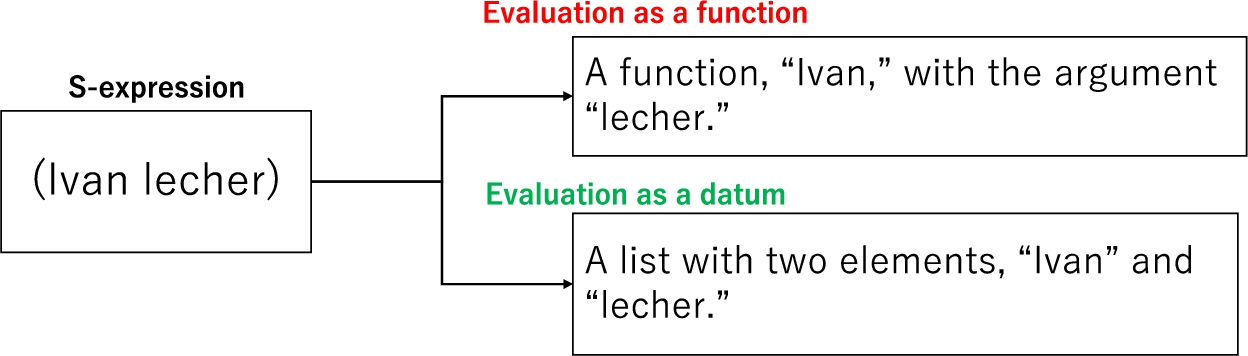
Fig. 5.
Example of evaluated S-expression as a function.
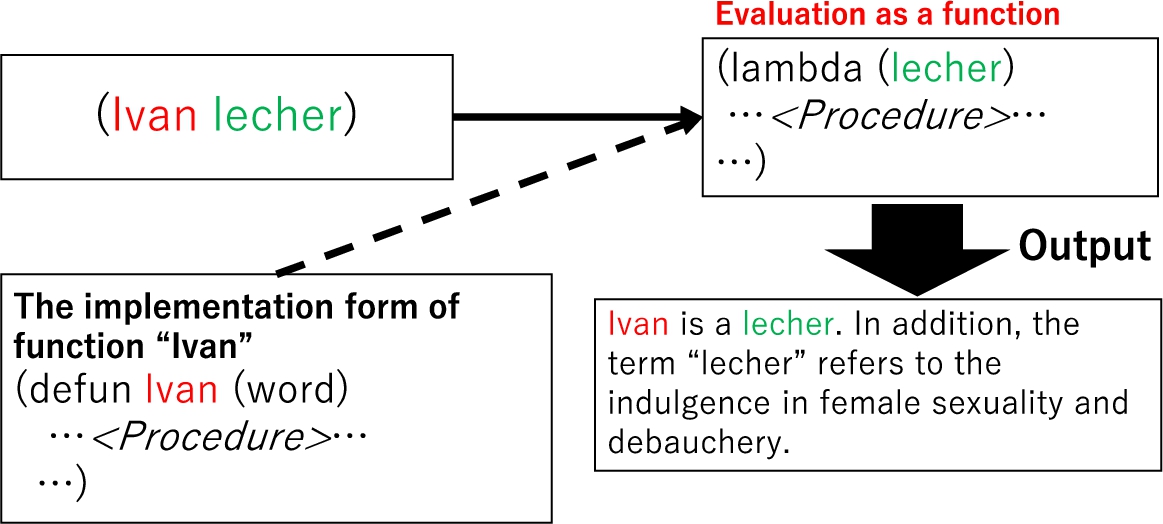
Fig. 6.
Daemon in a frame representation (a human).
3.The flow of story generation
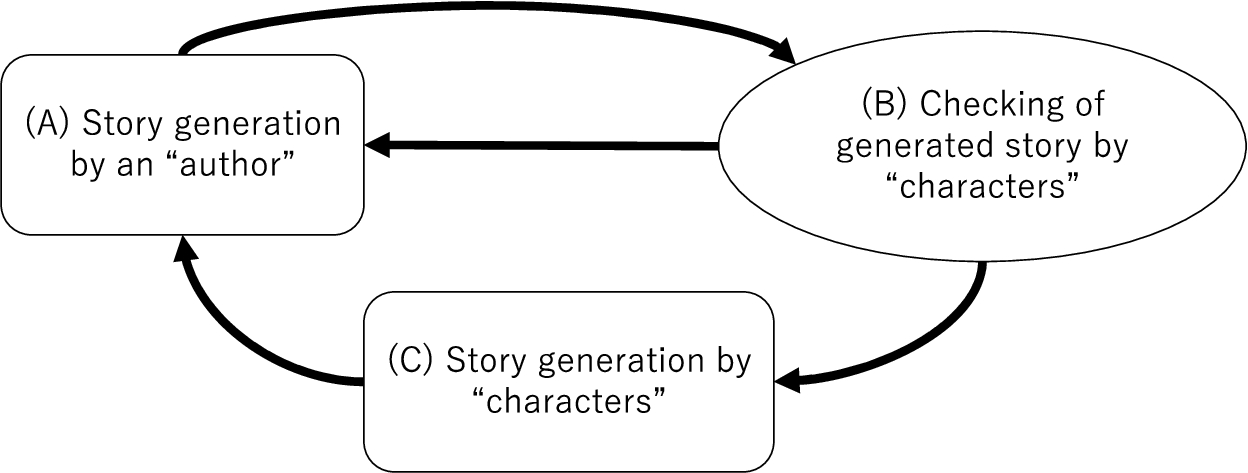
Next, we explain the flow of story generation in the proposed model. The model generates stories in the order shown in Fig. 7. The following subsections describe these three steps and their order.
Fig. 7.
Story generation cycle in the proposed model.
3.1.A basic mechanism for story generation
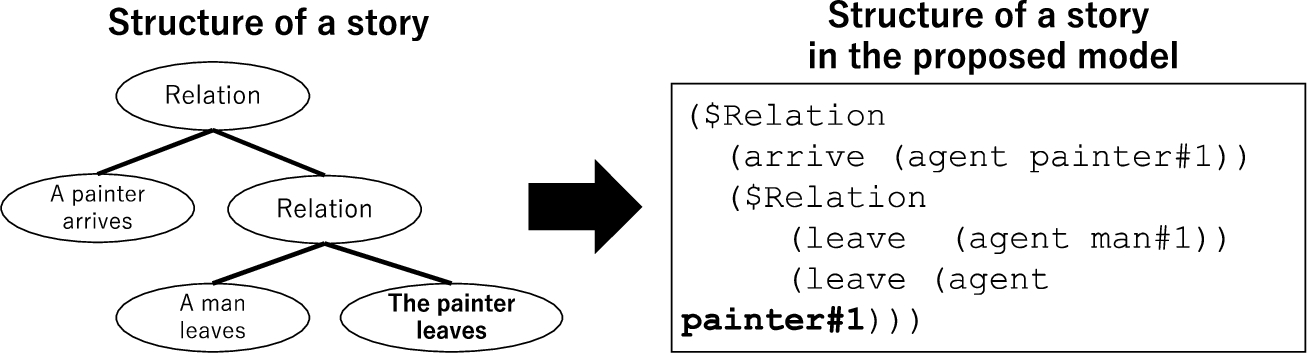
The tree structure shown in Fig. 8 represents the structure and expansion of a story. This structure follows the method in the Integrated Story Generation System (INGS) by Ogata (2019; 2020). Each middle node represents a relationship (e.g., a cause-effect relationship) that connects event concepts, and each terminal node represents an event concept in the story. The tree structure of a story inside the system is represented by a hierarchical list, as shown in Fig. 9.
Fig. 8.
Story generation process by expanding and transforming a story structure.
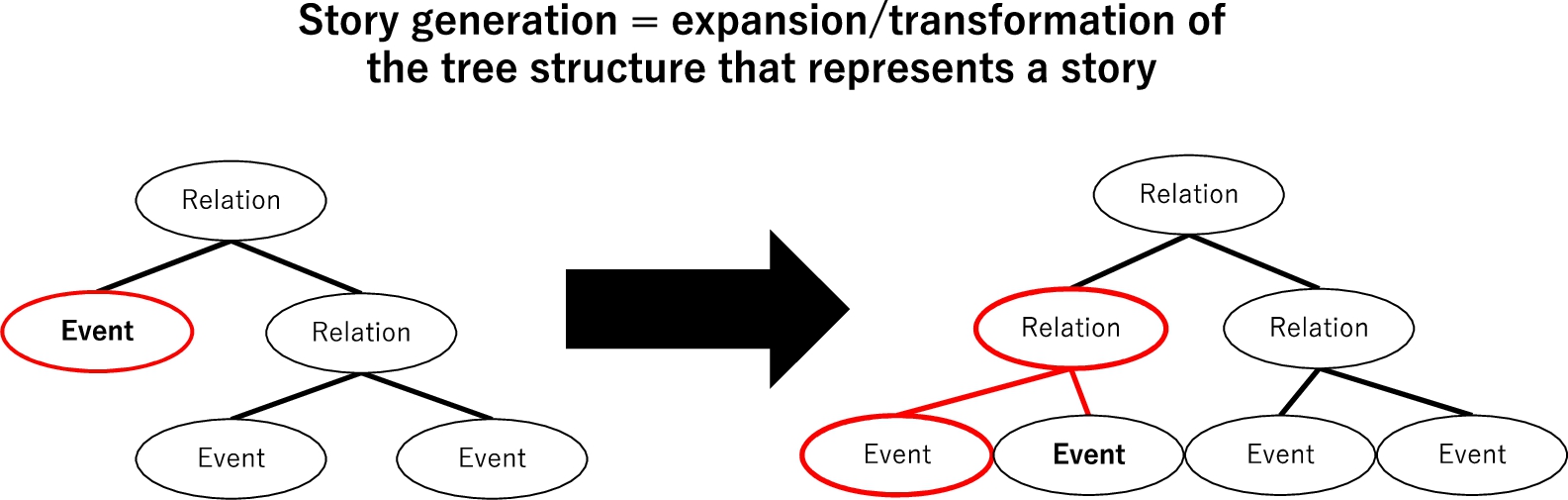
Fig. 9.
List structure that represents a story.
3.2.Story generation by an “author”
As shown in Fig. 8, story generation corresponds to the extension or transformation of a story-tree structure. We propose diverse story techniques (Ogata, 2019; 2020) as procedures. The coloring technique, introduced in Section 4 of this paper, is one such story technique. In this study, we treated coloring as a technique used by characters. In addition, the expansion and editing methods of a story by the author were not treated as a black box in this study. In the example shown in Section 5, “story generation by the author” shows story generation by characters by fixing certain events to be inserted in specific positions in the story.
In this example, we began the process from a stage in which the next story has already been generated. This story was prepared by cutting a segment of the story generation result using KOSERUBE (Imabuchi & Ogata, 2013). All coloring methods were used in this system. (In this paper, our system uses only Japanese language. Therefore, we attached Japanese pronunciation and translated sentences (English) for Japanese words and sentences except for long sentences).
従兄が花園で遊びに出かけた。 [Itoko ga hanazono de asobi ni dekaketa.] たわけ者が飛出しナイフ を窓ぎわに置いた。 [Tawakemono ga tobobidashi-naifu wo madogiwa ni oita.] イワンという名前の画 家が出国した。 [Ivan to iu namae no gaka ga shukkokushita.] イワンが冒険をたわけ者と競争した。 [Ivan ga bouken wo tawakemono to kyousoushita.] たわけ者が暴れた。 [Tawakemono ga abareta.] イワンに傷が付いた。[Ivan ni kizu ga tsuita.] たわけ者がイワンに競争で負けた。 [Tawakemono ga Ivan ni kyousou de maketa.] イワンが魔法の杖を利用した。 [Ivan ga mahou no tsue wo riyousita.] 魔法の杖が砕けた。 [Mahou no tsue ga kudaketa.] [The cousin went outside to play in the flower garden. An idiot jumped out and a knife was placed on the window sill. The painter, Ivan, left the country. Ivan competed with the wrongdoer for the adventure. The ruffian went on rampage. Ivan received a scar. The trickster defeated Ivan in a competition. Ivan used his magic wand. The magic wand shattered.]
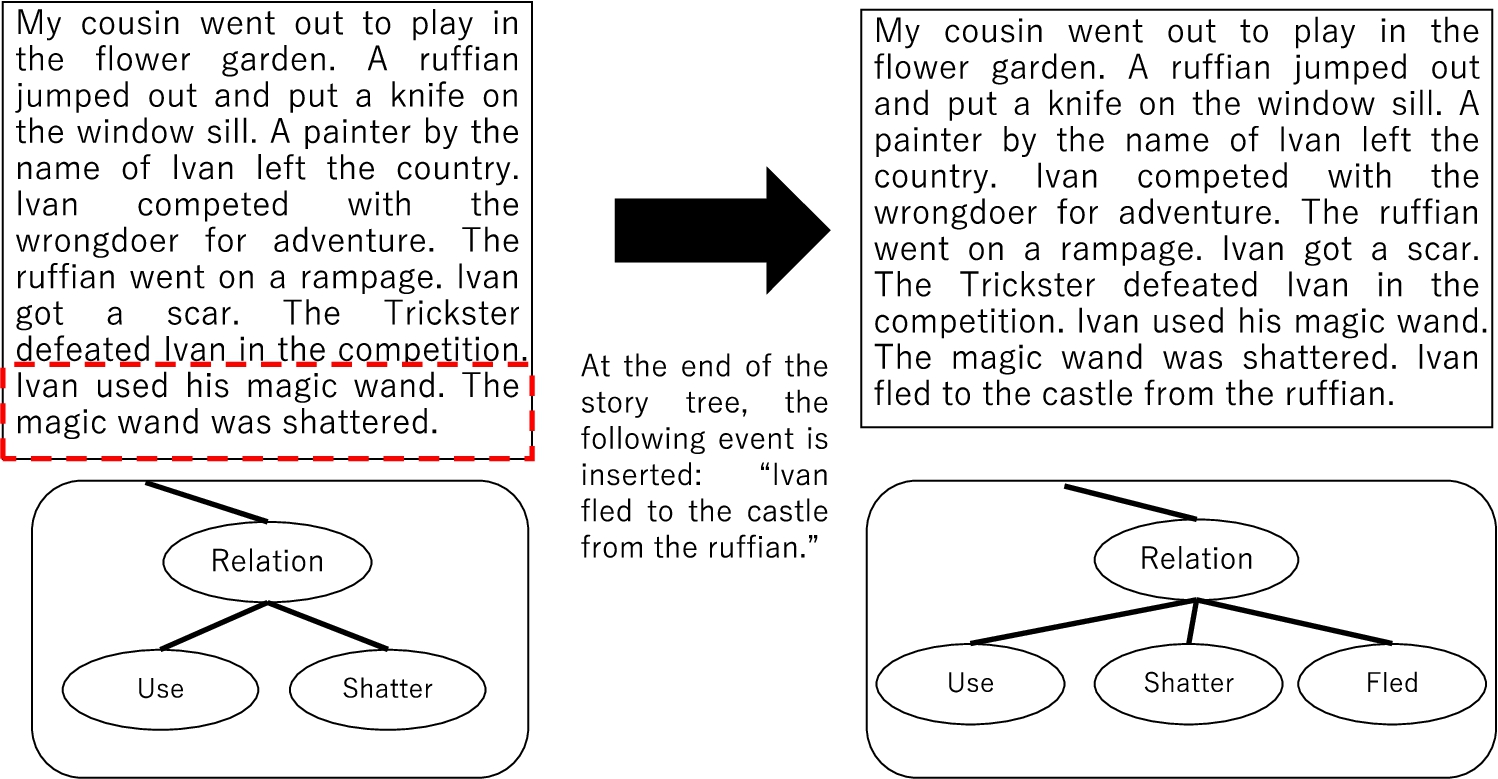
In this example, the story generation mechanism by the author appends the following four events in sequence, one per cycle, to the end of the story: 「イワンがたわけ者から城に逃げた。」 [Ivan ga tawakemono kara shiro ni nigeta.; “Ivan fled to the castle from the devil.”], 「メロスという名前の男が言い張 った。」 [Meros toiu namae no otoko ga iihatta.; “A man named Meros insisted’.”], 「メロスが報酬を親 王に要求した。」 [Meros ga houshu wo shinou ni youkyu shita.; “Meros demanded a reward from the king.”], 「親王がイワンと会った。」 [Shinou ga Ivan to atta; “The king met with Ivan.”]. Figure 10 shows that, in the first cycle, the first event is inserted into the story.
Fig. 10.
Story generation by an author.
3.3.Checking the generated story by characters
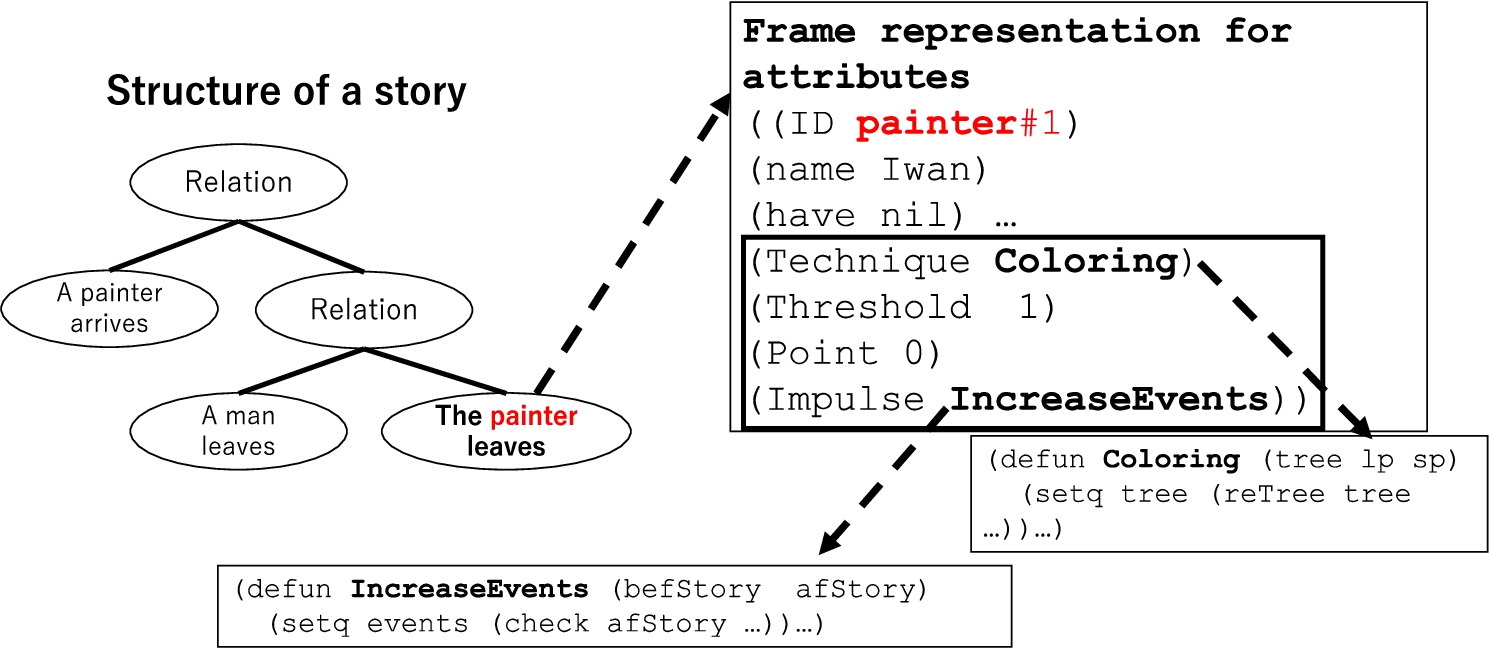
In the proposed model, a character may have information regarding story generation in addition to their personal attributes. In Fig. 11, the four slots enclosed by the frame contain information concerning story generation, whereas the other slots hold the character’s attributes. The definitions of the four slots are as follows:
Technique: A procedure to extend or edit a character’s story.
Threshold: The driving condition of the story technique was compared with the attribute value.
Point: The number of times the impulse condition is satisfied. When the threshold is satisfied, the attribute value is set to 0.
Impulse: A procedure used to check the expansion of and edits to the story structure. Each type of procedure is associated with a condition. If the expansion or edit satisfies this condition, the value is incremented.
Fig. 11.
Character frame in a story structure.
A character with the story technique has the frame shown in the following description. Although other characters are present in the story, the story generation presented in Section 3 includes only Ivan as a character with the story technique. This character drives the coloring of sexuality whenever an additional event occurs in the story.
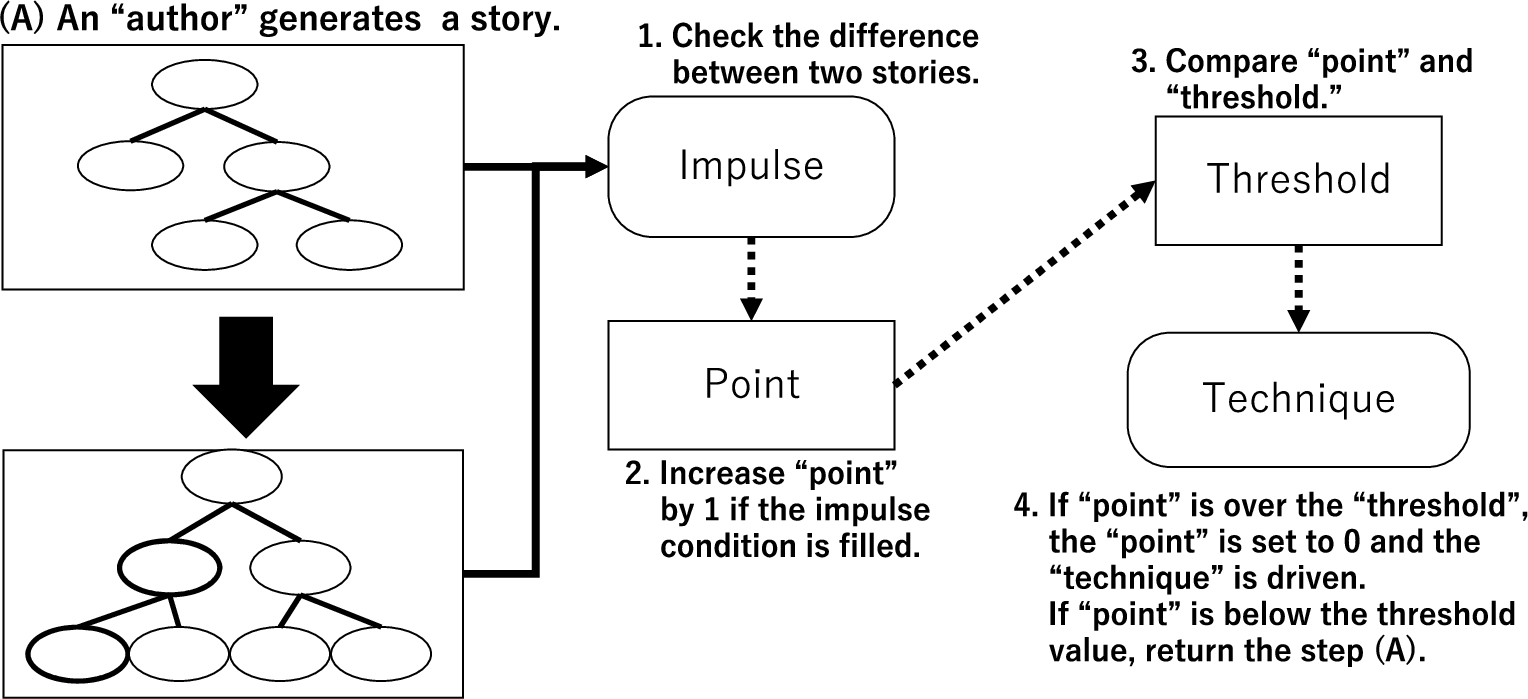
Fig. 12.
Relationships among impulse, point, threshold, and technique.
((ID painter#1) (name Ivan) (have nil) …
(Technique Coloring) (Threshold 1) (Point 0) (Impulse
IncreaseEvents))
3.4.Story generation by “characters”
The driven story technique uses one node of the tree structure as an argument to perform story generation, as shown in Fig. 13. The selected nodes are limited to those that can be extended or edited by the driven story technique, and any one of these nodes may be selected. In this study, characters employed the coloring technique described in Section 4. By using story techniques other than coloring, we can develop a story generation different from the one described here.
After the author generates the story, the characters drive the procedure stored in the stimulus to check the story expansion or edits, as shown in Fig. 14. In this case, the number of events in the story increases by 1 because of the author’s expansion. Therefore, the condition of the procedure stored in the stimulus is satisfied, and the attribute of Ivan likewise increases by 1. The threshold and attribute values are then compared. If the two values are equal, the story technique is used. In this case, the technique in question is a coloring related to sexuality, applied to Ivan himself. This cycle is repeated four times. Figure 15 shows the story before and after this series of processes. Here, bold text denotes events added to the story, whereas underlined text represents the results of coloring.
Fig. 13.
Driving mechanism of a story technique.
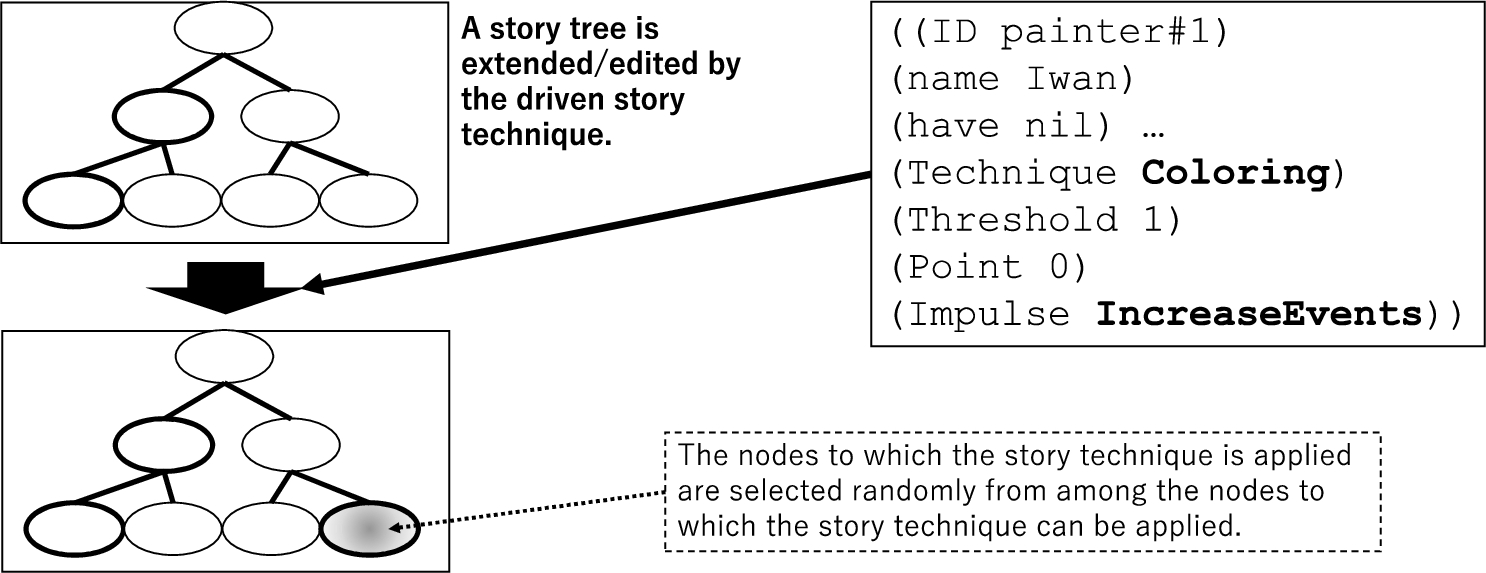
Fig. 14.
Checking the change in a story by characters.
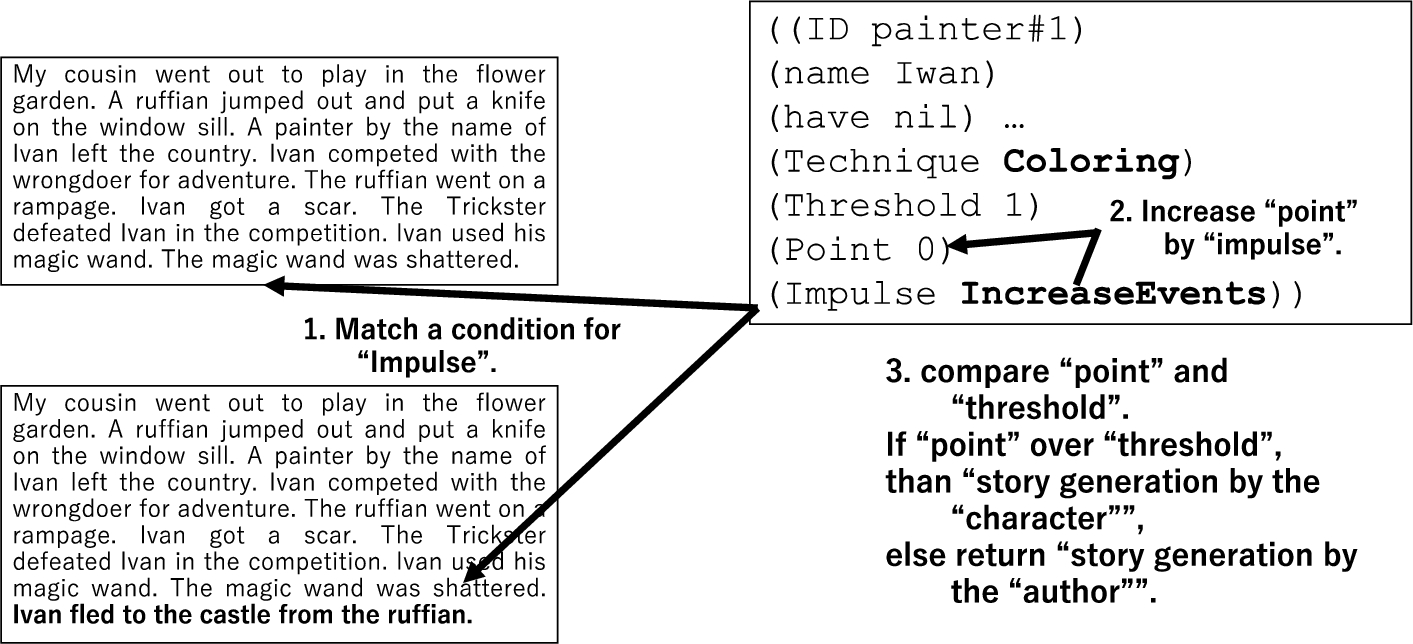
Fig. 15.
Comparison between the original and colored stories.

4.Methods of coloring
This section introduces the proposed coloring technique. The different methods in this technique are as follows: (1) In Section 4.1, we introduce a coloring method based on a previous study (Ono, Kawai & Ogata, 2022), which uses the noun concepts of sexuality. (2) In Section 4.2, we focus on a method that use adjectives and verbs. (3) In Section 4.3, we consider a coloring method using other stories. Moreover, (4) In Section 4.4, we extend a coloring method that use adjectives and verbs.
4.1.Coloring method using noun concepts
The coloring technique is a narrative technique proposed by us based on a method in novels described by Shimada (2009). The coloring technique is a narrative technique proposed by us based on a method in novels described by Shimada (2009). For example, Shimada quotes I’m Sorry, Mama by Natsuo Kirino11 as follows.
“アダムは不安そうな声を出した。アイ子は構わず、アダムの下着を剥がした。肉厚の体が現れた。
胸毛が渦巻き、臍を取り巻き、下腹部まで伸び、股間を通って背中まで伸びている。獣みたいだ。
アイ 子は可笑しくなって、アダムの禿頭の上に肉塊を載せた。
「ほら、似合う。あんたは獣だから」
アダムは肉から流れる血をたらたらと眉間に垂らしながら笑った。見る見るうちに、ずんぐりと埋も
れていたペニスが勃起した。”
[Adam sounded worried. Aiko didn’t care and pulled off Adam’s underwear. A thick, fleshy body was revealed. Chest hair swirled around his navel, extending down to his lower abdomen, through his crotch and down his back. He looks like a beast. Aiko found it funny and placed the mass of flesh on Adam’s bald head.
‘See, you look good. You’re a beast.’
Adam laughed, blood dripping from his flesh onto his brow. As he watched, his sloppily buried penis became erect.]
I’m sorry, mama, pp.90–91, (Kirino, 2007)
In this instance, the lumps of flesh and flowing blood are treated as symbols of bestial life, thereby giving the reader the impression of a wild sexual love affair from the text. The coloring we propose not only deals with impressions based on certain colors, but also with elements that symbolize certain impressions.
Coloring in the field of Love and Sex with Robot has a double meaning: it means not only coloring the story with a certain mood, but also coloring it with sexual desire. In the field of Love and Sex with Robot, coloring has a double meaning: it means not only coloring the story with a certain mood, but also coloring it with sexual desire.
In Japanese, the character for color not only refers to the visual stimulus color, but may also refer to sexual desire. For example, the Japanese word irogurui (色狂い) means “lecher.” Iro (色) is color and gurui (狂い) is madness. Irogurui (色狂い) means infatuation for color. However, this iro (色) is not color, but sexual desire.
As a concrete attempt to color, we implemented a method based on the concurrence relationships of noun concepts (Ono, Kawai & Ogata, 2022). We used concepts stored in the noun conceptual dictionary of the INGS (Ogata, 2015). Figure 16 presents an outline of the coloring technique. In coloring, the event concept in the story structure is used as an argument. A noun concept related to sexuality is given to a character, and an explanation of the noun concept is inserted into the story. Figure 17 shows an example of the coloring technique. The algorithm is as follows:
Fig. 16.
Coloring process using noun concepts related to love and sex.
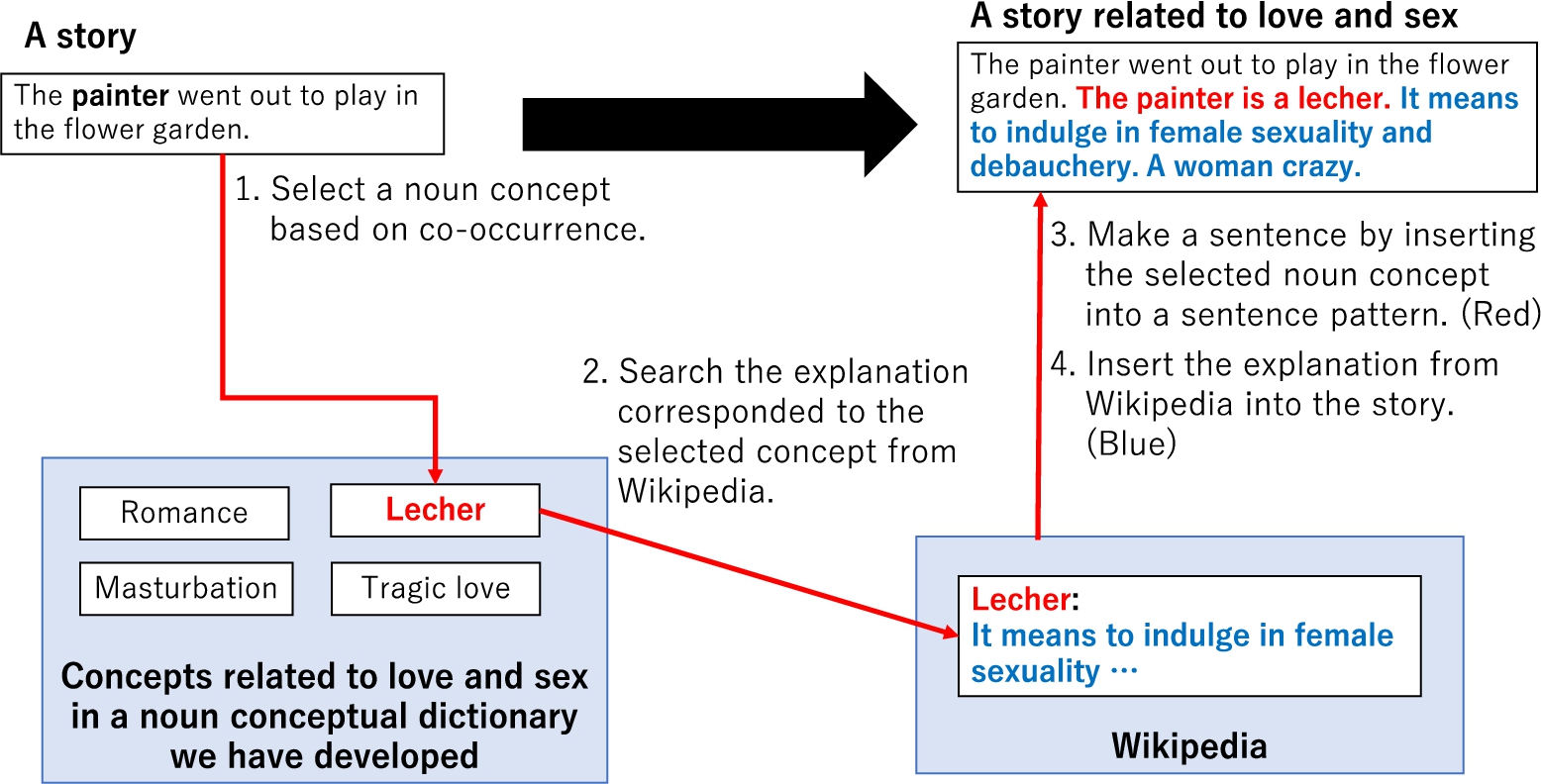
(1) This technique refers to the character in the event concept of an argument. The technique obtains concurrence information between the characters and all noun concepts related to sexuality shown in Table 2 in Ono, Kawai, & Ogata (2022), and selects the noun concept with the highest concurrence value. If the highest value is shared by multiple concepts, the selection is made based on the order in which the concepts are stored.
(2) This technique provides an explanation corresponding to the selected noun concept. This explanation is obtained from web encyclopedias and dictionaries, including Wikipedia (Japanese version, https://ja.wikipedia.org/) and Kotobank (https://kotobank.jp/). All information regarding articles corresponding to the noun concepts in Table 2 (Ono, Kawai, & Ogata, 2022) is pre-obtained and prepared as a knowledge base.
(3) This technique generates sentences by applying the selected noun concept to a sentence pattern. The generated sentences are concatenated immediately after the event concept is taken as an argument.
(4) This technique inserts the obtained explanation immediately after the sentences are generated by the noun concept.
Fig. 17.
Example of the coloring technique.

4.2.Coloring method using adjectives and adjective verbs
This method, which serves as the predecessor of the method described in Section 4.4, selects a single color, followed by adjectives from the color image scale (Kobayashi, 1981). For each selected adjective or adjectival verb, a noun concept related to sexuality is added to the attribute of the person to be colored. The physical part to be selected is determined randomly. The varying attribute is the appearance slot.
This implementation of the coloring technique can be extended depending on the data used and the way in which they are combined into the story. Of the methods presented here, we focus on combining adjectives and adjective verbs with colors. The coloring was prototyped for story generation with multiple characters, as described in Section 5.
This type of coloring method rewrites the characters’ attribute frames. In particular, it colors the characters using the adjective and adjectival verb concepts based on the color image scale22 (Kobayashi, 1981) – a scale that summarizes the common image of a color. The colors are plotted in two-dimensional space with a warm-cool horizontal axis and a soft-hard vertical axis. All modifiers, such as adjectives and adjectival verbs, are plotted in the same space. This allows us to identify the type of image evoked by a particular color or color scheme. We used this information to study how to apply colors that evoke specific images. For example, for the coloring of blue, we used adjectives and adjectival verbs that are located at the same coordinates as blue, and color schemes that contain blue.
Coloring by modifier concepts is performed by specifying a color. The input is a single-event concept, and the procedure rewrites the content of the attribute frame of the person (agent) in the input. Specifically, it adds a modifier concept for a specified color to the slot of the attribute frame. Events based on modifier concepts are then added to the tree structure of the story. Here, we use the modifiers “cool,” “clean,” and “pure” for blue. These are adjectival concepts that correspond to image words on the cool side of the color image scale. Figure 18 shown an example of coloring by modifier concepts.
Fig. 18.
Example of the coloring method using adjectives and adjectival verbs.

4.3.Coloring method by exchanging of elements in a story
Although coloring is usually achieved by inserting data to be used in the story’s structure, we propose a method that replaces existing elements in a story with different data. The characters, locations, and objects in the story are replaced with other words. We obtained elements for this method from our analysis of the Dōjōji legend (Kawai, Ono, & Ogata, 2021, 2022). The legend of Dōjōji is a love story originally written in Dainippon Hokkekyo Genki (Miraculous Tales of the Lotus Sutra from Japan), which has been handed down to the present in various forms, such as nō, ningyō-jōruri, and kabuki dance. This legend tells the story of a Buddhist monk named Anchin, who breaks his promise to a woman named Kiyohime on a visit to Kumano; consequently, Kiyohime, transformed into a snake by her anger, burns down the bell of the Dōjōji temple where he had fled.
A work may be specified for coloring by element substitution. The input is a single-event concept, and the procedure replaces the person (agent) and location in the input event concept with the components of the specified work. Here, the legend of Dōjōji was specified as the data for coloring, and the story’s main characters (Anchin and Kiyohime) as well as the locations of Dōjōji and Kumano were used as substitution elements.
The objective is to create simple sentence representations that modify the characters, locations, and objects that appear in the legend of Dōjōji. This system uses formulaic sentences in its sentence representation. Table 1 shown the formulaic sentences. The formulation is based on an analysis of the legend of Dōjōji presented by Kawai et al. (2022). Figure 19 shown an example of Coloring method by exchanging of elements in a story.
Table 1
Sentences for coloring method by exchanging of elements in a story
| Type | Element | Sentence |
| Character | 安珍 [Anchin] | ・老(いた)僧と一緒にいた安珍 [oita sō to issho ni ita Anchin; Anchin with an old monk] |
| ・清姫に一目惚れされた安珍 [Kiyohime ni hitomebore sareta Anchin; Anchin falls in love at first sight with Kiyohime] | ||
| ・清姫に追いかけられた安珍 [Kiyohime ni oikakerareta Anchin; Anchin chased by Kiyohime] | ||
| 清姫 [Kiyohime] | ・複数の侍女と暮らしていた清姫 [fukusu no jijo to kurashite ita Kiyohime; Kiyohime lived with several maidens] | |
| ・安珍に一目惚れした清姫 [Anchin ni hitomebore shita Kiyohime; [Kiyohime fell in love with Anchin at first sight] | ||
| ・安珍を追いかけた清姫 [Anchin wo oikaketa Kiyohime; Kiyohime chased after Anchin] | ||
| ・蛇に変身した清姫 [hebi ni henshin shita Kiyohime; Kiyohime transformed into a snake] | ||
| ・安珍に裏切られて蛇になった清姫 [Anchin ni uragirarete hebi ni natta Kiyohime; Kiyohime became a snake after being betrayed by Anchin] | ||
| 老(いた)僧 [oita sō; old monk] | ・安珍と一緒にいた老(いた)僧 [Anchin to issho ni ita oita sō; an old monk who was with Anchin] | |
| ・清姫に追いかけられた老(いた)僧 [Kiyohime ni oikakerareta oita sō; an old monk chased by Kiyohime] | ||
| 高席の僧 [kōseki no sō; monk of high-rank] | ・道成寺に暮らしていた高席の僧 [Dōjōji ni kurashiteita kōseki no sō; a monk of high-rank who lived in Dōjōji Temple] | |
| ・法華経を唱えた高席の僧 [hokekyō wo tonaeta kōseki no sō; a monk of high-rank who chanted the Lotus Sutra] | ||
| 通りすがりの人1 [tourisgari no hito 1; passerby 1] | ・安珍が帰ったことを清姫に伝えた通りすがりの人1 [Anchin ga kaetta koto wo Kiyohime ni tsutaeta tourisugari no hito 1; a passerby (1) who told Kiyohime that Anchin had left] | |
| ・清姫に問い掛けられた通りすがりの人1 [Kiyohime ni toikakerareta tourisugari no hito 1; a passerby (1) who was questioned by Kiyohime] | ||
| 通りすがりの人2 [tourisgari no hito 2; passerby 2] | ・清姫が追いかけて来たことを安珍に伝えた通りすがりの人2 [Kiyohime ga oikaketekita koto wo Anchin ni tsutaeta tourisugari no hito 2; a passerby (2) who told Anchin that Kiyohime had followed him] | |
| 蛇 [hebi; snake] | ・清姫が変身した蛇 [Kiyohime ga henshin shita hebi; a snake that Kiyohime transformed] | |
| ・大きな鐘に巻き付いた蛇 [ookina kane ni makitsuita hebi; a snake coiled around a large bell] | ||
| ・安珍を焼き殺した蛇 [Anchin wo yaki koroshita hebi; a snake that burned Anchin to death] |
Table 1
(Continued)
| Type | Element | Sentence |
| Location | 清姫の家 [Kiyohime no ie; Kiyohime’s home] | ・清姫が住んでいる家 [Kiyohime ga sundeiru ie; a house where Kiyohime lives] |
| ・安珍が泊まった清姫の家 [Anchin ga tomatta Kiyohime no ie; Kiyohime’s house where Anchin stayed] | ||
| 清姫の部屋 [Kiyohime no heya; Kiyohime’s room] | ・清姫がいる部屋 [Kiyohime ga iru heya; a room where Kiyohime lives] | |
| ・清姫が泣いた部屋 [Kiyohime ga naita heya; a room where Kiyohime cried] | ||
| 道成寺 [Dōjōji; Dōjōji Temple] | ・安珍と老(いた)僧が逃げ込んだ道成寺 [Anchin to o(ita) sō ga nigekonda Dōjōji; Dōjōji Temple where Anchin and the old monk escaped] | |
| ・大きな鐘がある道成寺 [ookina kane ga aru Dōjōji; Dōjōji Temple with a large bell] | ||
| ・複数の僧と高席の僧がいる道成寺 [fukusu no sō to kōseki no sō ga iru Dōjōji; Dōjōji Temple with several monks and a monk in high position] | ||
| ・蛇に鐘を焼かれた道成寺 [hebi ni kane wo yakareta Dōjōji; Dōjōji Temple bell burned by a snake] | ||
| ・鐘の中で安珍が焼き殺された道成寺 [kane no naka de Anchin ga yakikorosareta Dōjōji; Dōjōji Temple where Anchin was burned to death in the bell] | ||
| 桐目川 [Kirimegawa; Kirime River] | ・熊野の桐目川 [Kumano no Kirimegawa; Kirime River in Kumano] | |
| ・清姫が安珍を追いかけて渡った桐目川 [Kiyohime ga Anchin wo oikakete watatte Kirimegawa; the Kirime River that Kiyohime chased Anchin across] | ||
| 熊野 [Kumano] | ・清姫が住んでいる熊野 [Kiyohime ga sundeiru Kumano; Kumano where Kiyohime lives] | |
| ・安珍が目指していた寺がある熊野 [Anchin ga mezashiteita tera ga aru Kumano; Kumano, where the temple Anchin was aiming for is located] | ||
| ・安珍が清姫に嘘の約束をした熊野 [Anchin ga Kiyohime ni uso no yakusoku wo shita Kumano; Kumano where Anchin made a false promise to Kiyohime] | ||
| Object | 岩 [iwa; rock] | ・清姫が座って休んだ岩 [Kiyohime ga suwatte yasunda iwa; the rock where Kiyohime sits and rests] |
| ・清姫が座って炎を吐いた岩 [Kiyohime ga suwatte honoo wo haita iwa; the rock where Kiyohime sits and spit fire] | ||
| 鐘 [kane; bell] | ・蛇が巻き付いた道成寺の鐘 [hebi ga makitsuita Dōjōji no kane; A bell of Dōjōji Temple with a snake coiled around it] | |
| ・蛇が焼いた道成寺の鐘 [hebi ga yaita Dōjōji no kane; A bell of Dōjōji Temple burned by a snake] | ||
| ・蛇が安珍を焼き殺した道成寺の鐘 [hebi ga Anchin wo yakikoroshita Dōjōji no kane; A bell of Dōjōji Temple where the snake burned Anchin to death] | ||
| 夢 [yume; dream] | ・高席の僧が見た夢 [kōseki no sō ga mita yume; A dream of a monk of high-rank] | |
| ・安珍と清姫が登場する夢 [Anchin to Kiyohime ga tojō suru yume; A dream in which Anchin and Kiyohime appear] | ||
| 法華経 [Hokekyō; Lotus Sutra] | ・僧達が唱えた法華経 [sō tachi ga tonaeta hokekyō; The Lotus Sutra as chanted by the monks] | |
| ・安珍と清姫が救われた法華経 [Anchin to Kiyohime ga sukuwareta hokekyō; the Lotus Sutra that Anchin and Kiyohime saved] |
Fig. 19.
Example of the coloring method that exchanges elements in a story.

4.4.Coloring method using colors in a picture
The basic form of this method is equivalent to the adjective/pronoun-based coloring method described in Section 4.2. However, the number of specified colors is increased. To increase the number of colors and incorporate color imagery related to sexuality, multiple colors were used based on images of downtown areas in Japan. In addition, standardized text was prepared to express the mood of the images in the text.
To represent sexuality, we examined how we could approach coloring using adjectives. Here, we take the color codes that make up a particular image and compare the results with the color image scale.
Although this method selects adjectives and adjectival verbs from values with perfectly matching color codes, it does not necessarily match the color codes obtained from the image. Therefore, we attempted to match similar colors using color adjacency. HSV, which stands for hue, saturation (chroma), and value (brightness), is a method of expressing color as a quantity. In this study, we used hue to calculate the adjacency of colors. To obtain the RGB color code, we used the Image Color Picker tool (https://lab.syncer.jp/Tool/Image-Color-Picker/, SYNCER). Although it is possible to incorporate saturation into the color selection process, only lightness was considered for the purpose of this experiment. The procedure for obtaining adjectives and adjectival verbs was as follows: (1) Obtain the RGB color code. (2) Convert the RGB color code into an HSV color code. (3) Compare the color code map with the obtained HSV color code. (4) Obtain adjectives and adjectival verbs from a location that matches the color code map.
The image we prepared to obtain colors related to sexuality is of 歌舞伎町 [Kabukichō]33 (Shinjuku, Tokyo), a famous downtown area in Japan. The color code obtained from this image is shown in Fig. 20. Colors with a V value of 70% or higher when expressed in the HSV are shown in Fig. 21.
When a color is selected, the mechanism searches for its position on the color image scale map. The scheme of the color image scale map contains 16 categories, each of which includes one or more color scheme patterns, including three colors. The mechanism compares the colors in Fig. 21 with those included in the color scheme to search for the position of the colors acquired from Kabukichō in the color scale map. When the mechanism is unable to find the same color in the parameters, it searches for a color in which the value of hue is within the range of ±36. Next, the mechanism searches for a color scheme that matches the selected color, prioritizing the color schemes in categories adjacent to the specified category. For example, to match a color scheme from the gorgeous category, the mechanism chooses schemes from the casual and chic categories. In the next step, the mechanism determines the candidate of the adjectives and adjective verbs included in the gorgeous category. The following list details three categories of color schemes and related adjectives and adjectival verbs based on Kobayashi (1981). Because Kobayashi uses words of modification beyond the range of adjectives and adjectival verbs, we also included such words in this mechanism.
Gorgeous Category
– The adjectives and adjective verbs based on the color scheme related to 魅惑的な [miwakutekina; attractive]: あでやかな [adeyakana; florid], 艶っぽい [tsuyappoi; amorous], 華麗な [kareina; brilliant], セクシーな [sekushiina; sexy], 魅力的な [miryokutekina; attractive]
– The adjectives and adjective verbs based on the color scheme related to 豊潤な [hojun’na; abundant] in the color scheme of “gorgeous”: 豊かな [yutakana; rich], 装飾的な [soushokutekina; decorative], 豊潤な [hojun’na; abundant]
– The adjectives and adjective verbs based on the color scheme related to 豪華な [goukana; gorgeous]: 豪華な [goukana; gorgeous], 贅沢な [zeitakuna; luxurious], 円熟した [enjukushita; mellow], こってりした [kotterishita; lush], 充満した [jumanshita; full]
Casual Category
– The adjectives and adjective verbs based on the color scheme related to ポップな [pop]: 陽気な [youkina; cheerful], 快活な [kaikatsuna; vivacious], はつらつとした [hatsuratsutoshita; lively]
Chic Category
– The adjectives and adjective verbs based on the color scheme related to 風流な [huryuna; elegant]: 風流な [huryuna; elegant], 枯れた [kareta; withered], ひなびた [hinabita; rustic]
Attributes: Looks (agent)/ Appearance (object)/ Atmosphere (location)
– Adjectives/Adjective verbs: florid, amorous, brilliant, sexy, attractive, rich, decorative, abundant, gorgeous, luxurious, lush
– Attributes: Personality (agent)/ Appearance (object)/ Atmosphere (location)
– Adjectives/Adjective verbs: cheerful, vivacious, lively, elegant, withered, rustic, full
Fig. 20.
Colors of Kabuki-chō.

Fig. 21.
Colors used.

Table 2
Candidates of noun concepts according to attributes and topics
| Attributes / Topic | Noun concepts related to love and sex |
| Looks [agent] / Appearance [object]: Body parts | アヌス [anusu; anus], おっぱい [oppai; breasts], グランス [guransu; glans], クリトリス [kuritorisu; clitoris], しりっぽ [shirippo; hips], バスト [basuto; bust], ヒップ [hippu; hips], ペニス [penisu; penis], ヨーニ [yoni; yoni], 陰茎 [inkei; penis], 陰嚢 [in’nou; scrotum], 陰部 [inbu; mons veneris], 隠し所 [kakushidokoro; sexual organ], 会陰 [kaiin; perineum], 蟻の門渡り [ari no kado watari; perineum], 局部 [kyokubu; mons veneris], 玉門 [gyokumon; cunnus], 穴 [ana; anus], 腰 [koshi; waist], 差し乳 [sashichichi; titties], 出っ尻 [decchiri; buttock], 女陰 [join; cunnus], 尻 [shiri; hips], 尻っぺた [shirippeta; hips], 恥部 [chibu; mons veneris], 乳 [chichi; breasts], 乳首 [chikubi; nipples], 乳頭 [nyuto; nipples], 乳房 [chibusa; titties], 肛門 [komon; anus], 臀部 [denbu; buttock] |
| Personality [agent]: Tendency / Temperament | ドンファン [Don fan; Don Juan], 間男 [maotoko; paramour], 好き者 [sukimono; sensualist], 今業平 [ima Narihira; modern handsome man like Narihira], 純血 [junketsu; pureblood], 粋向き [ikimuki; handsome man], 粋人 [suijin; handsome man], エッチ [ecchi; lecher], サディスト [sadisuto; sadist], サド [Sado; Sade], スキーバニー [sukibani; ski bunny], スノーバニー [sunobani; snow bunny], ニンフォマニア [ninfomania; nymphomania], フェティシズム [fetishizumu; fetishism], ペデラスト [pederasuto; pederast], 艶福家 [enpukuka; handsome man], 漁色家 [rhyoshokuka; lady killer], 好色 [koushoku; amativeness], 出歯龜 [debagame; peeping tom], 初物食い [hatsumonogui; lady killer], 助平 [sukebei; lecher], 女たらし [on’natarashi; philanderer], 女好き [on’nazuki; woman admirer], 女道楽 [on’na doraku; woman hunting], 女郎買 [jorogai; buyer of the services of a whore], 色気違い [irokichigai; sexual obsession], 色狂い [irogurui; lecher], 色事師 [irogotoshi; lady killer], 色女 [iroon’na; seductive woman], 色情狂 [shikijokyo; erotomania], 色男 [irootoko; seductive man], 色魔 [shikima; lady killer], 尻軽 [shirigaru; promiscuous person], 甚助 [jinsuke; jealous man], 精力家 [seiryokuka; energetic man], 男たらし [otokotarashi; coquette], 軟派 [nanpa; lecher], 濡れ事師 [nuregotoshi; philanderer], 発展家 [hattenka; playboy] |
Table 2
(Continued)
| Attributes / Topic | Noun concepts related to love and sex |
| Atmosphere [location]: Emotion | アガペー [agape; agape], プラトニックラブ [puratonikku rabu; platonic love], べたぼれ [betabore; deep love], ラブ [rabu; love], ロマンス [romansu; romance], 愛 [ai; love], 愛し [itoshi; beloved], 愛しさ [itoshisa; love and kindness], 横恋慕 [yokorenbo; illicit love], 岡惚れ [okabore; unrequited love], 可愛がり [kawaigari; being affectionate], 君寵 [kuncho; being in the lord’s favor], 敬愛 [keiai; respect and friendship], 交際 [kosai; intercourse], 惚れ [hore; fall in love], 惚れ込み [horekomi; infatuation], 妻恋 [tsumagoi; mutual love], 思い [omoi; feeling], 思いのたけ [omoi no take; one’s whole heart], 執心 [shushin; obsession], 首っ丈 [kubittake; lovesick], 純愛 [jun’ai; pure love], 初恋 [hatsukoi; first love], 鍾愛 [shoai; deep affection], 情愛 [joai; warmheartedness], 相愛 [souai; reciprocal love], 他愛 [taai; considerateness], 寵愛 [choai; favor], 得恋 [tokuren; a love become accomplished], 熱愛 [netsuai; ardent love], 悲恋 [hiren; disappointing love], 父性愛 [huseiai; paternal love], 片思い [kataomoi; one-sided love], 片恋 [katakoi; one-sided love], 慕情 [bojou; longing], 盲愛 [moai; dotage], 恋い焦がれ [koikogare; being deeply in love with someone], 恋しさ [koishisa; affection], 恋愛 [ren’ai; love], 恋情 [renjou; love], 恋心 [koigokoro; feelings of love], 恋着 [renchaku; infatuation], 恋仲 [koinaka; love relationship], 恋煩い [koiwazurai; lovesickness], 恋風 [koikaze; love’s zephyr], 恋慕 [renbo; love], 恋路 [koiji; love affair], 戀 [koi; yearning], 戀い [koi; yearning], 眷恋 [kenren; deep love], アバンチュール [abanchuru; adventure], アムール [amuru; amour], ラムール [ramuru; lamour], 悪女の深情け [akujo no fukanasake; cloying affection of an ugly woman], 仇情け [adanasake; to be encouraged by bad treatment and to have a positive outcome], 狂恋 [kyouren; mad love], 懸想 [kesou; fall in love], 好宜 [kogi; warm friendship], 思し召し [oboshimeshi; intention], 邪恋 [jaren; immoral love], 殉情 [junjo; martyrdom], 情 [nasake; emotion], 情合い [joai; affectionate], 深間 [fukama; intimacy], 深情け [fukanasake; deep love], 相思 [soshi; mutual love], 寵 [chou; favor], 薄情け [usunasake; spurious affection], 比翼 [hiyoku; happily married couple], 比翼の鳥 [hiyoku no tori; happily married couple], 慕わしさ [shitawashisa; dear], 恋 [koi; love], 連理 [renri; eternal love], 舐犢 [shitoku; doting parent], いや [iya; detesting], セプテンバーセックス [seputenba sukkusu; September sex], ヘテロ [hetero; hetero], 艶 [tsuya; fascination], 色事 [irogoto; love], 色恋 [irokoi; love], 性愛 [seiai; sexual love], 男色 [danjiki; sodomy], ソドミー [sodomi; sodomy], ゲイ [gei; gay], ジェロントフィリア [jerontofiria; gerontophilia], ナルシシズム [narushishizumu; narcissism], 同性愛 [doseiai; homosexuality], 偏愛 [hen’ai; partiality], 失恋 [shitsuren; lost love], ハートブレイク [hatobureiku; heartbreak], ブロークンハート [burokun hato; broken heart], 子煩悩 [kobon’nou; adoring parent], 愛情 [aijou; affection], 愛着 [aichaku; attachment], 愛慕 [aibo; adoration], 愛林 [airin; Arbor Day in Japan], 親愛 [shin’ai; friendship and affection], 親愛感 [shin’aikan; feeling of friendship and affection], 親心 [oyagokoro; parental love], 親馬鹿 [oyabaka; doting parent], 人類愛 [jinruiai; humanity], 仁愛 [jin’ai; humanity], 動物愛護 [dobutsu aigo; protection of animals], 同士愛 [doshiai; fellow feeling], 愛玩 [aigan; treasure], 父性愛 [fuseiai; paternal love], 自愛 [jiai; take care of oneself], 博愛 [hakuai; philanthropy], 汎愛 [han’ai; philanthropy], 母性愛 [boseiai; maternal affection], 隣人愛 [rinjin’ai; good-neighborliness], 自重 [jicho; taking care of oneself], いとおしさ [itooshisa; affection], いとおしみ [itooshimi; covetousness], コンパニオネート [conpanioneto; companionate], 猫かわいがり [nekokawaigari; doting], 師弟愛 [shiteiai; master-disciple love], 可愛がり [kawaigari; being affectionate], 愛敬 [aikyou; charm], 愛顧 [aiko; patronage], 愛護 [aigo; protection], 溺愛 [dekiai; doting] |
Based on the story presented in Fig. 22, the story of Fig. 23, colored using adjectives and adjectival verbs, was generated via the aforementioned method. Adjectives, pronouns, and noun concepts were inserted into the attribute frame based on the color image scale. For representing coloring method using colors in a picture by sentences, there are following three types of sentence forms. Italic style words (X, Y, N, Instance) are variables. The words in X and Y describe the characteristics of Kabukichō. One of “neon,” “lights,” “atmosphere” is inserted into X, whereas one of “karaoke,” “bar,” “hotel,” “crowded,” is inserted into Y. For Instance, the target of the coloring is inserted, for N, a noun concept related to sexual love is inserted.
For characters: 「歌舞伎町の X の Y のような N である Instance」[Instance that is a N such as X of Y of Kabukichō.]
For objects: 「歌舞伎町の X の Y のような N に似たInstance」[Instance that similar to a N such as X of Y of Kabukichō.]
For locations: 「歌舞伎町の X の Y のような N に適したInstance」[Instance that suitable for N such as X of Y of Kabukichō.]
5.Examples of story generation using coloring methods
In this section, we describe the generation of stories based on multiple characters. In this example, we start the processing from the stage where the story in Fig. 22 has already been generated. The following eight events are then inserted in each cycle: “the princess learns the truth,” “the princess tells the truth,” “the prince learns the truth,” “Melos’ deceit is exposed,” “Ivan is promoted to prince,” “the king forgave the fool,” “the king pardoned Meros,” and “the king gave Ivan his reward.” As in Section 5, the author generates the story, and the characters check the expansions or edits made. However, the conditions under which the story technique is applied differ for each character.
In a manner common to all colorings, only one coloring may be applied to a single component. Furthermore, if an attribute is assigned to a constituent by coloring, the attribute’s expression is limited to a single event. However, coloring based on substitution of a constituent replaces the very constituent that was the subject of the coloring, so the change spills over to other events.
Each character uses a story method. Figure 24 shows the final results. In this figure, underlined words are colored by sexuality, italicized words are colored by modifiers, and bold words are colored by substitution.
- Ivan: coloring on sexual love/Threshold: 1/ Impulse: change of “location,” number of location instances
- taunter: adjective/pronoun coloring/Threshold: 1/ Impulse: decrease in “wellness,” Number of relationships
King: coloring by element exchange/threshold: 1/ impulse: change in number of additional events, number of person instances
Melos: image-based coloring/threshold: 1/ impulse: change in “possession,” number of object instances
Fig. 22.
Original story.

Fig. 23.
Example of the coloring method using colors in a picture.

Fig. 24.
Example of story generation using coloring by multiple characters.

6.Consideration of results and future works
This section introduces the proposed coloring technique. Section 6.1 shows the consideration of the story generation in Section 5. In Section 6.2, we discuss limitations and challenges of the coloring technique. In Section 6.3, we consider the extension to robotics.
6.1.Consideration of example of story generation using the coloring technique
In Section 5, the results shown in Fig. 24 were generated by repeating four cycles of event insertion by the author and coloring by the character, to a story prepared in advance. In the framework of story generation based on mechanisms by author and character, we proposed coloring techniques that intersperse words and other information to provide an atmosphere related to love and sex in a story, and implemented several experimental systems dependent upon these methods. In this system, the character Ivan functioned as a person who was able to drive the coloring technique that adds many sexual words to create a sexy atmosphere for the story. However, the lengthy explanations accompanying the inserted sexual words gave the impression of cutting off the story flow; therefore, we will examine how to edit the inserted explanations. As shown in Fig. 24, in the case of story generation using a single character, the story flow appears to be cut off by the long explanations accompanying the inserted concepts of sexuality. Although the system in this study uses a format in which all stored knowledge is inserted purely for coloring, it is necessary to consider how to edit the inserted explanations in the future. For example, the results of this study can be treated as a way to increase the influence of characters on story generation, while the use of shortened explanations can be considered as a way to decrease the influence of characters on story generation.
Figure 24 shows examples dealing with “story generation by multiple characters.” In this figure, the author repeated the cycle of inserting events one by one 8 times, and four “characters,” each with a different story technique, performed story generation based on their own thresholds and impulse (“sexual coloring,” “coloring by modifying concepts,” “coloring by element substitution,” or “coloring method using colors in a picture”). The story was generated on the basis of the respective thresholds and stimuli. In this example, as in the case of the story generation with a single character, the long descriptions emphasized coloration related to sexuality, and other colorations were consequently less noticeable. Therefore, in the future, it is necessary to revise the story generation method by characters using story techniques in varying ways, such as by adjusting the threshold and amount of data.
The number of characters doing the coloring also affects the diversity and range of creativity of the generated stories. For example, Fig. 23 in Section 4.4 is an example of a generated story where a single character does the coloring. The amount of change is small because only a small number of characters meet the requirements for their coloring. On the other hand, the amount of change in Fig. 24 is large because of the large number of characters to be colored. In other words, the system can adjust the diversity and range of creativity of the generated stories by reducing the number of characters to be colored if it dares to reduce the changes in the story and, conversely, increasing the number of characters to be colored if it dares to change the story more.
6.2.Discussion of the limitations and challenges of the coloring technique
Three issues are discussed here. The first is the concept dictionary, the second is the function of daemons in the attribute frame, and the third is the treatment of cultural background in coloring.
A. Concept Dictionary: The coloring technique refers to the concept dictionary developed by Ogata (2015). By referring to this concept dictionary, the authors narrow down the references to a specific range of references in order to achieve coloring with a sexual element. This range of references was determined experimentally by the authors, who did not look through the concept dictionary and investigate exactly where the sexual elements are distributed in the concept dictionary. Therefore, a more precise definition of a sexual element and its distribution should be investigated. For example, if the focus is on stimuli that cause sexual arousal, it is conceivable that some people are sexually aroused by cars, or that there are other examples in Japan that are not roughly majority owned. For this reason, we will look at examples based on the majority in Japan.
B. Daemon functionality in attribute frames: As described in Section 2.4, the proposed coloring technique is stored in the attribute frames of the characters and is controlled like a daemon, depending on the state of the story. As a result, the coloring technique is controlled at a different time from the control of the main story generation mechanism, which we called “author” in Section 3. This generative mechanism represents the game mechanism introduced in Section 2.2. In this paper, the characters only used the coloring technique, but the types of stories generated can be expanded by combining story generation techniques other than the coloring technique developed by Ogata (2020). Attempts to combine different story generation techniques will be a future challenge.
C. Treatment of cultural background in coloring: The coloring techniques proposed by the authors are based solely on the use of color impressions in Japanese culture. In addition, the coloring technique proposed in Section 4.4 is based on a neon scene in a Japanese city center. It needs to be investigated whether this Japanese perception of color is specific to the Japanese cultural sphere or whether it is a universal perception worldwide. On the other hand, the authors have attempted an approach based on the Japanese cultural context (Kawai, Ono & Ogata, 2021) and consider it interesting to approach the sensation in a specific cultural sphere rather than a universal sensation.
6.3.Expansion towards robot technology
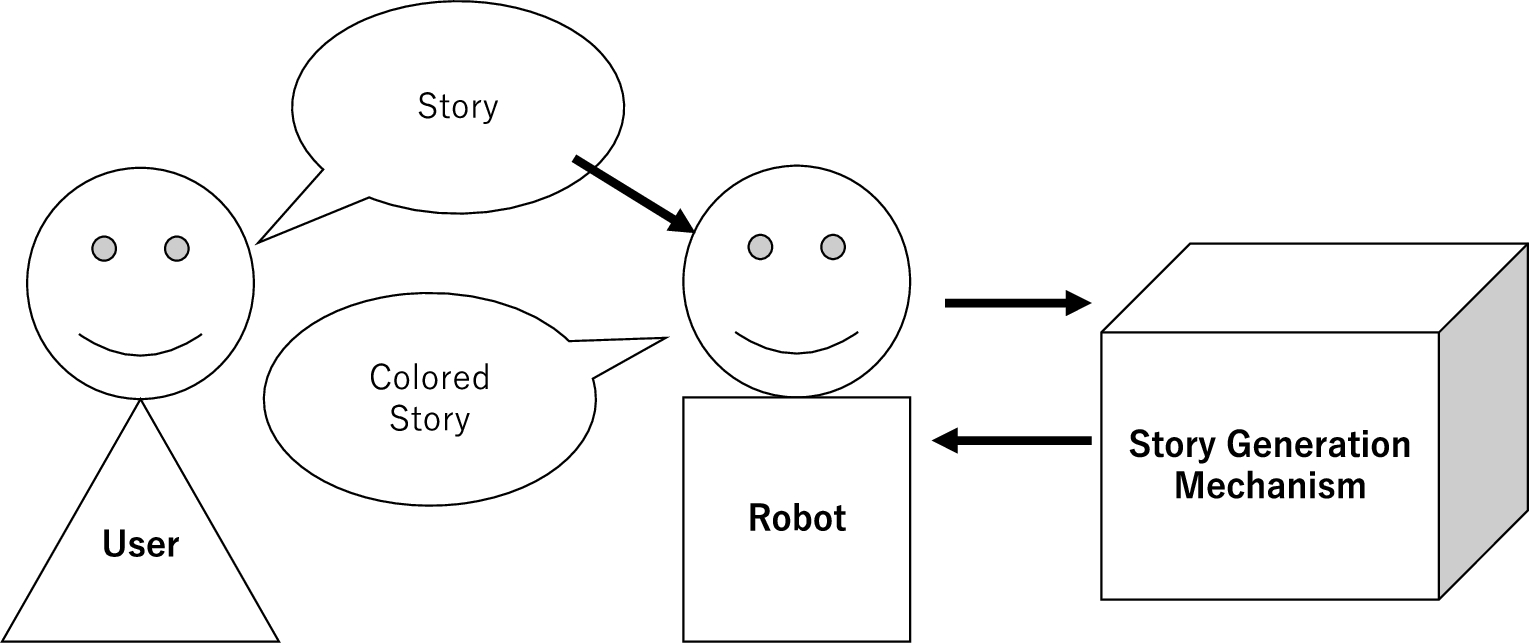
In the future, we aim to combine our story generation mechanisms with robotic technologies. Here, we preliminarily consider combining the story generation technique by coloring with a method using a robot. The role of the interactive robot is to act as a character in the behavior of the system described in Section 3. The robot colors the story provided by the user, and tells the user the result. The relationship between the user, robot, and story generation system is illustrated in Fig. 25. Through this process, the user inputs a story into the robot. In response to the user’s input, the robot proposes a story that has been modified by coloring while showing a narrative that behaves like a character in the story.
In this section, we describe the system using the RoBoHoN Wi-Fi model (model number: SR-04M-Y). In the following section, we present a preliminary experiment. For the sake of simplicity, this attempt simply uses a robot as an interface medium for the coloring narrative generation described earlier, and does not use the threshold in the above description. Based on the common input story described in Section 3, the user designates a coloring method from a list of candidates using the noun concepts of sexuality, other stories, adjectives, and adjectival verbs, and narrates a colored story in the following order: (1) The robot narrates the original input story. (2) The user selects the coloring method. (3) The robot generates a colored story based on the original story and narrates it. Through the system implementation using the robot, we could execute the robot’s narration using the three types of coloring methods. In addition, attempts are made to change the impression by physical changes through the robot. For example, the robot provides lighting that changes in conjunction with the color selected by the coloring, and for text added to the story by the coloring, the robot reads it out slowly for emphasis.
Fig. 25.
Relationships between a user, robot, and story generation mechanism.
7.Conclusion
This study designed a story generation system framework based on techniques used in story-generating games with automatic narrative generation, Lisp s-expressions, and Minsky’s frame theory. As the theoretical background, we presented methods of story generation based on the idea of coloring. Because coloring is a general technique that intersperses or inserts words and other information into a story to create a certain atmosphere, it is effective for creating imagery relating to love and sex. We proposed a coloring technique based on four different methods (“sexual coloring,” “coloring by modifying concepts,” “coloring by element substitution,” or “coloring method using colors in a picture”). In story generation, this study presented a situation where one or more characters employ coloring methods related to love and sex to mix such an atmosphere into the story, and demonstrated several kinds of experimental or prototype systems using coloring theory. The result shown that the number of characters doing the coloring also affects the diversity and range of creativity of the generated stories. However, as this attempt has various problems including the quality of coloring, future work will continue. In addition, this study aims to apply the developed techniques to robotic technologies. Although we presented a system image where a robot corresponded to a story generation character, story and narrative generation using the technique proposed in this paper will have multiple other possibilities that may contribute to robotic technology.
For example, the robot controls the lighting, which changes in conjunction with the colors chosen by the coloring, and the text added to the story by the coloring is read slowly by the robot for emphasis. Attempts to generate stories through interaction with the robot can also be used for entertainment and mental health care.
Notes
1 Natsuo Kirino is a Japanese writer. Her famous novel, Out (Kirino, 2018), was nominated for the Edgar® Award for the best novel 2004. I’m Sorry, Mama here have not been translated to English. (The author’s webpage: https://www.kirino-natsuo.com/eng/index.html.)
2 The color image scale is a map used in the field of design that illustrates the correspondence between adjectives and colors from three different scales: the color image scale, the color scheme image scale, and the language image scale.
3 Kabukichō is an entertainment district in Shinjuku, Tokyo. Kabukichō has many restaurants, host clubs, cabarets, love hotels and nightclubs. However, Kabukichō was not just an “entertainment district,” but a centre of new culture in Japan, where many cultured persons, artists and persons of theatre gathered. In and around Kabukichō there have also been many artistic attempts to combine traditional and modern culture. For example, the young kabuki actor Nakamura Kantaro and others still hold kabuki performances in Kabukichō (https://www.bunkamura.co.jp/english/cocoon/20240503.html (English language), https://www.bunkamura.co.jp/cocoon/lineup/24_kabuki.html (Japanese language)).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS KAKENHI) under Grant No. 21K17870.
References
1 | Bendel, O. ((2020) ). Love dolls and sex robots in unproven and unexplored fields of application. Journal of Behavioral Robotics, 12: (1), 1–12. |
2 | Genette, G. ((1985) ). Monogatari no Deisukuru: Hōhō Ron no Kokoromi (H. Hanawa & R. Izumi, Trans.). Tokyo: Suiseisha. (Original: Genette, G. (1972). Discours du Récit in Figures III. Paris: Seuil). |
3 | Gervás, P. ((2013) ). Story generator algorithms. In The Living Handbook of Narratology. University of Hamburg. https://www.lhn.uni-hamburg.de/node/35.html. |
4 | Groos, K. ((1901) ). The Play of Man (E.L. Baldwin, Trans.). NY: Appleton. |
5 | Imabuchi, S. & Ogata, T. ((2013) ). A generation mechanism of macro stories based on propp-based story grammar combined with an integrated narrative generation system. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Engineering and Applied Science (pp. 2455–2463). |
6 | Kawai, M., Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2021) ). Analyzing the relationship between the legend of Dōjōji and the Kabuki-dance Kyōganoko Musume Dōjōji to develop prototyping systems. Journal of Robotics, Networking and Artificial Life, 8: (3), 151–160. doi:10.2991/jrnal.k.210922.001. |
7 | Kawai, M., Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2022) ). Prototyping narrative representation system using a Kabuki dance and legendary story for the narration function of robots. Journal of Future Robot Life, 3: (2), 147–181. |
8 | Kirino, N. ((2007) ). I’m Sorry, Mama. Tokyo: Shueisha. |
9 | Kirino, N. ((2018) ). Out (S. Snyder, Trans.). NY: Vintage Books. (Original: Kirino, N. (1997). Out. Tokyo: Kodansha). |
10 | Kobayashi, S. ((1981) ). The aim and method of the color image scale. Color Research & Application, 6: (2), 93–107. doi:10.1002/col.5080060210. |
11 | Levy, D. ((2009) ). Love and Sex with Robots: The Evolution of Human-Robot Relationships (English Edition, Kindle Ver.). NY: HarperCollins e-books. |
12 | Mccarthy, M. & Leiman, T. ((2021) ). Sex with robots: How should lawmakers respond? The Bulletin, 43: (7), 34–36. |
13 | Minsky, M. ((1974) ). A framework for representing knowledge. Technical report, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. |
14 | Natsume, S. ((2007) a). Bungaku-ron jō [The Theory of Literature 1]. Tokyo: Iwanami Shoten. (Original book published in 1907). |
15 | Natsume, S. ((2007) b). Bungaku-ron ge [The Theory of Literature 2]. Tokyo: Iwanami Shoten. (Original book published in 1907). |
16 | Ogata, T. ((2015) ). Building conceptual dictionaries for an integrated narrative generation system. Journal of Robotics, Networking and Artificial Life, 1: (4), 270–284. doi:10.2991/jrnal.2015.1.4.6. |
17 | Ogata, T. ((2019) ). An integrated narrative generation system: Synthesis and expansion. In T. Ogata (Ed.), Internal and External Narrative Generation Based on Post-Narratology: Emerging Research and Opportunities (pp. 1–108). PA: IGI Global. doi:10.4018/978-1-5225-9943-2.ch001. |
18 | Ogata, T. ((2020) ). Internal and External Narrative Generation Based on Post-Narratology: Emerging Research and Opportunities. PA: IGI Global. doi:10.4018/978-1-5225-9943-2. |
19 | Ono, J., Kawai, M. & Ogata, T. ((2022) ). Toward love and sex narrative generation using a noun conceptual dictionary. Journal of Future Robot Life, 3: (1), 17–37. |
20 | Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2017) ). A method of story generation for creating “surprise” using “gap techniques”: An approach to an automatic narrative generation game based on table-talk role playing games. Cognitive Studies, 24: (3), 410–430. |
21 | Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2018) ). Surprise-based narrative generation in an automatic narrative generation game. In T. Ogata and S. Asakawa (Eds.), Content Generation Through Narrative Communication and Simulation (pp. 162–185). PA: IGI Global. |
22 | Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2020) ). unchiku generation using a narrative explanation mechanism. In E. Ishita, N.L.S. Pang and L. Zhou (Eds.), Digital Libraries at Times of Massive Societal Transition (LNCS, Vol. 12504: , pp. 240–247). Switzerland: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-64452-9_21. |
23 | Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2021) a). Surprise and story in an automatic narrative generation game: Gap technique for story generation based on surprise. In T. Ogata (Ed.), Post-Narratology no Syōsō: Jinkō Chinō no Jidai no Narratology ni Mukete 1 (pp. 99–130). Tokyo: Shin’yosha. |
24 | Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2021) b). Multiple story generation by “Story techniques that are included in a story”. In The 2021 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence Book of Abstracts (p. 119). |
25 | Ono, J. & Ogata, T. ((2021) c). Development of “a story as a generation system” in an automatic narrative generation game. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Meeting of Japanese Cognitive Science Sosiety (pp. 473–475). |
26 | Shimada, M. ((2009) ). Shōsetsu Sahō ABC [Manners of a Novel]. Tokyo: Sinchosha. |




