Bet v 1 potential allergens are involved in anthracnose resistance of strawberry varieties
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Bet v 1 family identified as one major plant food allergen class, is highly homologous to pathogenesis-related protein 10 (PR-10), but its biological function involved in disease resistance is still unclear.
OBJECTIVE:
This study aims to investigate whether Bet v 1 potential allergens participate in the resistance of berry crops against fungal pathogen.
METHODS:
Allergenicity of Bet v 1 proteins in strawberry (Fragaria) was evaluated by bioinformatics methods. Their expression in response to anthracnose and between susceptible and resistance varieties was analyzed.
RESULTS:
19 Bet v 1 homologous proteins were identified and 15 of them were considered as allergen candidates. RNA-seq analysis indicated most of these Fra a 1s expressed in fruits could be largely induced by the invasion of anthracnose pathogen Colletotrichum. The mRNA level of fruit major allergen Fra a 1.05 in the resistant variety Shenyang (SY) was 20∼50 fold higher compared with those in the susceptible cultivar and two diploid wild species. Immunoblotting using Birch (Betula pendula) Bet v 1 allergen-specific IgG antibody confirmed the large-scale accumulation of potential cross-reactive antigens in SY fruit.
CONCLUSIONS:
Strawberry Bet v 1 potential allergens exhibit their correspondence with anthracnose resistance that might be instructive to future breeding strategies.
1Introduction
Over the past three decades, with the increasing of allergy incidence, allergen identification becomes the prime concern worldwide for clinical diagnosis and treatment [1]. Plant food allergens, being within the most consumed substances by human, are almost impossible to avoid and should be investigated especially for patients suffering from them in daily life, despite the relatively mild immune responses they render, such as oral allergy syndrome, dermatitis or asthma [2].
There are mainly four types of plant-derived allergen families, cupin, prolamin, profilin and Bet v 1 [3]. Bet v 1 is the major inhalant allergen that can cause allergy known as hay fever in millions of adults worldwide, in Northern Europe, Russia, Northeast China and North America areas in particular where birch trees are prevalent [4]. Patients at the same time always clinically manifest allergy to Rosaceae fruits, mostly apple, and to a lesser extent, pear, peach and cherry fruit, as the same epitopes shared with fruit homologue allergens and their cross-reactivity with birch-specific IgE antibodies [5–7], generally presenting an oral syndrome as tingling, itching, edema of oral tissues or even the systemic anaphylaxis [8]. What is noteworthy about strawberry fruit is that, the high amount of histamine it contains can cause the allergic toxicity especially when consumed in large quantities, but strawberry IgE-mediated hypersensitivity indeed exists and should be differentiated clinically [9]. Since causative allergens in most fruits have not been identified and characterized, figuring out Bet v 1 homologous isoforms in fruit crops and their allergenicity is a prerequisite for understanding their roles in fruit allergy and provides insights for disease prevention in future.
Pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins are the key ingredients of plant innate immunity system, by phyhormone (e.g., salicylic acid, jasmonic acid) fine-tuning PR protein accumulation especially in infected sites [10] or interacting with cytosolic immune receptors [11] to suppress pathogen further invasion. Among PR protein classes, PR-10 members showed a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activities against bacteria, viruses and fungi [12–14], and their expression could be induced by pathogen infection [15–17]. PR-10 over-expressed transgenic plants revealed enhanced adaption to abiotic and biotic stress [11, 18, 19]. Bet v 1s, highly homologous to PR-10 family members [4], besides causing sensitization have the capacity to function as important molecules regulating diverse biological processes. Experiments proved that these proteins had activities such as RNA binding [14], enzyme catalyzing [20], and also lipid transfer in non-plant organisms [5]. Bet v 1 strawberry homolog Fra a 1 was reported to be involved in fruit pigment formation by acting as the anthocyanin transporter [21], and the amount of this allergen was quantitatively variable in relation to different genotypes and seasonal factors [22]. However the connection between these multifunctional panallergens and plant defense is still unknown and enigmatic.
In this study, our hypothesis was that contents of Bet v 1 allergens in crops were relevant to plant resistance and defense response to biotic stress. To test this, firstly we pinpointed the potent Bet v 1 allergens in the berry fruit crop strawberry. Expression profiles of strawberry allergens were characterized. In addition, Bet v 1 abundance under fungi pathogen (Colletotrichum) infection and in strawberry varieties with different disease resistance were also measured and compared. The new insight of interplay between allergen and defense will be potentially useful for marker-assisted breeding of fruit crops.
2Materials and methods
2.1Protein family identification and phylogenetic tree construction
The amino acid sequence of known allergen Fra a 1[23] (renamed Fra a 1.05), whose corresponding GDR gene ID is gene07080-v1.0-hybrid (Table 1), was selected to conduct BLASTP against non-redundant protein sequence (nr) database of NCBI. The hit ones with E-value<10–5 were then used as query sequences for TBLASTN in NCBI. The obtained sequences in strawberry were also performed TBLASTN against Fragaria vesca genome database from Rosaceae genome datasets (GDR) v1.0 ab hybid gene transcripts. Sequences with identity above 95%were excluded. Remaining sequences were then searched in pfam database, the ones not annotated as Bet v 1 (PF00407) family members were also removed [24].
Table 1
19 Bet v 1 proteins predicted in strawberry genomes
| Abbreviated protein namea | Species | Allergenicity | NCBI accession ID | Blasted GDR gene IDc (Identity %) |
| Fra a 1.01 | Fragaria×ananassa | possible | BBE27861.1 | gene07085 (98.74) |
| Fra a 1.02 | possible | AHZ10959.1 | gene07064 (100) | |
| Fra a 1.03b | allergend | ACX47058.1 | gene07082 (100) | |
| Fra a 1.04b | allergend | ACX47057.1 | gene07065 (98.12) | |
| Fra a 1.05b | allergend | ABD39049.1 | gene07080 (100) | |
| Fra c 1.01b | Fragaria chiloensis | possible | ADN05762.1 | gene05185 (97.45) |
| Fra v 1.01b | Fragaria vesca | allergend | XP_004296887.1 | gene07080 (100) |
| Fra v 1.02 | not possible | XP_004296884.1 | gene07077 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.03 | not possible | XP_011463622.1 | gene07078 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.04 | not possible | XP_004296883.1 | gene07076 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.05 | not possible | XP_004290824.1 | gene11094 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.06 | possible | XP_004298700.1 | gene32299 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.07b | possible | XP_004296890.1 | gene07083 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.08b | allergend | XP_004296886.1 | gene07082 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.09 | possible | XP_004296889.1 | gene07081 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.10 | possible | XP_011461766.1 | gene04962 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.11 | possible | XP_011461765.1 | gene05185 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.12b | possible | XP_004295081.1 | gene05123 (100) | |
| Fra v 1.13 | possible | XP_004295080.1 | gene05122 (100) |
aProtein abbreviation were named according to WHO/IUIS allergen nomenclature (http://www.allergen.org/). bAntigen molecules identified by Allergome database. cFragaria vesca v1.0 hybrid version. dProven or putative allergens included in Allergen Online database.
Multiple sequence alignments were performed by using MUSCLE program [25], and then adjusted manually in GENEDOC software [26]. Alignment results were imported and neighbor-joining tree was finally generated by MEGA7 with parameters: 1,000 bootstrap replications, Poisson substitution model and pairwise deletion treatment [27]. The constructed phylogenetic tree was visualized and displayed by iTOL tool [28].
2.2Allergen prediction analysis
Possible allergenicity of Bet v 1 families was evaluated by three strategies. Firstly, all sequences were screened by FAO/WHO with the criterion of eight or more exact match in a stretch of consecutive amino acids [29]. Then two approaches (full-length alignments, 80 amino acid alignments) of FASTA comparisons in Allergen Online database were adopted, and the strict criterion of >70%identity was set. To ensure the prediction accuracy, SVM method under Algpred [30] was also used, and only proteins identified by all methods were regarded as potential allergens. Linear epitopes among each potential allergens were predicted and ones with blast identities >90%were selected out by IEDB database.
2.3Gene expression pattern analysis
Candidate Bet v 1 protein sequences of strawberry were blast against GDR Fragaria vesca Genome v1.0 ab hybrid gene protein database, RNA-seq data of the identical ones at strawberry tissues (seedling, seed, leaf, flower, receptacle) were searched and collected by using eFP server (http://mb3.towson.edu/efp/cgi-bin/efpWeb.cgi) [31, 32].
2.4RNA sequencing and data analysis
RNA samples obtained from Jiuxiang leaves at 0 h, 24 h, 72 h, and 96h post inoculation (hpi) of Colletotrichum fructicola (C. fructicola) were reverse transcribed, cDNA libraries were constructed and then sequenced, and raw reads were submitted to NCBI SRA database [33, 34]. Transcriptome profiles of Bet v 1 genes were screened and collected. Microarray data of Camarosa to Colletotrichum acutatum (C. acutatum) infection (GSE56296) [35] were downloaded from NCBI GEO database. Recruited data were then normalized and viewed by MeV version 4.7.4 program [36].
2.5Fungal pathogen inoculation and symptom quantification
C. fructicola, isolate CGMCC3.17371 of C. gloeosporioides species complex, was used in our inoculation experiments. –80°C preserved conidia were firstly cultured on solid potato/dextrose/agar (PDA) medium for 4-5 days at 28°C, then hypha were collected and transferred to fresh liquid PDA medium for another round propagation. Conidia suspension with a concentration of 106/ml was finally used for strawberry inoculation. The strawberry varieties used included SY, Benihoppe, Hawaii 4 (HW4), and Yellow wonder (YW). For leaf inoculation, 10–20 ml spore mixtures with 0.01%Tween-20 (v/v) were sprayed on strawberry leaves. For strawberry fruits, droplets of 20 ul spore suspensions with 0.01%Tween-20 were placed on 2 mm deep and 1 mm wide wound spots at the fruit surface. The above treated materials were all grown under the uniform environmental conditions: 12 h light per day, 125μmolm–2s–1 photo flux density, 70%relative humidity (RH), and the constant temperature 25°C.
Lesion sizes of the infected fruits were calculated by ImageJ software. Relative quantification of C. fructicola biomass was performed by measuring Actin-7 (gene18570-v1.0-hybrid, the reference one) and cutinase encoding gene KB020836.1 expression values. Related specific primers were in Supplementary Table 1.
2.6DNA/ RNA extraction and qPCR/ qRT-PCR
Infected fruit tissues were collected 5 days after C. fructicola inoculation. After being grounded into powder in liquid nitrogen, samples were subjected to DNA extraction with the modified CTAB method [37]. Six tissues (root, stem, stolon, leaf, flower and fruit) of strawberry varieties were collected and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Total RNA was extracted using Omega plant RNA kit (Omega Bio-Tek, USA). After DNA contamination was removed with gDNA eraser, cDNA was synthesized by PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit (Takara, China). Both qPCR and qRT-PCR were performed on Roche Light Cycler 480 machine, TB Green™ Premix Ex Taq™ (Takara, China) was used, and three step program settings were adopted. Expression levels of Fra a 1.05, Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.02 were normalized against those of CHP1 (gene19238-v1.0-hybrid) and GAPDH1 (gene18492-v1.0-hybrid) as the reference genes. Corresponding primers were listed in Supplementary Table 1.
2.7Protein extraction and Immunoblot analysis
Strawberry fruits were fine grounded and then digested with extraction buffer (2%SDS, 80mM Tris-HCl, 41mM DTT, 10%glycerol) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). After quantification by BCA protein assay kit (Beyotime, China), 20 ug of total proteins were separated by 12%SDS-PAGE. For immunoblotting analysis, 1:1000 primary rabbit polyclonal IgG antibody that can react with Birch major pollen allergen Bet v 1-A protein (Abcam, UK) was applied. After HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Proteintech USA, 1:5000) was incubated at RT for 2 h, Fra a 1 proteins at 17∼18 kD were detected by Aplegen Omega Lum C machine (USA). β-Actin was used as the loading control.
3Results
3.1Identification and evolutionary relationships of Bet v 1 homologs in strawberry genome
To explore potential Bet v 1 proteins in strawberry, the major allergen Fra a 1 (Fra a 1.05), known as the first identified strawberry Bet v 1 homolog reacting with IgE from allergic patients [23], was chosen as the query one against nr database and GDR sequences. 19 putative Bet v 1s from 3 strawberry species (F. ananassa, F.chiloensis and F. vesca) were ultimately obtained after matching up to pfam database, which can be divided into 3 clades (Table 1, Fig. 1). Interestingly, 3 homologous proteins Fra v 1.03, Fra v 1.04 and Fra v 1.05 in Fragaria vesca predicted to be non-allergens were clustered together, implicating there might be a direct correlation between Bet v 1 allergenicity and amino acid sequences.
Fig. 1
15 putative Bet v 1 proteins in strawberry and their expression profiles at diverse tissues. 3 sequence redundant allergen proteins, Fra v 1.01, Fra c 1.01 and Fra v 1.08, were eliminated from this analysis. The phylogenetic tree (NJ) showed the evolutionary relationship between strawberry allergen proteins, and three clades are color-coded blue, green, and yellow, respectively. Bootstrap values between 60%and 100%were indicated by red circles. RPKM values above 2000 were colored in purple. Anther, carpel, pollen and ovule were floral organs at the early stage [31]; Style, wall, cortex and pith were receptacle parts at the early stage [32].
![15 putative Bet v 1 proteins in strawberry and their expression profiles at diverse tissues. 3 sequence redundant allergen proteins, Fra v 1.01, Fra c 1.01 and Fra v 1.08, were eliminated from this analysis. The phylogenetic tree (NJ) showed the evolutionary relationship between strawberry allergen proteins, and three clades are color-coded blue, green, and yellow, respectively. Bootstrap values between 60%and 100%were indicated by red circles. RPKM values above 2000 were colored in purple. Anther, carpel, pollen and ovule were floral organs at the early stage [31]; Style, wall, cortex and pith were receptacle parts at the early stage [32].](https://content.iospress.com:443/media/jbr/2021/11-1/jbr-11-1-jbr200627/jbr-11-jbr200627-g001.jpg)
3.2Bioinformatic prediction of Bet v 1 potential allergens
We searched all these sequence duplicates in Allergome database, and found out 8 among them had been listed as known allergen proteins (Table 1). Next, by using sequence-based FAO/WHO method [29], and fasta comparison methods in Allergen Online database [38], combined with Algpred approaches based on SVM module, finally 15 proteins, 6 from octoploid strawberry and 9 from woodland strawberry, identified by all strategies were considered as potential Bet v 1 allergens (Table 2, Supplementary Table 2). Among them, 5 proteins were identical to allergens collected in Allergen Online database, and linear epitopes of 7 members had identities higher than 90%blast against immune antigen epitopes in IEDB database (Table 2, Supplementary Table 3).
Table 2
Allergenicity evaluation of strawberry Bet v 1 homologous proteins by different strategies
| Abbreviated protein name | FAO/WHO | Allergen Online | Algpred | IEDB |
| Fra a 1.01 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra a 1.02 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra a 1.03 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra a 1.04 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
| Fra a 1.05 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
| Fra c 1.01 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra v 1.01 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
| Fra v 1.02 | N | N | Y | |
| Fra v 1.03 | Y | N | Y | |
| Fra v 1.04 | Y | N | Y | |
| Fra v 1.05 | Y | N | Y | |
| Fra v 1.06 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
| Fra v 1.07 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra v 1.08 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra v 1.09 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
| Fra v 1.10 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
| Fra v 1.11 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra v 1.12 | Y | Y | Y | |
| Fra v 1.13 | Y | Y | Y | Y1 |
Note: Y = possible allergen; N = not possible. Y1 indicates identity of linear epitopes blast against immune antigen epitope > 90%.
3.3Strawberry Bet v 1 possible allergens are widely expressed in fruits
Furthermore, to figure out expression profiles of Bet v 1 allergens in edible parts, RNA-seq data of 15 strawberry representatives, 5 present in octoploid strawberry and 10 in wild species, in strawberry tissues were found and analyzed. As illustrated in Fig. 1, more than half of them had a relative high expression in receptacle, suggesting Bet v 1 may be the major allergen class in strawberry fruits. We also noted that Fra v 1.09 was specially expressed in anther, implying it probably was a principle strawberry pollen allergen, which may have the potential to cross-react with Birch Bet v 1 and cause allergic rhinitis and asthma [39]. Two genes Fra a 1.05 and Fra a 1.01 displayed ubiquitous expression both in vegetative and reproductive organs, from which we deduce they might be related to environmental stress response.
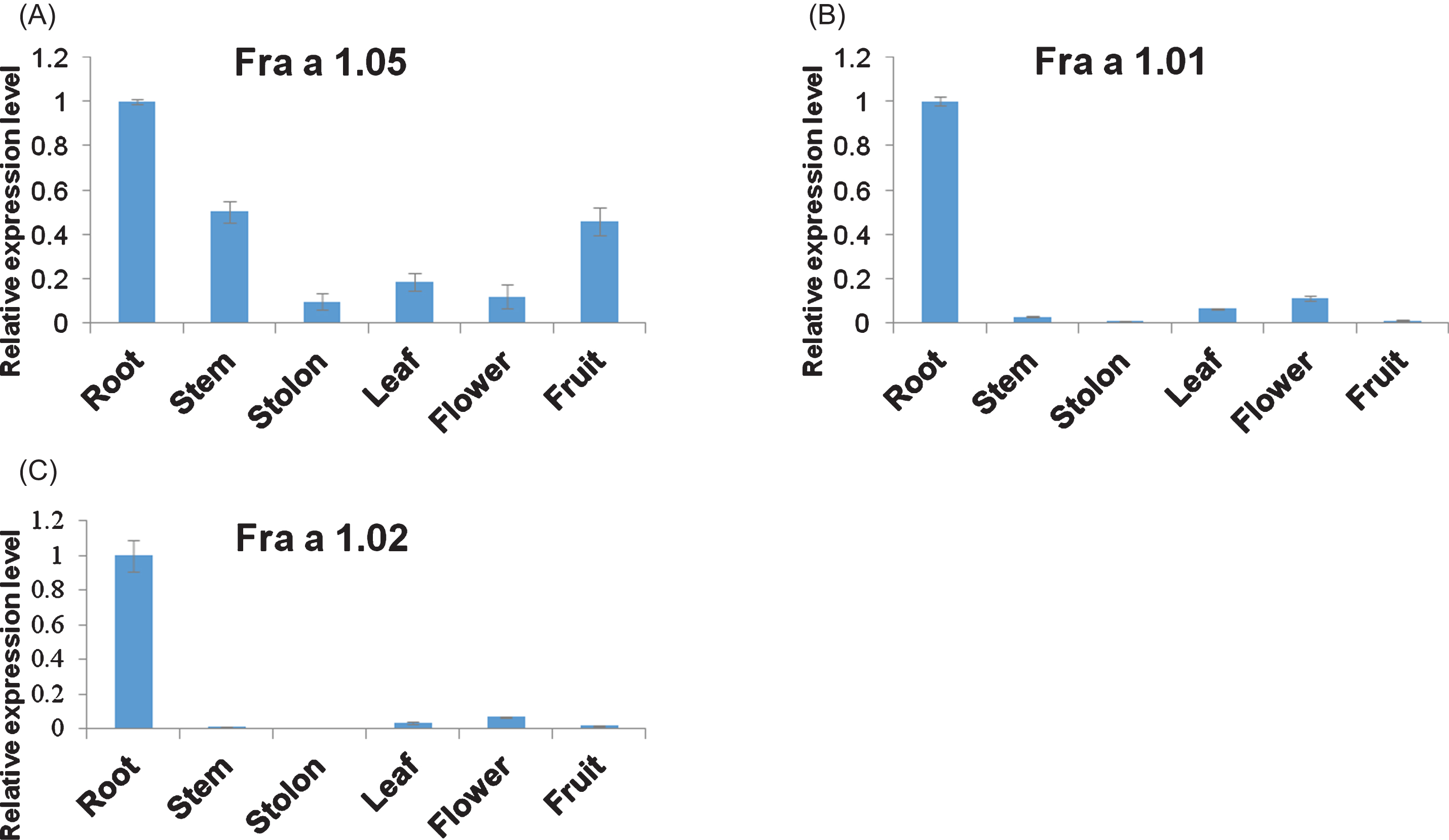
To figure out Bet v 1 isoforms present in fruits of Fragaria×ananassa, tissue expression profiles of Fra a 1.05, Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.02 genes were analyzed, the latter of which was once documented mainly expressed in fruit tissues [40]. qRT-PCR results showed that Fra a 1.05 was ubiquitously transcribed in root, stem, stolon, leaf, flower and fruit tissues, especially abundant in root, stem and fruit, while both Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.02 proteins were only predominant in strawberry root tissue (Fig. 2). Although the relative comparison of gene transcriptional levels may be not accurate, in great contrast to Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.02 mRNA levels, we could conclude Fra a 1.05 gene was the main isoform of Bet v 1s in the strawberry fruit organ (Supplementary Figure 1).
Fig. 2
Spatial expression analysis of Fra a 1.05, Fra a 1.01, and Fra a 1.02 genes in strawberry. mRNA levels of Fra a 1.05 (A), Fra a 1.01 (B), and Fra a 1.02 (C) in six tissues were measured by qRT-PCR. Expression values in the root tissue were set as 1. Data were shown as mean±standard deviation derived from three biological and three technical replicates.
3.4Colletotrichum infection could induce the transcription of most Bet v 1 possible allergens in strawberry
To verify Bet v 1 function in stress defense, at the same time to understand the correlation between potential allergenicity and defense, plants of strawberry susceptible cultivar Jiuxiang were treated with pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum genus C. fructicola. 15 Bet v 1 gene expression data from RNA-sequencing at 0 h, 24 h, 72 h, and 96 h after C. fructicola inoculation were collected, standardized and compared. From Fig. 3(A), we could see that 12 possible allergen encoding genes we identified were dramatically induced except Fra a 1.03 genes, among which 11 members were early response genes, while the expression level of Fra a 1.05 genes only got elevated since 72 hpi. Transcription of 3 non-allergen genes Fra v 1.03, Fra v 1.04 and Fra v 1.05 were also regulated by C. fructicola invasion, implying the biological function in biotic stress and allergenicity of Bet v 1proteins were not segregated.
Fig. 3
Bet v 1 expression response to Colletotrichum invasion. (A) Relative mRNA levels of 15 putative strawberry Bet v 1s after the C. fructicola inoculation. Log2 (fold change) values at 24 hpi, 72 hpi, 96 hpi versus 0 hpi were computed and clustered. RNA-seq data of the remaining 3 predicted strawberry allergens were not found in our collection. Plant growth and inoculation conditions have been previously described [34]. (B) Expression changes of 5 putative strawberry allergens 5 days after the C. acutatum infection. Data of the rest putative allergens were not found in this microarray analysis (GSE56296) [35].
![Bet v 1 expression response to Colletotrichum invasion. (A) Relative mRNA levels of 15 putative strawberry Bet v 1s after the C. fructicola inoculation. Log2 (fold change) values at 24 hpi, 72 hpi, 96 hpi versus 0 hpi were computed and clustered. RNA-seq data of the remaining 3 predicted strawberry allergens were not found in our collection. Plant growth and inoculation conditions have been previously described [34]. (B) Expression changes of 5 putative strawberry allergens 5 days after the C. acutatum infection. Data of the rest putative allergens were not found in this microarray analysis (GSE56296) [35].](https://content.iospress.com:443/media/jbr/2021/11-1/jbr-11-1-jbr200627/jbr-11-jbr200627-g003.jpg)
As to C. acutatum infection, microarray data of strawberry cultivar Camarosa 5 days after spray were analyzed. 4 Bet v 1 genes, Fra v 1.11, Fra a 1.03, Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.04 were activated as well, but Fra a 1.05 gene was kept undisturbed (Fig. 3(B)). From above results we propose Bet v 1s in response to external biotic stimuli may be specialized and differentiated, but most of the putative allergen genes could be transcriptional activated.
3.5Fra a 1 allergen contents in fruits of strawberry resistance variety SY are remarkably higher than those in susceptible cultivars
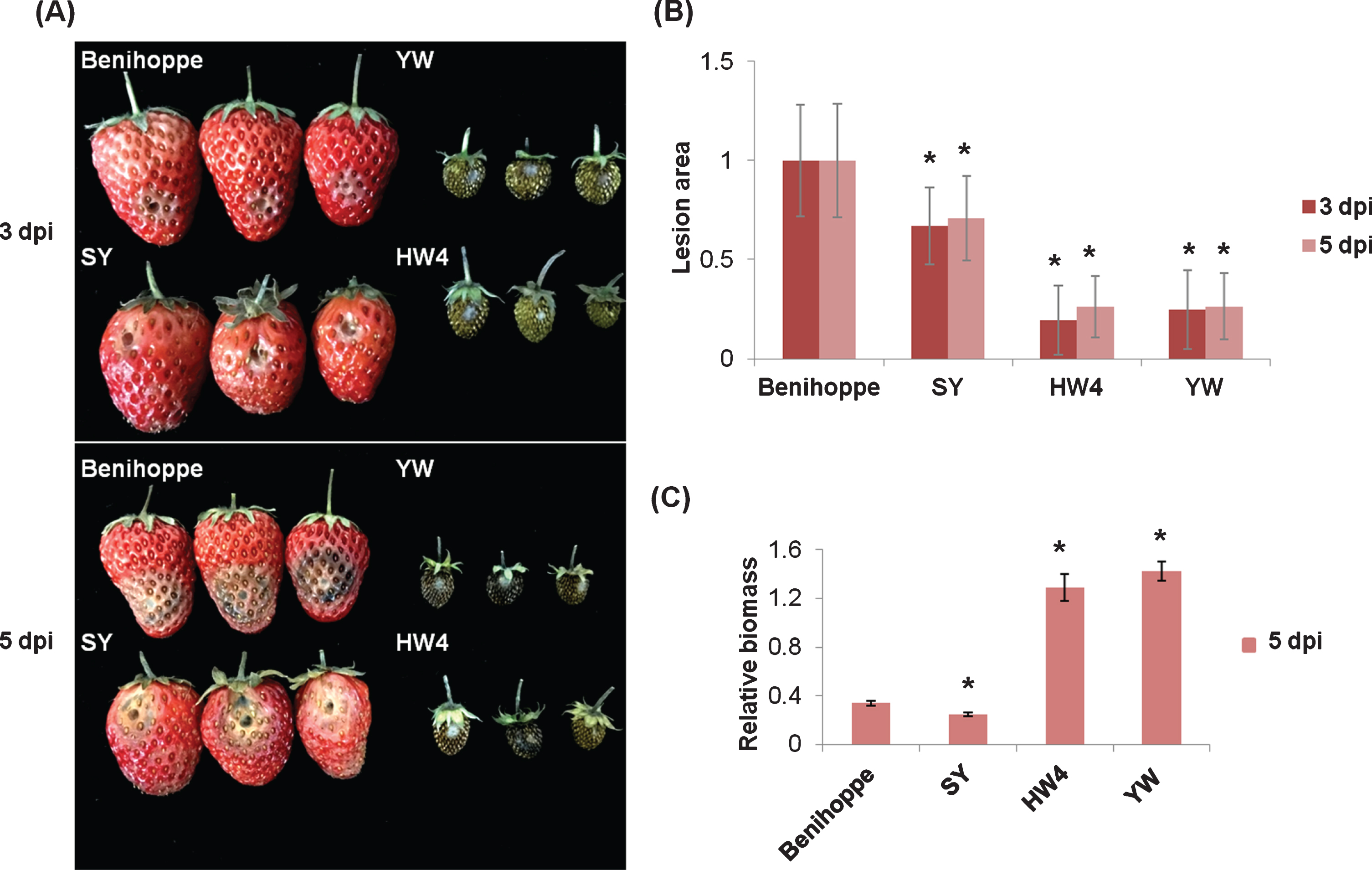
In order to evaluate resistance differences of strawberry varieties to C. fructicola, symptoms of two octoploid cultivars SY and Benihoppe, and two diploid wild species HW4 and YW at 3 dpi and 5 dpi were monitored (Fig. 4(A)). Lesion areas were accordingly measured (Fig. 4(B)), and relative biomass values were calculated at 5 dpi by genomic DNA quantification (Fig. 4(C)). Results showed that SY fruits were the least susceptible ones among these four varieties, although leave tissues of HW4 and YW showed more resistant to C. fructicola (Supplementary Figure 2) than those of cultivated strawberry.
Fig. 4
Resistance assessment of four strawberry varieties to C. fructicola. (A) Strawberry fruits of Benihoppe, SY, YW and HW4 at the turning stage were treated with C. fructicola. Pictures were taken at 3 dpi and 5 dpi. (B) Lesion size was measured by ImageJ, and values of the control group “Benihoppe” at 3 dpi and 5 dpi were set as 1. Error bars indicated the standard deviation of at least 10 samples. (C) The biomass of C. fructicola relative to strawberry in infected fruits at 5 dpi was measured by qPCR. Error bars indicated the standard deviation of three technical replicates. Asterisks indicated statistically significant differences (Student’s t-test, *P < 0.01).
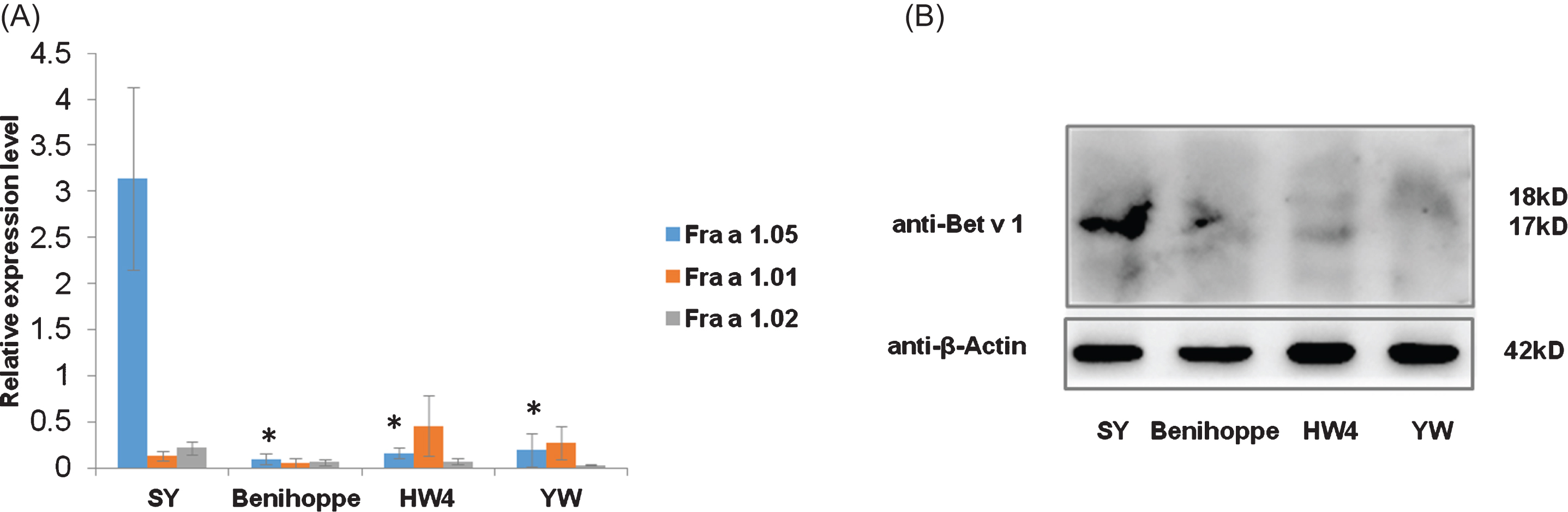
mRNA levels of three genes mainly expressed in fruit organs Fra a 1.05, Fra a 1.01, and Fra a 1.02 in SY, Benihoppe, HW4 and YW were quantified by qRT-PCR. Surprisingly Fra a 1.05 mRNA abundance in fruits of resistant variety SY was 20∼50 fold higher compared with those in the susceptible cultivar and diploid wild species, indicating Fra a 1.05 mRNA level might correlate with plant defense ability (Fig. 5(A)). Immunoblotting test detected by the antibody of Birch major pollen allergen further confirmed the total content of cross-reactive Bet v 1 proteins in SY fruits was the highest (Fig. 5(B)), implying more potential allergens were expressed in this strawberry resistant variety, and fruit safety might be compromised by its anthracnose resistance improvement.
Fig. 5
Measurement of potential allergen levels in four strawberry varieties. (A) Relative mRNA levels of Fra a 1.05, Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.02 in Benihoppe, SY, YW and HW4 measured by qRT-PCR. Data were shown as mean±standard deviation from three biological and three technical replicates. Asterisks indicated statistically significant differences (Student’s t-test, *P < 0.01). (B) Bet v 1 protein contents in fruits of Benihoppe, SY, YW and HW4 by immunoblotting analysis. Contents of Bet v 1 possible allergens in 20 ug of total proteins were examined by the antibody of Birch Bet v 1 allergen. Strawberry Bet v 1 homologous proteins were detected at 17∼18 kD. Fruit samples used were generated under the uniform natural conditions instead of artificially inoculated ones.
4Discussion and conclusion
Bet v 1 proteins are one of the major allergens in foods consumed in raw. Here we screened out 19 Bet v 1 homologs in strawberry genome. Besides 5 known allergens, 10 extra proteins were predicted as potential ones that might have IgE cross-reactivity with known ones and possible clinical activities.
The Fra a 1.05 protein we named and analyzed here, is the same as Fra.a 1.01e38 or an identical ortholog in diploid species gene07080 encoding protein, or Fra a 1 the first identified as the ortholog of Bet v 1 [41, 42], or Fra a 1.01 in other studies [43, 44]. The five Bet v 1 homologs we found in Fragaria×ananassa correspond to the allelic isoforms of Fra a 1.01, according to the rules of nomenclature [40], except BBE27861.1, which we think probably is a novel allele. Fra.a 1.02, instead of Fra.a 1.01e or Fra a 1.05, was once believed to be the major allergenic isoform as its high ability to active basophils in seven of eight atopic patients, as well as having the highest mRNA level in red fruits [40]. On the contrary, Ishibashi et al. [43] demonstrated Fra a 1.01 provided the most important antigens from both the translational expression abundance aspect and IgE-binding capacity, which is in concert with our experimental results. In our analysis, Fra a 1.05 was ubiquitously and intensively transcribed in diverse organs of strawberry cultivar Benihoppe, while Fra a 1.02 mRNAs were specifically located in root, leaf and flower (Fig. 2), which patterns are quite similar with the protein accumulation profiles [43] presented by immunoblotting in Ishibashi’s study, but not the transcriptional ones. We assume this could attribute to RT-PCR primers designed (location or sequence identity) and different strawberry genotypes used.
The comparison of Fra a 1.05 (Fra a 1.01e), Fra a 1.01 and Fra a 1.02 mRNA abundance in four strawberry varieties proved that Fra a 1.05 gene expression is uplifted to a fairly high level (20∼50 fold) in fruits of the strawberry resistant cultivar SY, while kept low at the susceptible cultivar and diploid species fruits (Fig. 5), indicating the positive correlation between the Fra a 1.05 mRNA content and plant resistance ability. What we find intriguing is, the expression of both Fra a 1.05, Fra a 1.02 and Fra a 1.01 genes could be induced by Colletotrichum challenge, and it seems that Fra a 1.02 and Fra a 1.01 was even more responsive to the pathogen (Fig. 3), however only Fra a 1.05 gene plays a role in anthracnose defense exclusively in the resistant genotype compared to the susceptible ones, which we suggest could be used as a candidate molecular marker for anthracnose resistance assessment and resistant variety selection.
Immunoblotting detection using Birch Bet v 1-A allergen IgG antibody has the capacity to bring out all homologous allergenic isoforms that may have cross-reactivity with it in each strawberry variety. We observed no more than a trace of Bet v 1 homologous proteins in fruits of two yellow-fruited species HW4 and YW, which conforms to clinical manifestation that white strawberries could be tolerated by strawberry-allergic individuals [42, 45], and also the results of proteomic analysis in red and white varieties [42]. Since the protein band in SY fruit sample appeared at 17∼18 kD, based on molecular weight we expect it as the mixed isoforms of at least Fra a 1.01, Fra a 1.02 and Fra a 1.05. This result implies that Fra a 1 content in fruits of different strawberry varieties is variable, and there might be more potent allergens in those of resistant plants. Breeding varieties resistant to anthracnose may increase the likelihood that consumers become sensitized and reactive to strawberry allergens, particularly for Northern Europe, Northern US, Russia and Northeast China where patients react sensibly to Bet v 1. In other words, it would be more advisable to pursue plant resistance improvement and select low allergenic germplasm at the same time during food crop breeding [22, 46].
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grant from Shanghai Sailing Program 18YF1420800 to J Yang, Shanghai Municipal Agricultural Commission key basic research project No. 6-1-4 to K Duan and Hu Nong Ke Zhong Zi-2017-2-1 to Q Gao.
Supplementary material
[1] The supplementary material is available in the electronic version of this article: https://dx.doi.org/10.3233/JBR-200627.
References
[1] | World allergy organization (wao) white book on allergy, update. Milwaukee, Wisconsin: World Allergy Organization; 2013. |
[2] | Wang J . Oral allergy syndrome. In: Metcalfe DD, Sampson HA, Simon RA, editors. Food allergy: Adverse reaction to foods and food additives. 301. 4th ed. Boston: Blackwell Publishing; (2013) . pp. 672–7. |
[3] | Breiteneder H , Radauer C . A classification of plant food allergens. The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology. (2004) ;113: (5):821–30. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.01.779 |
[4] | Breiteneder H , Pettenburger K , Bito A , Valenta R , Kraft D , Rumpold H , et al. The gene coding for the major birch pollen allergen betv1, is highly homologous to a pea disease resistance response gene. EMBO J. (1989) ;8: (7):1935–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03597.x |
[5] | Neudecker P , Schweimer K , Nerkamp J , Scheurer S , Vieths S , Sticht H , et al. Allergic cross-reactivity made visible: Solution structure of the major cherry allergen pru av 1. J Biol Chem. (2001) ;276: (25):22756–63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101657200 |
[6] | Gao ZS , van de Weg WE , Schaart JG , Schouten HJ , Tran DH , Kodde LP , et al. Genomic cloning and linkage mapping of the mal d 1 (pr-10) gene family in apple (malus domestica). Theor Appl Genet. (2005) ;111: (1):171–83. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-2018-4 |
[7] | Chen L , Zhang S , Illa E , Song L , Wu S , Howad W , et al. Genomic characterization of putative allergen genes in peach/almond and their synteny with apple. BMC Genomics. (2008) ;9: :543. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-543 |
[8] | Ma S , Sicherer SH , Nowak-Wegrzyn A . A survey on the management of pollen-food allergy syndrome in allergy practices. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. (2003) ;112: (4):784–8. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(03)02008-6 |
[9] | Mohamed GG , El-Hameed AK , El-Din AM , El-Din LA . High performance liquid chromatography, thin layer chromatography and spectrophotometric studies on the removal of biogenic amines from some egyptian foods using organic, inorganic and natural compounds. The Journal of Toxicological Sciences. (2010) ;35: (2):175–87. doi: 10.2131/jts.35.175 |
[10] | Ali S , Mir ZA , Tyagi A , Bhat JA , Chandrashekar N , Papolu PK , et al. Identification and comparative analysis of brassica juncea pathogenesis-related genes in response to hormonal, biotic and abiotic stresses. Acta Physiol Plant. (2017) ;39: (12):1–15. doi: 10.1007/s11738-017-2565-8 |
[11] | Choi DS , Hwang IS , Hwang BK . Requirement of the cytosolic interaction between pathogenesis-related protein10 and leucine-rich repeat protein1 for cell death and defense signaling in pepper. The Plant Cell. (2012) ;24: (4):1675–90. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.095869 |
[12] | Fan S , Jiang L , Wu J , Dong L , Cheng Q , Xu P , et al. A novel pathogenesis-related class 10 protein gly m 4l, increases resistance upon phytophthora sojae infection in soybean (glycine max [l. ] merr.). PloS One. (2015) ;10: (10):e0140364. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140364 |
[13] | Flores T , Alape-Giron A , Flores-Diaz M , Flores HE . Ocatin. A novel tuber storage protein from the andean tuber crop oca with antibacterial and antifungal activities. Plant Physiol. (2002) ;128: (4):1291–302. doi: 10.1104/pp.010541 |
[14] | Park CJ , Kim KJ , Shin R , Park JM , Shin YC , Paek KH . Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper functions as a ribonuclease in an antiviral pathway. Plant J. (2004) ;37: (2):186–98. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01951.x |
[15] | Xiong JS , Zhu HY , Bai YB , Liu H , Cheng ZM . Rna sequencing-based transcriptome analysis of mature strawberry fruit infected by necrotrophic fungal pathogen botrytis cinerea. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. (2018) ;104: :77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2018.08.005 |
[16] | Gijzen M , Toljamo A , Blande D , Kärenlampi S , Kokko H . Reprogramming of strawberry (fragaria vesca) root transcriptome in response to phytophthora cactorum. PloS One. (2016) . 11: (8). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161078 |
[17] | Besbes F , Habegger R , Schwab W . Induction of pr-10 genes and metabolites in strawberry plants in response to verticillium dahliae infection. BMC Plant Biol. (2019) ;19: (1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1718-x |
[18] | Agarwal P , Dabi M , More P , Patel K , Jana K , Agarwal PK . Improved shoot regeneration, salinity tolerance and reduced fungal susceptibility in transgenic tobacco constitutively expressing pr-10a gene. Front Plant Sci. (2016) ;7: :217. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00217 |
[19] | Jain S , Kumar A . The pathogenesis related class 10 proteins in plant defense against biotic and abiotic stresses. Adv Plants Agric Res. (2015) ;150: :1–11. doi: 10.15406/apar.2015.03.00077 |
[20] | Samanani N , Liscombe DK , Facchini PJ . Molecular cloning and characterization of norcoclaurine synthase, an enzyme catalyzing the first committed step in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis. Plant J. (2004) ;40: (2):302–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02210.x |
[21] | Munoz C , Hoffmann T , Escobar NM , Ludemann F , Botella MA , Valpuesta V , et al. The strawberry fruit fra a allergen functions in flavonoid biosynthesis. Mol Plant. (2010) ;3: (1):113–24. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp087 |
[22] | Tulipani S , Marzban G , Herndl A , Laimer M , Mezzetti B , Battino MJFC . Influence of environmental and genetic factors on healthrelated compounds in strawberry. (2011) ;124: (3):p.906–13. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.018 |
[23] | Karlsson AL , Alm R , Ekstrand B , Fjelkner-Modig S , Schiott A , Bengtsson U , et al. Bet v 1 homologues in strawberry identified as ige-binding proteins and presumptive allergens. Allergy. (2004) ;59: (12):1277–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00585.x |
[24] | Punta M , Coggill PC , Eberhardt RY , Mistry J , Tate J , Boursnell C , et al. The pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) ;40: (Database issue):D290–301. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1065 |
[25] | Edgar RC . Muscle: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. (2004) ;32: (5):1792–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340 |
[26] | Nicholas KB , Nicholas HB , DW Deerfield HN , Nicholas K , Nicholas HJ , Nicholas K. R. , Nicholas H. B. J , Nicholas A , Nicholas DW , H Nicholas H . Gauch. Genedoc: A tool for editing and annotating multiple sequence alignments. EMBNET NEWS. (1997) ;4: :14. doi: |
[27] | Kumar S , Stecher G , Tamura K . Mega7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. (2016) ;33: (7):1870–4. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 |
[28] | Letunic I , Bork P . Interactive tree of life (itol): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England). (2007) ;23: (1):127–8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl529 |
[29] | FAO/WHO. Evaluation of allergenicity of genetically modified foods. Rome, Italy2001. pp. 1-27. |
[30] | Saha S , Raghava GP . Algpred: Prediction of allergenic proteins and mapping of ige epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. (2006) ;34: (Web Server issue):W202–W9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl343 |
[31] | Hollender CA , Kang C , Darwish O , Geretz A , Matthews BF , Slovin J , et al. Floral transcriptomes in woodland strawberry uncover developing receptacle and anther gene networks. Plant Physiol. (2014) ;165: (3):1062–75. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.237529 |
[32] | Kang C , Darwish O , Geretz A , Shahan R , Alkharouf N , Liu Z . Genome-scale transcriptomic insights into early-stage fruit development in woodland strawberry fragaria vesca. The Plant cell. (2013) ;25: (6):1960–78. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.111732 |
[33] | Zhang L , Huang X , He C , Zhang QY , Zou X , Duan K , et al. Novel fungal pathogenicity and leaf defense strategies are revealed by simultaneous transcriptome analysis of colletotrichum fructicola and strawberry infected by this fungus. Front Plant Sci. (2018) ;9: :434. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00434 |
[34] | Zhang QY , Zhang LQ , Song LL , Duan K , Li N , Wang YX , et al. The different interactions of colletotrichum gloeosporioides with two strawberry varieties and the involvement of salicylic acid. Hortic Res. (2016) ;3: :16007. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2016.7 |
[35] | Amil-Ruiz F , Garrido-Gala J , Gadea J , Blanco-Portales R , Munoz-Merida A , Trelles O , et al. Partial activation of sa- and ja-defensive pathways in strawberry upon colletotrichum acutatum interaction. Front Plant Sci. (2016) ;7: :1036. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01036 |
[36] | Saeed AI , Sharov V , White J , Li J , Liang W , Bhagabati N , et al. Tm4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. BioTechniques. (2003) ;34: (2):374–8. doi: 10.2144/03342mt01 |
[37] | Liu L , Wang CL , Peng WY , Yang J , Lan MQ , Zhang B , et al. Direct DNA extraction method of an obligate parasitic fungus from infected plant tissue. Genet Mol Res. (2015) ;14: (4):18546–51. doi: 10.4238/2015.December.28.1 |
[38] | Aalberse RC . Structural biology of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2000) ;106: (2):228–38. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.108434 |
[39] | D’Amato G , Cecchi L , Bonini S , Nunes C , Annesi-Maesano I , Behrendt H , et al. Allergenic pollen and pollen allergy in europe. Allergy. (2007) ;62: (9):976–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01393.x |
[40] | Franz-Oberdorf K , Eberlein B , Edelmann K , Hucherig S , Besbes F , Darsow U , et al. Fra a 1.02 is the most potent isoform of the bet v 1-like allergen in strawberry fruit. J Agric Food Chem. (2016) ;64: (18):3688–96. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00488 |
[41] | Musidlowska-Persson A , Alm R , Emanuelsson C . Cloning and sequencing of the bet v 1-homologous allergen fra a 1 in strawberry (fragaria ananassa) shows the presence of an intron and little variability in amino acid sequence. Mol Immunol. (2007) ;44: (6):1245–52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.06.004 |
[42] | Hjerno K , Alm R , Canback B , Matthiesen R , Trajkovski K , Bjork L , et al. Down-regulation of the strawberry bet v 1-homologous allergen in concert with the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in colorless strawberry mutant. Proteomics. (2006) ;6: (5):1574–87. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200500469 |
[43] | Ishibashi M , Nabe T , Nitta Y , Tsuruta H , Iduhara M , Uno Y . Analysis of major paralogs encoding the fra a 1 allergen based on their organ-specificity in fragaria x ananassa. Plant Cell Rep. (2018) ;37: (3):411–24. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2237-6 |
[44] | Ishibashi M , Okochi S , Sone K , Noguchi Y , Uno Y . Seasonal variation of the major allergen fra a 1 in strawberry fruit. Hortic J. (2019) ;88: (3):354–63. doi: 10.2503/hortj.UTD-051 |
[45] | Franzoberdorf K , Eberlein B , Edelmann K , Bleicher P , Kurze E , Helm D , et al. White-fruited strawberry genotypes are not per se hypoallergenic. Food Res Int. (2017) ;100: :748–56. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.076 |
[46] | Diamanti J , Capocasa F , Balducci F , Battino M , Hancock J , Mezzetti B . Increasing strawberry fruit sensorial and nutritional quality using wild and cultivated germplasm. PloS One. (2012) ;7: (10):e46470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046470 |




