Cognitive Impairment in Fall-Related Studies in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
Background: There is increasing evidence to suggest a tight relationship between cognitive impairment and falls in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Here, we draw attention to a potentially significant flaw in the existent falls-related research, namely the apparent exclusion of patients with cognitive impairment or dementia.
Objective: Our objective was to review all published, on-going or scheduled fall-related intervention studies, in order to investigate the extent to which cognitively impaired individuals with PD were included in these studies.
Methods: We analyzed published controlled trials regarding falls and PD in commonly used databases, as well as relevant ongoing clinical trials registered within the World Health Organization database, clinicaltrials.gov and the European Clinical Trials Database.
Results: Fourteen of the fifteen published studies included had explicit cognitive exclusion criteria as part of their study protocol. Most of the 54 on-going PD fall-related studies excluded patients with cognitive impairment.
Conclusions: This suggests that individuals with cognitive impairment or dementia are excluded from fall-related research studies. We strongly recommend that future work in this area should include a representative sample of patients with PD, including subjects with cognitive decline.
INTRODUCTION
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a complex heterogeneous neurodegenerative disorder. In order to capture the overall picture of PD, it is important to consider not only the typical motor problems such as tremor, bradykinesia, postural instability, and levodopa-induced motor complications, but also non-motor symptoms, such as pain, depression and cognitive impairment. Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and PD dementia (PDD) are frequent and incidence increases with age, disease duration, and disease severity [1]. Even though there is still some debate regarding the definition, MCI is considered a cognitive decline that is not normal for age but with basically normal functional activities, and that appears to place patients at risk of progressing to dementia[1–3].
A growing body of class II evidence suggests that there is an increased risk of falls in the presence of cognitive impairment [4–7] as well as in dementia [8, 9] and this trend is present in both community-dwelling and institutionalized older populations. An evidenced based review from the American Academy of Neurology (ANN) pooled data from five studies and indicated an absolute risk of falling of 47% among individuals with dementia during study follow-up [6, 10–13]. Similar findings were reported in populations with PD [14–17]. A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover, double-blind study demonstrated that one acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil, may have some symptomatic effect on cognitive deficits with a concomitant significant reduction in the number of falls in non-demented individuals with PD [18].
A more restrictive protocol that reduces or eliminates cognitively impaired individuals from fall intervention studies may have a substantive impact on the representativeness of the study sample. Consequently, current findings with respect to pharmacological [18] and non-pharmacological interventions [19–22] may fall short in providing the best possible evidence for appropriate management in individuals with cognitive impairment and may not be able to be extrapolated to this population. This methodological flaw was recently also highlighted in the study by Amar (2015) that defended that individuals with PD with moderate cognitive impairment face complex problems and warrant inclusion in falls research [23]. Ultimately, if individuals with MCI or dementia are at greater risk for falls, they should be included in specific fall-related research studies in order for the results of these studies to be relevant and applicable to the types of patients seen in actual clinical practice.
The primary goal of this review was to assess the extent of inclusion of individuals with PD and with MCI or dementia in published, on-going or in planning clinical controlled trials which had falls and/or fall-related outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design: Systematic review
Literature search for published studies
We conducted a systematic search for all controlled trials regarding pharmacologic and non-pharmacological interventions for falls in PD that were published as full text papers up to May 2015. We used the electronic databases Medline, EMBASE, Cochrane Library Central Database and PEDro using the MeSH terms “PD”, or “Parkinson disease” AND “falls” AND “intervention” AND “prevention” to complete the literature search. Full text copies of potentially relevant trials were retrieved and their reference lists were systematically checked.
Literature search for ongoing studies
We also analyzed the major characteristics of ongoing clinical trials from the online open-access World Health Organization (WHO-ICTRP), the Clinical trial.gov database and the European Clinical Trials database (EudraCT) that proposed to evaluate the efficacy and/or safety of therapeutic interventions for the prevention or management of falls in PD. Within these databases, a search was performed for ongoing controlled trials regarding PD and falls using the following keywords: “Parkinson disease” AND “falls”. The studies were hand sorted to exclude duplicate entries and studies that were not related to therapeutic interventions for falls in PD. Data regarding study variables, particularly exclusion on the grounds of cognitive scores were extracted from each study.
Selection criteria for studies
We included published controlled trials regarding therapeutic interventions or prevention of falls for individuals with PD with fall or fall related outcomes. The type of participants in these interventions included: individuals with a diagnosis of PD; any duration and stage of PD; all ages; any drug, surgical or rehabilitation interventions; and any duration of intervention.
Data extraction
From the published and the on-going trials reviewed we searched the following information for source of support:
a) General characteristics of the trials (scientific study name or main identification number, year of publication, authors, publication status, study design, exclusion criteria related to cognition status, control group, gait and falls related inclusion criteria, drop-outs and adverse effects);
b) Characteristics of participants (number of participants in each group, age, gender, diagnostic criteria, disease severity measures);
c) Characteristics of interventions (type of intervention - pharmacological, surgical, physiotherapy/occupational/speech, dose, mode of administration, duration of follow up);
d) Characteristics of outcome measures (primary outcome measure, secondary or other outcomes and assessment method used for fall recording).
We determined the number of trials that excluded participants due to cognitive impairment regardless of the definition of cognitive impairment used. Extraction of all data was conducted by two independent reviewers (JMD and CG), with disagreements resolved by a third rater (JD).
RESULTS
Characteristics of included studies
Regarding the published intervention-related studies, the search in the databases identified 722 records, of which 15 trials met the inclusion criteria for this review, in which a total of 1380 individuals participated (Fig. 1). There were 14 trials evaluating a non-pharmacological intervention and 1 trial for pharmacological intervention. Thirteen of the trials [19, 20, 22, 24–32, 45] had a parallel group design and two cross-over trials [18, 21]. Chung et al. [18] was a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover design and double-blind trial. All trials were published in a full paper format. The trial characteristics of the 15 controlled trials that met our pre-defined inclusion criteria are summarized in Table 1.
Regarding the ongoing clinical trials, as of May, 2015, there were 19 registered trials regarding falls in PD in the WHO-ICTRP that met the inclusion criteria. From the European Clinical Trials database 2 additional clinical pharmacological trials were included. Within the ClinicalTrials.gov database there were 33 registered trials regarding falls in PD after been when crossed check. The main characteristics of all on-going trials are described in Table 2.
Participant characteristics
Participant characteristics of published trials were variable (Table 1). A clear diagnosis of PD was predominant with the exception of one published trial [26] which instead included participants with a diagnosis of Parkinsonism and no delineation of the characteristics of that terminology. The majority of the studies included individuals in stage II-III on the Hoehn and Yahr scale although six studies also included individuals in stage I [26]. The mean age of participants across trials ranged from 63 (±8.0) and 74, 5 (±9.7) years. Fall history was a common inclusion criteria ranging from 2 or more falls in the previous 12 months to 2 or more near falls per week.
Participant characteristics of the on-going trials were also widely variable and are described in Table 2.
Exclusion criteria related to cognitive status
Fourteen of the fifteen published intervention-related studies (n = 14) had explicit cognition exclusion criteria included as part of the study protocol. One study did not mention cognition aspects in the exclusion or inclusion criteria [24]. Forty-two of the fifty-four of the on-going studies registered in the WHO, EudraCT and Clinical Trials.gov database also had explicit cognition exclusion criteria.
Exclusion based on cognitive scores indicative of dementia was common. Eleven published and thirty-one on-going studies included in this review excluded participants based on a low Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) score (with the cutoff scores ranging from “less than 23” to “25 or lower”) (N = 42). Harro (2014) excluded participants if they had impaired cognitive functioning evidenced by a score of 20 or less on the Saint Louis Mental Status Examination (SLUMS) [27]. None of the studies specifically considered mild cognitive impairment as part of the exclusion criteria.
Due to the consistent nature of the exclusion of individuals with MCI or dementia, we were unable to analyze possible variables or characteristics that could be related to the rate of exclusion by MCI or dementia.
Intervention characteristics
The interventions being investigated were widely varied and predominately studies of non-pharmacological (i.e. rehabilitation based) interventions with only one pharmacological intervention [18] of a total of 15 published intervention-related studies used in this review.
In the on-going studies, 41 were non-pharmacological while only 12 were pharmacologically based.
Physiotherapy was the primary component of the non-pharmacological interventions and included treadmill training alone or with turning exercises [15, 19, 27], cueing gait program [14, 27], strength and balance programs [12, 13, 16, 28, 29], home-based programs [16, 30], teaching strategies for falls preventions [13], tai chi and exercise programs [17], muscle power training [30, 45], technology-assisted balance and gait training [31], and hydrotherapy perturbation-based balance training [32].The duration of the interventions varied from minimum 6 weeks to 6 months. The only pharmacological intervention consisted of 6 weeks of donepezil or placebo with a 3 week washout between phases.
Common outcome measures used for falls assessment
Outcome measures related to falls included: rates of falling, frequency of falls, frequency of near falls, fear of falling, number of fallers, and number of injurious falls. This was repeatedly measured by using falls diaries, calendars, postcards, and telephone reminders or interviews.
Drop-outs and adverse effects
There were limited reporting regarding adherence, adverse events and drop-outs. The study by Nieuwboer et al. [21] reported that one participant dropped out 3 weeks after randomization due to a necessary change of drug. Ashburn et al. [20] reported that drop-outs occurred in the intervention group (1 partner unwell, 1 disliked exercises, 1 died, 1 withdrew for no reason, 1 withdrew due to falls) and control group (4 unwell, 2 died, and 1 moved away). Allen et al. [19] described that the exercise group had no major adverse events but had 3 drops outs, 1 due to no longer wished to participate and 2 developed health problems unrelated to the intervention. Chung et al. [18] reported that 4 participants dropped out before the second phase (2 on active drug, 1 each during placebo phase and washout) and were excluded from the data analysis. Additionally, before the second crossover period, 2 more participants withdrew but were included in the analysis. Goodwin et al. [24] reported one pelvic fracture by a control group participant.
DISCUSSION
There is a lack of inclusion of individuals with PD with mild cognitive impairment and/or dementia in fall-related intervention studies and this continues to be prevalent in currently ongoing and scheduled trials. This may represent a serious methodological flaw with implications regarding the interpretation and clinical application of current and future fall interventions. This ultimately may lead to – at least partly – inadequate treatment recommendations for those who “really” fall (i.e. the cognitively impaired patients), and may really be useful only for a minority of the target population.
Cognitive status factors have long been recognized as having an important impact on management in PD but are frequently not addressed in the context of physiotherapy. In particular, impaired attention and executive function may exacerbate the difficulties with multitasking and contribute to falls. Cognitively impaired individuals often lose the capacity to prioritize tasks and when performing a dual task activity, they tend to reduce priority and/or attention to the gait or balance task, and focus more upon the completion of the secondary task [33]. This places these individuals at an increased risk for falling under complex multitask circumstances testing [34]. In a study by Allcock et al. [35], it was shown that the association of attentional deficits with postural instability translates into increased fall frequency measured prospectively over a 1 year study period. Another 12-month longitudinal cohort study of 102 older people without dementia (52 subjects with PD and 50 age and sex-matched controls) concluded that mild cognitive impairment might contribute to falls risk beyond conventional risk factors in older people with and without PD [14].
These findings raise a fundamental question. Should individuals with MCI and/or dementia be more widely considered or even recruited for specific fall intervention studies? Cognitively impaired individuals may be less able to comply with certain treatment and assessment components of trials and may also have higher adverse events and drop-out rates. Additionally, the design of clinical trials typically attempts to minimize confounding variables. Certain forms of cognitive impairment may independently contribute to falls (e.g., impulsive movements related to frontal lobe dysfunction). Hence, excluding cognitive impairment is defensible on these bases and so doing interventions to reduce falls should initially be shown as efficacious among non-demented PD patients. Subsequently, the strategy could be applied to those with cognitive impairment. Burton et al., (2015) [36] recently did a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of exercise programs to reduce falls in older people with dementia who are living in the community. Three RCTs [37–39], with high quality and one single-group pre- and post-test pilot study [40] were included. Participants were included if they had a diagnosis by a doctor/specialist, or a validated test, such as the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Saint Louis Mental Status Examination (SLUMS), the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale, or the National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke, Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders Association (NINCDS-ADRDA) Alzheimer’s criteria. Results from this review suggested that an exercise program may potentially assist in preventing falls of older people with dementia living in the community. If such inclusion is possible in people without PD but with dementia, it is plausible to think it can and should also be applied to PD patients with cognitive impairment.
A better understanding of the reasons that underlie the exclusion of individuals with cognitive impaired may allow clinicians and researchers to better identify possible solutions to overcome barriers associated to this exclusion. Due to the consistent nature of the exclusion of individuals with MCI or dementia in our review, we were unable to objectively analyze or identify any potential variables/characteristics (i.e. study type, number of participants, study duration, etc.) that could be related to the rate of exclusion by MCI or dementia. Additionally, the information provided by the WHO-ICTRP and in published trials was limited and insufficient to allow for a profound analysis of possible justifications for exclusion due to cognitive impairments. However, an important factor has to be noted. From our review, the reason for exclusion is dementia, as screened by tests of global cognitive dysfunction (i.e. Mini-Mental State Examination <24 and UPDRS part I). Different data collection methods for cognition are an important future line of research in this area because instruments such as the MMSE may not identify specific cognitive deficits, such as executive and attentional deficits which are the type of frontal lobe deficits that are more impaired in fallers [41]. Alternative options could include the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), which is sensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction and has been shown to be effective as a bedside test for evaluating the risk of falls [42].
Future studies should attempt to design assessment and intervention procedures that include individuals with cognitive limitations by considering several strategies. Screening for cognitive deficits should routinely be included in the work-up of individuals with falls so clinicians can become aware of the testing with regards to the individuals profile and cross reference this data with physical capacity. Actively involving carers in monitoring and encouraging participation between therapist visits for the assigned exercise program was identified as a facilitating factor for inclusions of individuals with dementia [38, 39]. Participants and families may be more likely to enter a clinical trial if they properly understand the potential health benefits (e.g. improved quality of life) that could be realized via free high-quality treatment and follow-up by expert clinicians as part of the study. Difficulties associated with traveling to a facility may be minimized if performing the follow-up evaluations in the participant’s home is considered. Incorporating telemedicine and/or remote monitoring may also enhance the ability of this population to participate in many studies. Targeted cognitive training may offer a novel treatment option for falls that is worthy of an increased research and clinical focus. If the degree of cognitive impairment can affect the success of interventions for falls prevention [43]; cognitive training interventions may also be considered of particular interest to reduce this limitation as it may be able to improve cognitive processes thus reducing falls. Additionally, a study by Allan (2009) suggested that to prevent falls in mild-moderate dementia, possible management strategies could also include management of the potentially modifiable factors such as symptomatic orthostatic hypotension, autonomic symptoms and depression instead of prioritising strength and balance exercises that are more difficult for those with cognitive impairment to adhere [44]. Finally, appropriate resource support including financial support for such trials that recognizes the potential extra workload involved might better facilitate this recruitment. The existence of specific guidelines for recruiting cognitive impaired people may also increase the likelihood of researchers to recruit these individuals.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, our findings suggests that due to the historical and ongoing exclusion of individuals with cognitive impairments, it is unclear if some intervention approaches for falls are effective and safe for this population. We highlight the substantial impact of restrictive protocol exclusion criteria on cognitive impaired PD patients. Even though participation of individuals with cognitive impairment in clinical trials may not always be desirable or feasible, it is still important to determine if they are disproportionately disqualified from participation and as a result, underrepresented in these trials, particularly in relationship to their respective motor problems.
Increasing participation of this population in clinical trials is critical in order to increase the external validity of the studies.
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT OF INTEREST RELATED TO RESEARCH COVERED IN THIS ARTICLE
All relevant disclosures and conflict of interests are detailed/ described/ listed at the end of this article.
Appendix
List of Ongoing Clinical trials identification name and registry number from the WHO, EudraCT and Clinical trial.gov databases.
| WHO | |
| 1 | Boston University. A Multifactorial Exercise Program to Reduce Falls in People With Parkinson Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02302144 NLM Identifier: NCT02302144. |
| 2 | University of Nevada, Las Vegas. High-intensity Exercise and Fall Prevention Boot Camp for Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02230267 NLM Identifier: NCT02230267 |
| 3 | Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Alberta Innovates and Health Solutions and University of Calgary (Canada). Ambulosono - A music walking program for patients with Parkinson Disease. In: ISRCTNregistry [Internet]. BioMed Central 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://isrctn.com/ISRCTN06023392 NLM Identifier: ISRCTN06023392 |
| 4 | Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust (UK). A randomised controlled trial of the effectiveness of PDSAFE to prevent falls among people with Parkinson disease. In: ISRCTNregistry [Internet]. BioMed Central 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://isrctn.com/ISRCTN48152791 NLM Identifier: ISRCTN48152791 |
| 5 | University of Southampton (UK). A randomised controlled trial of the effectiveness of PDSAFE to prevent falls among people with Parkinson disease: Stage 1 Pilot. In: ISRCTNregistry [Internet]. BioMed Central 2013- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://isrctn.com/ISRCTN14719805 NLM Identifier: ISRCTN14719805 |
| 6 | La Trobe University. A single group pilot study of the feasibility, safety and efficacy of an Argentine tango dance intervention for people living with Parkinson’s disease. In: ANZCTR.org.au [Internet]. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry 2013 -[cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12613001058763.aspx |
| 7 | VU University Medical Center (Netherlands). Improving Mobility and balance in Parkinson disease through circuit Class Training: Effects on clinical outcomes, posturography and brain connectivity. In: ISRCTNregistry [Internet]. BioMed Central 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://isrctn.com/ISRCTN47046299 NLM Identifier: ISRCTN47046299 |
| 8 | National Taiwan University Hospital. Freezing of Gait Correction and Fall Prevention in People With Parkinson’s Disease: Developing and Application of a Real-time Somatosensory Stimulation System. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01772186 NLM Identifier: NCT01772186 |
| 9 | Tel-Aviv Sourasky Medical Center. V-TIME: A Treadmill Training Program Augmented by Virtual Reality to Decrease Fall Risk in Older Adults, Patients With Parkinson’s Disease and Individuals With Mild Cognitive Impairments. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2012- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01732653 NLM Identifier: NCT01732653 |
| 10 | The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Effects of an Innovative Balance Training Programme in Enhancing Postural Control and Reducing Falls in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2011- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01427062 NLM Identifier: NCT01427062 |
| 11 | Department of Veterans Affairs. Effects of Vitamin D in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2010- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01119131 NLM Identifier: NCT01119131 |
| 12 | Oregon Health and Science University. Cholinergic Augmentation in Frequently Falling Subjects With Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2009- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00912808 NLM Identifier: NCT00912808 |
| 13 | The University of Melbourne. Home based rehabilitation to reduce falls in people with Parkinson’s disease: a randomised controlled trial. In: ANZCTR.org.au [Internet]. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry 2008- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12608000390381.aspx NLM Identifier: ACTRN12608000390381 |
| 14 | The University of Sydney. Exercise to prevent falls in people with Parkinson’s disease. In: ANZCTR.org.au [Internet]. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry 2008- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12608000303347.aspx NLM Identifier: ACTRN12608000303347 |
| 15 | Radboud University. Reduction of Falls in the Elderly - Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2007- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00518648 NLM Identifier: NCT00518648 |
| 16 | Peninsula Medical School (UK). The effect of targeted exercise on falls and function for people with Parkinson’s disease (Group Exercise Trial for Parkinson’s disease - GET uP study). In: ISRCTNregistry [Internet]. BioMed Central 2007- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://isrctn.com/ISRCTN50793425 NLM Identifier: ISRCTN50793425 |
| 17 | Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust (UK). Can support group-based exercise reduce risk factors for falling in people with Parkinson’s disease? In: ANZCTR.org.au [Internet]. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry 2007- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12607000193471.aspx NLM Identifier: ACTRN12607000193471 |
| 18 | University of Melbourne. A randomized controlled trial of strategy training compared to exercises to prevent falls and improve mobility in people with Parkinson’s Disease. In: ANZCTR.org.au [Internet]. Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry 2006- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12606000344594.aspx NLM Identifier: ACTRN12606000344594 |
| 19 | Action Medical Research (UK). Randomised controlled trial of a home-based exercise programme to reduce fall frequency among people with Parkinson’s disease. In: ISRCTNregistry [Internet]. BioMed Central 2004- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://isrctn.com/ISRCTN63503875 NLM Identifier: ISRCTN63503875 |
| EudraCT | |
| 1 | A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial to evaluate the effect of Rivastigmine on gait in people with Parkinson’s disease who have fallen. The ReSPonD Study. EudraCT Number: 2011-003053-25 |
| 2 | An Open-Label, Multi-Center, Follow-Up Study Designed to Evaluate the Long-Term Effects of Rasagiline in Parkinson’s Disease Subjects who Participated in the ADAGIO Study EudraCT Number: 2009-011541-24. |
| Clinical trial.gov | |
| 1 | Radboud University. Reduction of Falls in the Elderly - Parkinson’s Disease (REFINE-PD). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2007- [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00518648. NLM Identifier: NCT00518648 |
| 2 | The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. The Effects of the Hopeful Outdoor Parkinson Exercise (HOPE) Program on Improving Balance Performance in Parkinsonian Non-fallers and Single Fallers. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01799681. NLM Identifier: NCT01799681 |
| 3 | Radboud University. Efficiency of Physiotherapeutic Care in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2006 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00330694. NLM Identifier: NCT00330694. |
| 4 | Chelsea Therapeutics. A Two Part Study (306A/306B) to Assess Droxidopa in Treatment of NOH in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2010 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01176240 NLM Identifier: NCT01176240 |
| 5 | Oregon Research Institute. Study of Tai Chi Exercise and Balance in Persons With Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2008 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00611481 NLM Identifier: NCT00611481. |
| 6 | Department of Veterans Affairs. Telemedicine Intervention to Improve Physical Function. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2012 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01639469. NLM Identifier: NCT01639469 |
| 7 | Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. Dual Task Practice in Parkinson’s Disease (Duality-PD). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2011 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01375413. NLM Identifier: NCT01375413 |
| 8 | University of California, San Francisco. Computer-Based Balance Training for People With Parkinson’s Disease). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2010 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01162226. NLM Identifier: NCT01162226 |
| 9 | Radboud University. Integrated Multidisciplinary Care for Parkinson’s Disease: a Controlled Trial. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2007 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00518791. NLM Identifier: NCT00518791. |
| 10 | Memorial Medical Center. The Effects of Vitamin D and Bone Loss in Parkinson’s Disease (PDVD3). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2009 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00907972. NLM Identifier: NCT00907972 |
| 11 | Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. Laser Light Cues for Gait Freezing in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2006 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00320242. NLM Identifier: NCT00320242 |
| 12 | Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hong Kong. Effectiveness of Physiotherapy Interventions for Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2010 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01076712. NLM Identifier: NCT01076712 |
| 13 | McGill University Health Center. Tango for Treatment of Motor and Non-motor Manifestations in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2012 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01573260. NLM Identifier: NCT01573260 |
| 14 | Chulalongkorn University. Treadmill and Music Cueing for Gait Training in Mild to Moderate Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2008 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00750945. NLM Identifier: NCT00750945 |
| 15 | University of British Columbia. Ambulosono Rasagiline Musical Walking Study. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02207387. NLM Identifier: NCT02207387 |
| 16 | Laval University. The Effect of Exercise Training on Gait and Quality of Life in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2012 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01701128. NLM Identifier: NCT01701128 |
| 17 | University of Erlangen-Nürnberg. Stability and Balance in Locomotion Through Exercise (StaBLE). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01856244. NLM Identifier: NCT01856244 |
| 18 | New York Institute of Technology. Effect of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine on Parkinson Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02107638. NLM Identifier: NCT02107638 |
| 19 | Rush University Medical Center. Varenicline for Gait and Balance Impairment in Parkinson Disease (Chantix-PD). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2011 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: http://www.svedem.sehttps://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01341080. NLM Identifier: NCT01341080 |
| 20 | The Swedish Research Council. BETA Study: Improving Balance Function in Elderly by Progressive and Specific Training and Physical Activity. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2011 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01417598.NLM Identifier: NCT01417598 |
| 21 | Oregon Health and Science University. Effects of Cholinergic Augmentation on Measures of Balance and Gait. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT02206620. NLM Identifier: NCT02206620 |
| 22 | Oregon Health and Science University. The Effect of Donepezil on Gait and Balance in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2012 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01521117. NLM Identifier: NCT01521117 |
| 23 | Stony Brook University. Walking While Talking: The Effect of Doing Two Things at Once in Individuals With Neurological Injury or Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01917903. NLM Identifier: NCT01917903 |
| 24 | University of Sao Paulo. Spinal Cord Stimulation for the Treatment of Motor and Nonmotor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease (SCSPD). In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2015 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02388204. NLM Identifier: NCT02388204 |
| 25 | Henry Ford Health System. Study to Assess the Clinical Benefit and Safety of Droxidopa in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02066571. NLM Identifier: NCT02066571 |
| 26 | Universidad de Granada. Exercise Intervention and Dexterity in Parkinson. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2012 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01749917. NLM Identifier: NCT01749917 |
| 27 | University of Dublin, Trinity College. A Randomised Controlled Trial (RCT) to Evaluate Use of an Individual Auditory Cueing Device’s (IACD’s) on Freezing and Gait in People With Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2008 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT0072746. NLM Identifier: NCT0072746. |
| 28 | Habilita, Ospedale di Sarnico. Efficacy of a Robotic-assisted Gait Training in Addition to a Conventional Physical Therapy in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2014 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02164162. NLM Identifier: NCT02164162 |
| 29 | University of Sao Paulo General Hospital. Balance Training in Parkinson’s Disease Using Cues. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01960985. NLM Identifier: NCT01960985 |
| 30 | Boston University. Mobile Health Technology to Promote Physical Activity in Persons With Parkinson Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01955889. NLM Identifier: NCT01955889 |
| 31 | University of Iceland. The Effect of High-Volume Walking With Visual Cues (VC) in Parkinson's Disease In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2011 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01391741. NLM Identifier: NCT01391741 |
| 32 | Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc- Université Catholique de Louvain. Effects of Exercise on Long-Range Autocorrelations in Parkinson’s Disease. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2015 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02419768. NLM Identifier: NCT02419768. |
| 33 | Chelsea Therapeutics. A Clinical Study of Patients With Symptomatic NOH to Assess Sustained Effects of Droxidopa Therapy. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). 2013 - [cited 2015 May 06]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01927055. NLM Identifier: NCT01927055 |
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
Bastiaan R. Bloem has served as an editorial board member of Movement Disorders, currently serves as an editorial board member of Physiotherapy Canada, is Associate Editor for the Journal of Parkinson’s disease, received honoraria from serving on the scientific advisory board for Danone, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, UCB and received research support from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, the Michael J Fox Foundation, the Prinses Beatrix Foundation, the Stichting Parkinson Fonds, the National Parkinson Foundation and the Parkinson Vereniging.
Joaquim J. Ferreira has held consultancy functions with GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, TEVA, Lundbeck, Solvay, Abbott, BIAL, Merck-Serono, Merz, Ipsen; has received grants from GlaxoSmithKline, Grunenthal, Fundaçao MSD (Portugal) and Teva; has been a member of the European Huntington Disease Network and has been employed by Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Faculdade de Medicina de Lisboa. None of the other authors have any financial disclosures to report.
REFERENCES
1 | Litvan I, Aarsland D, Adler CH, Goldman JG, Kulisevsky J, Mollenhauer B, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Troster AI, Weintraub D(2011) MDS Task Force on mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Critical review of PD-MCIMov Disord26: 18141824 |
2 | Williams-Gray CH, Evans JR, Goris A, Foltynie T, Ban M, Robbins TW, Brayne C, Kolachana BS, Weinberger DR, Sawcer SJ, Barker RA(2009) The distinct cognitive syndromes of Parkinson’s disease: 5 year follow-up of the CamPaIGN cohortBrain132: 29582969 |
3 | Janvin CC, Larsen JP, Aarsland D, Hugdahl K(2006) Subtypes of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Progression to dementiaMov Disord21: 13431349 |
4 | Asada T, Kariya T, Kinoshita T, Asaka A, Morikawa S, Yoshioka M, Kakuma T(1996) Predictors of fall-relatedinjuries among community-dwelling elderly people with dementiaAge Ageing25: 2228 |
5 | Clark RD, Lord SR, Webster IW(1993) Clinical parameters associated with falls in an elderly populationGerontology39: 117123 |
6 | Lord SR, Clark RD(1996) Simple physiological and clinical tests for the accurate prediction of falling in older peopleGerontology42: 199203 |
7 | Salgado RI, Lord SR, Ehrlich F, Janji N, Rahman A(2004) Predictors of falling in elderly hospital patientsArch Gerontol Geriatr38: 213219 |
8 | Buchner DM, Larson EB(1988) Transfer bias and the association of cognitive impairment with fallsJ Gen Intern Med3: 254259 |
9 | Shaw FE(2007) Prevention of falls in older people with dementiaJ Neural Transm114: 12591264 |
10 | Morris JC, Rubin EH, Morris EJ, Mandel SA(1987) Senile dementia of the Alzheimer’s type: An important risk factor for serious fallsJ Gerontol42: 412417 |
11 | Nakamura T, Meguro K, Sasaki H(1996) Relationship between falls and stride length variability in seniledementia of the Alzheimer typeGerontology42: 108113 |
12 | Resnick B(1999) Falls in a community of older adults: Putting research into practiceClin Nurs Res8: 251266 |
13 | Tinetti ME, Speechley M, Ginter SF(1988) Risk factors for falls among elderly persons living in thecommunityN Engl J Med319: 17011707 |
14 | Camicioli R, Majumdar SR(2010) Relationship between mild cognitive impairment and falls in older people with and without Parkinson’s disease: 1-Year Prospective Cohort StudyGait Posture32: 8791 |
15 | Latt MD, Lord SR, Morris JG, Fung VS(2009) Clinical and physiological assessments for elucidating falls risk in Parkinson’s diseaseMov Disord24: 12801289 |
16 | Melton LJ3rd, Leibson CL, Achenbach SJ, Bower JH, Maraganore DM, Oberg AL, Rocca WA(2006) Fracture risk after the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: Influence of concomitant dementiaMov Disord21: 13611367 |
17 | Wood BH, Bilclough JA, Bowron A, Walker RW(2002) Incidence and prediction of falls in Parkinson’s disease: Aprospective multidisciplinary studyJ Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry72: 721725 |
18 | Chung KA, Lobb BM, Nutt JG, Horak FB(2010) Effects of a central cholinesterase inhibitor on reducing falls inParkinson diseaseNeurology75: 12631269 |
19 | Allen NE, Canning CG, Sherrington C, Lord SR, Latt MD, Close JCT, O’Rourke SD, Murray SM, Fung VSC(2010) The effects of an exercise program on fall risk factors in people with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trialMov Disord25: 12171225 |
20 | Ashburn A, Fazakarley L, Ballinger C, Pickering R, McLellan LD, Fitton C(2007) A randomised controlled trial of a home based exercise programme to reduce the risk of falling among people with Parkinson’s diseaseJ Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry78: 678684 |
21 | Nieuwboer A, Kwakkel G, Rochester L, Jones D, van Wegen E, Willems AM, Chavret F, Hetherington V, Baker K, Lim I(2007) Cueing training in the home improves gait-related mobility in Parkinson’s disease: The RESCUE trialJ Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry78: 134140 |
22 | Protas EJ, Mitchell K, Williams A, Qureshy H, Caroline K, Lai EC(2005) Gait and step training to reduce falls in Parkinson’s diseaseNeuroRehabilitation20: 183190 |
23 | Amar K, Stack E, Fitton C, Ashburn A, Roberts HC(2015) Fall frequency, predicting falls and participating in falls research: Similarities among people with Parkinson’s disease with and without cognitive impairmentParkinsonism Relat Disord21: 5560 |
24 | Goodwin VA, Richards SH, Henley W, Ewings P, Taylor AH, Campbell JL(2011) An exercise intervention to prevent falls in people with Parkinson’s disease: A pragmatic randomised controlled trialJ Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry82: 12321238 |
25 | Li F, Harmer P, Fitzgerald K, Eckstrom E, Stock R, Galver J, Maddalozzo G, Batya SS(2012) Tai chi and postural stability in patients with Parkinson’s diseaseN Engl J Med366: 511519 |
26 | Toole T, Maitland CG, Warren E, Hubmann MF, Panton L(2005) The effects of loading and unloading treadmillwalking on balance, gait, fall risk, and daily function in ParkinsonismNeuroRehabilitation20: 307322 |
27 | Harro CC, Shoemaker MJ, Frey O, Gamble AC, Harring KB, Karl KL, McDonald JD, Murray CJ, VanDyke JM, Tomassi EM, VanHaitsma RJ(2014) The effects of speed-dependent treadmill training and rhythmic auditory-cued overgroundwalking on balance function, fall incidence, and quality of life in individuals with idiopathic Parkinson’sdisease: A randomized controlled trialNeuroRehabilitation34: 541556 |
28 | Smania N, Corato E, Tinazzi M, Stanzani C, Fiaschi A, Girardi P, Gandolfi M(2010) Effect of balance training on postural instability in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s diseaseNeurorehabil Neural Repair24: 826834 |
29 | Canning CG, Sherrington C, Lord SR, Close JC, Heritier S, Heller GZ, Howard K, Allen NE, Latt MD, Murray SM, O’Rourke SD, Paul SS, Song J, Fung VS(2015) Exercise for falls prevention in Parkinson disease: A randomized controlled trialNeurology84: 304312 |
30 | Paul SS, Canning CG, Song J, Fung VS, Sherrington C(2014) Leg muscle power is enhanced by training in people with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled trialClin Rehabil28: 275288 |
31 | Shen X, Mak MK(2015) Technology-assisted balance and gait training reduces falls in patients with Parkinson’sdisease: A randomized controlled trial with 12-month follow-upNeurorehabil Neural Repair29: 103111 |
32 | Volpe D, Giantin MG, Maestri R, Frazzitta G(2014) Comparing the effects of hydrotherapy and land-based therapy on balance in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized controlled pilot studyClin Rehabil28: 12101217 |
33 | Bloem BR, Valkenburg VV, Slabbekoorn M, Willemsen MD(2001) The Multiple Tasks Test: Development and normal strategiesGait Posture14: 191202 |
34 | Bloem BR, Valkenburg VV, Slabbekoorn M, van Dijk JG(2001) The multiple tasks testStrategies in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Brain Res137: 478486 |
35 | Allcock LM, Rowan EN, Steen IN, Wesnes K, Kenny RA, Burn DJ(2009) Impaired attention predicts falling in Parkinson’s diseaseParkinsonism Relat Disord15: 110115 |
36 | Burton E, Cavalheri V, Adams R, Browne CO, Bovery-Spencer P, Fenton AM, Campbell BW, Hill KD(2015) Effectiveness of exercise programs to reduce falls in older people with dementia living in the community: A systematic review and meta-analysisClin Interv Aging10: 421434 |
37 | Pitkala KH, Poysti MM, Laakkonen ML, Tilvis RS, Savikko N, Kautiainen H, Strandberg TE(2013) Effects of theFinnish Alzheimer disease exercise trial (FINALEX): A randomized controlled trialJAMA Intern Med173: 894901 |
38 | Suttanon P, Hill KD, Said CM, Williams SB, Byrne KN, LoGiudice D, Lautenschlager NT, Dodd KJ(2013) Feasibility, safety and preliminary evidence of the effectiveness of a home-based exercise programme for older people with Alzheimer’s disease: A pilot randomized controlled trialClin Rehabil27: 427438 |
39 | Wesson J, Clemson L, Brodaty H, Lord S, Taylor M, Gitlin L, Close J(2013) A feasibility study and pilot randomised trial of a tailored prevention program to reduce falls in older people with mild dementiaBMC Geriatric13: 89 |
40 | Mackintosh SF, Sheppard LA A Pilot. Falls-prevention Programme for Older People with Dementia from A Predominantly Italian Background. Hong Kong Physiotherapy Journal 23, 20-26. |
41 | Hausdorff JM, Doniger GM, Springer S, Yogev G, Simon ES, Giladi N(2006) A common cognitive profile in elderly fallers and in patients with Parkinson’s disease: The prominence of impaired executive function and attentionExp Aging Res32: 411429 |
42 | Kim JS, Jang W, Cho JW, Ahn JY, Kim HT(2013) Bedside cognitive assessments and falls risk in Parkinson’s diseaseNeurol Sci34: 7578 |
43 | Oliver D, Connelly JB, Victor CR, Shaw FE, Whitehead A, Genc Y, Vanoli A, Martin FC, Gosney MA(2007) Strategies to prevent falls and fractures in hospitals and care homes and effect of cognitive impairment: Systematic review and meta-analysesBM334: 82 |
44 | Allan LM, Ballard CG, Rowan EN, Kenny RA(2009) Incidence and Prediction of Falls in Dementia: A Prospective Study in Older PeoplePLoS One4: e5521 |
45 | Morris ME, Menz HB, McGinley JL, Watts JJ, Huxham FE, Murphy AT, Danoudis ME, Iansek R(2015) A randomized controlled trial to reduce falls in people with Parkinson’s diseaseNeurorehabil Neural Repairdoi: 10.1177-1545968314565511 |
Figures and Tables
Fig.1
Flow diagram for data extraction.
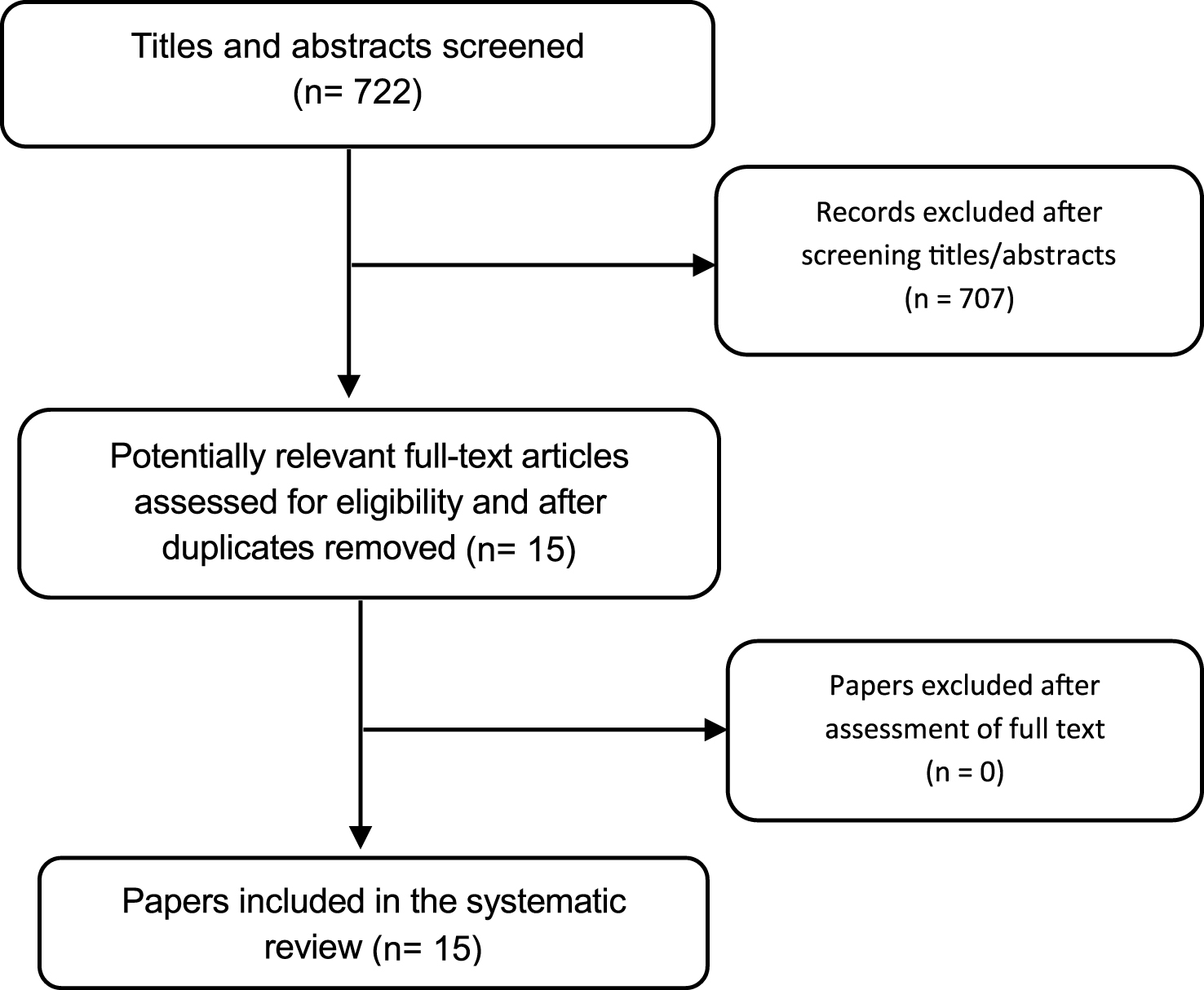
Table 1
Summary of characteristics of 15 published Clinical Trials regarding fall interventions in Parkinson disease
| Study &study design | Participants | Exclusion criteria related to cognitive status | Gait and fall-related inclusion criteria | Type of Intervention | Study Duration | Primary or Secondary outcomes related to falls | Method of falls data collection |
| Toole, 2005 [26] | 23 participants with Parkinsonism. | Significant dementia or other disorders of comprehension. | Able to walk with firm, continuous support of one | Physiotherapy: Treadmill walking for 20 | 6 weeks with 4 weeks follow-up. | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: Number of falls during dynamic posturography. | Fall register during dynamic |
| RCT, Parallel. | Stage 1–4 HY. | person to help carry weight or | minutes per day for 3 days | posturography. | posturography | ||
| Age = 74.5±9.7 years. | assist with balance. | per week for 6 weeks. | assessment. | ||||
| Protas, 2005 [22] | 18 participants with idiopathic PD. | Low scores on all scales of the Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status | 1) Postural instability and gait difficulty predominant PD, 2) | Physiotherapy: gait and stepping and turning | 8 weeks with 2 week follow-up. | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: Fall frequency. | Phone call. |
| RCT, Parallel. | Stage 3-4 HY. | Examination (Cognistat). | freezing episodes, and/or a | training on a treadmill. | |||
| Exercised group | history of falls, and 3) ability to | 1 hour per day, three times | |||||
| age=71.3±7.4 years. | stand and walk with or without assistance. | per week for 8 weeks. | |||||
| Control group age=73.7±8.5 years. | |||||||
| Nieuwboer, | 153 participants | Cognitive impairment | Mild to severe gait | Physiotherapy: | 6 weeks with 6 | SECONDARY OUTCOMES: | Falls diary to |
| 2007 [21] | with PD. | (MMSE Scores <24) | disturbance with score | 3-week home cueing | week follow-up. | Falling as a measure of possible | indicate the |
| Single-blind | Stage 3-4 HY. | superior to 1 on the Unified | program using a prototype | adverse cueing effects. | number of falls as a | ||
| randomised | Exercise group age: | Parkinson’s Disease Rating | cueing device, followed by | measure of possible | |||
| crossover trial. | 72.7±9.6 years. Control group age: 71.6±8.8 years. | Scale (UPDRS; item 29). | 3 weeks without training. | program adverse effects. | |||
| Ashburn, 2007 | 142 participants | Failure on screening test (MMSE). | Patients with independently | Physiotherapy: muscle | 8 weeks with 6 | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: | Monthly self- |
| [20] | with PD, | Non intact gross cognitive | mobile, living at home in the | strengthening, range of | months follow-up. | Self-reported falling or not at 8 | completed diaries. |
| RCT with | Stage 3-4 HY. | impairment. | community, experiencing | movement, balance | weeks and 6 months. | ||
| blinded | Exercise group age | Failure on screening test (MMSE). | more than one fall in the | training and walking (inside | |||
| assessment, Parallel. | = 72,7±9.6 years. Control group=71.6±8.8 years. | previous 12 months. | and outside). Teaching of strategies for falls prevention and movement initiation and compensation. | ||||
| Control group: usual care which included contact with a local PD nurse. | |||||||
| Allen, 2010 [19] | 48 participants with PD. | Significant cognitive impairment (MMSE <24). | 1) Able to walk independently (with or without an aid); | Physiotherapy: a monthly exercise class and | 6-months. | SECONDARY OUTCOMES: Number of Falls. Falls risk factors | Monthly falls diaries. |
| RCT with blinded assessment, Parallel. | Exercise group age= 66±10 years. Control Group age = 68±7 years. | falling with a score of 25 cm | 2) fallen in the last year, or were deemed to be at risk of targeted leg muscle or less on the Functional Reach test or if they failed to reach criterion on one of the balance tests in the QuickScreen Clinical Falls Risk Assessments. | exercised at home 3 times weekly. The intervention strength, balance, and freezing. Control group received usual care. Both groups received standardized falls prevention advice in the form of a booklet. | (leg muscle weakness, poor balance, and freezing of gait). | ||
| Chung, 2010 [18] | 23 participants with probable idiopathic | MMSE score <25 or nearly falling 2 or more | Baseline frequency of falling | Pharmacological 6 weeks of donepezil or | 15 weeks. | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: Number of daily falls and near falls. | Weekly postcards. |
| Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, double-blind, crossover. | PD. Hoehn & Yahr staging indicating moderate baseline disease (mean 3.2, SD 0.4). Age 68.3±10.8 years. | times per week. | placebo with a 3-week washout between phases | ||||
| Smania 2010 [28] RCT | 64 participants with idiopathic PD. Stage 3-4 HY. Experimental group age= 67.64±7.41. Control group age=67.26±7.18. | MMSE score <23 | Outpatients that did not require assistance to rise from chairs or beds. | Intervention group: balance training consisting of feedforward and feedback postural reactions training. Control group: active joint mobilization, muscle stretching, and motor coordination exercises. | 21 treatment sessions (50 minutes each) and a 1 month follow-up. | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: Number of falls. | Falls diary |
| Goodwin, 2011 | 130 participants | Cognitive status not mentioned as | History of two or more falls in | Physiotherapy | 10 week group | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: | Weekly diaries to |
| [24] | with PD. | exclusion criterior. | the previous year and who | Intervention group: strength | intervention | Number of falls. | register Falls and |
| RCT, Parallel. | Stage 1-4 HY. | Excluded if unable to follow | were able to mobilize | and balance training | period and 10 | fall-related injuries. | |
| Intervention group | written or verbal instructions in | independently. | program with | week follow-up | |||
| age= 72.0±8.6 years. Control group age=70.1±8.3 years. | English. | supplementary home exercises. 10 once weekly group exercise sessions, with twice weekly home exercises. Control group: usual care with medical or allied health. | period. | ||||
| Li, 2012 [25] | 195 participants | MMSE score <24 | Ability to stand unaided and | 3 exercise intervention | 6 months with 3 | SECONDARY OUTCOMES: | Monthly fall |
| RCT, Parallel. | with PD. Stage 1-4 HY. Tai chi group age=68±9 years. Resistance Group age= 69±8 years. | walk with or without an assistive device. | groups: Tai Chi, resistance Training or stretching. 60-minute exercise sessions twice weekly for 24 weeks. | months follow-up. | Number of falls. | calendars. | |
| Harro, 2014 | 20 participants with | Saint Louis Mental Status | Ability to walk continuously | Speed-dependent treadmill | 6 weeks training | SECONDARY OUTCOMES: | Monthly self-report |
| [27] | PD. Stage 1-3 HY. | Examination (SLUMS) <20 or less. | without physical assistance for | training (SDTT) group. | with 3 and 6 | Fall incidence. | fall calendars |
| Single-blind RCT | Mean age 66.1 yrs. | 5 minutes with or without an assistive device. | Rhythmic auditory-cued (RAC). | month follow-up | |||
| Paul, 2014 [30] | 40 participants with | MMSE score <24 | Ability to walk independently | Intervention group: muscle | 12 weeks with 6 | SECONDARY OUTCOMES: | Monthly falls diaries. |
| RCT, Parallel. | PD. | with or without an aid. | power training. | month follow-up. | Number of falls in six months of | ||
| Stage 1-4 HY. Experimental group age= 68.1±5.6 Control group age=64.5±7.4 years. | Control group: low intensity exercises of same muscle groups independently at home. 45 minutes, twice a week for 12 weeks. | follow-up. | |||||
| Volpe, 2014 | 34 participants with | MMSE score <25 | Ability to walk without any | Intervention group: | 2 months. | SECONDARY OUTCOMES: | Falls diary or tele |
| [32] | PD. | assistance. | hydrotherapy treatment | Number of falls | phone interview. | ||
| RCT, Parallel. | Stage 2.5-3 HY. Intervention Group age= 68±7. Control group age=66±8. | with focus on perturbation-based balance training. Control group: land-based rehabilitation treatment with same type of exercises. 60 minutes of treatment, five days a week for two months. | |||||
| Cannings, | 231 participants | MMSE score <24 | Ability to walk independently | Exercise group: PD-WEBB | 6 months. | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: | Monthly falls diaries. |
| 2015 [29] | with PD. | with or without a walking aid, | program with progressive | Fall rates and proportion of | |||
| RCT, Parallel. | Stage 2-4 HY. | and one or more falls in the | balance and lower limb | fallers during the intervention | |||
| Experimental group | past year or at risk of falls | strengthening exercises. | period. | ||||
| age= 71.4±8.1. | based on physical | Control group: usual-care | |||||
| Control group age=69.9±9.3. | assessment. | from their medical practitioner and community services. Exercises were practiced for 40 to 60 minutes, 3 times weekly for 6 months. | |||||
| 49 participants with | MMSE score <23 | Ability to walk independently | Intervention group: | 12-week | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: | Monthly phone | |
| Shen, 2015 [31] | PD. Stage 2-3 HY. Experimental group age= 63.3±8.0. Control group age=65.3±8.5. | for 10 meters. | technology assisted balance and gait training. Active control group: strengthening exercises. 2 phases of 4-week Supervised laboratory training, 3 sessions per week, separated by 4 weeks of self-supervised home-based training at a frequency of 5 sessions per week. | intervention period. | number of fallers, fall rate, and the time to first fall. | calls. | |
| Morris, 2015 [45] | 210 participants with PD. Stage 1-4 | MMSE score <24 | Medically able and safe to perform | Group 1: progressive resistance strength training | 14 months, with an initial 8 weeks of | PRIMARY OUTCOMES: falls rate. | Monthly falls calendars. |
| RCT, Parallel. | HY. All participants aged=67.9±9.6. | the interventions. | coupled with falls prevention education. Group 2: movement strategy training combined with falls prevention education, Control group: life-skills information not related to falls. 8 weeks of out-patient therapy once per week and a structured home program. | intervention, followed by 12 months of ongoing falls measurement. |
Abbreviations: MMSE = Mini-Mental State examination; RCT = Randomised controlled trial; HY = Hoehn & Yahr; PDQ39 = Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire.
Table 2
Ongoing Clinical trials characteristics with individuals with Parkinson's disease regarding falls interventions from the WHO, EudraCT and Clinical trial.gov databases
| Source | Number of clinical studies | ||
| WHO | EudraCT | Clinical trial.gov | |
| Number of studies | 19 | 2 | 33 |
| Study design | |||
| Randomized control trial | 16 | 2 | 27 |
| Controlled trial | 3 | 0 | 6 |
| Exclusion by cognition status | |||
| Excluded based on mini mental score | 12 | 0 | 19 |
| Excluded based on other cognitive parameter | 4 | 1 | 6 |
| Missing data | 3 | 1 | 8 |
| Type of Intervention | |||
| Pharmacological | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Surgical | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Physiotherapy/occupational | 17 | 0 | 24 |
| Sample size | |||
| Inferior 50 | 8 | 0 | 19 |
| Between 50-100 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
| Superior 100 | 8 | 2 | 11 |
| Disease Stage | |||
| Stage I-II | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Stage II-III | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Stage III-IV | 7 | 0 | 14 |
| Stage V | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Missing data | 9 | 0 | 11 |
| Method of falls data collecting | |||
| Diaries | 6 | 0 | 7 |
| Calendars | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Post cards | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Phone calls | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Questionnaires | 11 | 0 | 7 |
| Missing data | 0 | 2 | 16 |
| Fall outcome measure | |||
| Primary outcome | 8 | 1 | 5 |
| Secondary outcome | 4 | 1 | 12 |
| Study duration | |||
| Inferior 8 weeks | 4 | 0 | 5 |
| Between 8-24 weeks | 4 | 0 | 17 |
| Superior to 24 weeks | 8 | 2 | 9 |
| Missing data | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| Recruiting Status | |||
| Recruiting | 5 | 0 | 12 |
| Non recruiting | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Completed | 12 | 0 | 13 |
| Other | 0 | 2 | 6 |
WHO- www.who.int./trialsearch/AdvSearch.aspx. EudraCT – www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search. Clinical trial.gov - www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search.



